
Exhibit 99.5

KPMG
cutting through complexity
Valuation of Asbestos-Related
Disease Liabilities of former James
Hardie entities (“the Liable Entities”)
to be met by the AICF Trust
Prepared for Asbestos Injuries
Compensation Fund Limited
(“AICFL”)
As at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015

|
||||||||
| KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd | ABN: 91 144 686 046 | |||||||
| Australian Financial Services Licence No. 392050 | Telephone: +61 2 9335 7000 | |||||||
| 10 Shelley Street | Facsimile: +61 2 9335 7001 | |||||||
| Sydney NSW 2000 | DX: 1056 Sydney | |||||||
| www.kpmg.com.au | ||||||||
| PO Box H67 | ||||||||
| Australia Square NSW 1215 | ||||||||
| Australia | ||||||||
21 May 2015
Narreda Grimley
General Manager
Asbestos Injuries Compensation Fund Limited
Suite 1, Level 6, 56 Clarence Street
Sydney NSW 2000
| Cc | Matthew Marsh, Chief Financial Officer, James Hardie Industries plc |
Paul Miller, General Counsel, Department of Premier and Cabinet, The State of New South Wales
The Board of Directors, Asbestos Injuries Compensation Fund Limited
Dear Narreda
VALUATION OF ASBESTOS-RELATED DISEASE LIABILITIES OF FORMER JAMES HARDIE ENTITIES (“THE LIABLE ENTITIES”) TO BE MET BY THE AICF TRUST
We are pleased to provide you with our Annual Actuarial Report relating to the asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities which are to be met by the AICF Trust.
The report is effective as at 31 March 2015 and has taken into account claims data and information provided to us by AICFL as at 31 March 2015.
If you have any questions with respect to the contents of this report, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Yours sincerely
|
|
| |
| Neil Donlevy MA FIA FIAA | Jefferson Gibbs BSc FIA FIAA | |
| Executive, KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd | Executive, KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd | |
| Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries (London) Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia |
Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries (London) Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia |
© 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of
independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG
International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the
KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International.

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Table of Contents
| Executive Summary |
i | |||||||
| 1 | Scope and Purpose |
1 | ||||||
| 1.1 | Introduction |
1 | ||||||
| 1.2 | Scope of report |
2 | ||||||
| 1.3 | Areas of potential exposure |
6 | ||||||
| 1.4 | Data reliances and limitations |
8 | ||||||
| 1.5 | Uncertainty |
8 | ||||||
| 1.6 | Distribution and use |
9 | ||||||
| 1.7 | Date labelling convention used in this Report |
10 | ||||||
| 1.8 | Author of the report |
10 | ||||||
| 1.9 | Professional standards and compliance |
10 | ||||||
| 1.10 | Control processes and review |
11 | ||||||
| 1.11 | Funding position of the AICF Trust |
11 | ||||||
| 1.12 | Basis of preparation of Report |
11 | ||||||
| 2 | Data |
12 | ||||||
| 2.1 | Data provided to KPMG Actuarial |
12 | ||||||
| 2.2 | Data limitations |
12 | ||||||
| 2.3 | Data reconciliation and testing |
12 | ||||||
| 2.4 | Data conclusion |
15 | ||||||
| 3 | Valuation Methodology and Approach |
16 | ||||||
| 3.1 | Previous valuation work and methodology changes |
16 | ||||||
| 3.2 | Overview of current methodology |
16 | ||||||
| 3.3 | Disease type and class subdivision |
18 | ||||||
| 3.4 | Numbers of future claims notifications |
20 | ||||||
| 3.5 | Incidence of claim settlements from future claim notifications |
25 | ||||||
| 3.6 | Average claim costs of IBNR claims |
25 | ||||||
| 3.7 | Proportion of claims settled for nil amounts |
26 | ||||||
| 3.8 | Pending claims |
27 | ||||||
| 3.9 | Insurance Recoveries |
28 | ||||||
| 3.10 | Cross-claim recoveries |
32 | ||||||
| 3.11 | Discounting cashflows |
33 | ||||||
| 4 | Claims Experience – Mesothelioma Claim Numbers |
34 | ||||||
| 4.1 | Overview |
34 | ||||||
| 4.2 | Profile of mesothelioma claims |
37 | ||||||
| 4.3 | External statistics on mesothelioma claims incidence |
42 | ||||||
| 4.4 | Base valuation assumption for number of mesothelioma claims |
44 | ||||||
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 5 | Claims Experience – Claim numbers (non-mesothelioma diseases) |
45 | ||||||
| 5.1 | Overview |
45 | ||||||
| 5.2 | Asbestosis claims |
45 | ||||||
| 5.3 | Lung cancer claims |
45 | ||||||
| 5.4 | ARPD & Other claims |
46 | ||||||
| 5.5 | Workers Compensation and Wharf claims |
46 | ||||||
| 5.6 | Summary of base claims numbers assumptions (including mesothelioma) |
47 | ||||||
| 5.7 | Baryulgil |
47 | ||||||
| 6 | Exposure and Latency Experience and Incidence Pattern Assumptions |
48 | ||||||
| 6.1 | Exposure information |
48 | ||||||
| 6.2 | Latency period of reported claims |
50 | ||||||
| 6.3 | Modelled peak year of claims |
54 | ||||||
| 6.4 | Pattern of future claim notifications assumed |
56 | ||||||
| 7 | Claims Experience – Average Claims Costs and Average Legal Costs |
58 | ||||||
| 7.1 | Overview |
58 | ||||||
| 7.2 | Mesothelioma claims |
59 | ||||||
| 7.3 | Asbestosis claims |
61 | ||||||
| 7.4 | Lung cancer claims |
62 | ||||||
| 7.5 | ARPD & Other claims |
63 | ||||||
| 7.6 | Workers Compensation claims |
64 | ||||||
| 7.7 | Wharf claims |
65 | ||||||
| 7.8 | Mesothelioma large claim size and incidence rates |
66 | ||||||
| 7.9 | Summary average claim cost assumptions |
68 | ||||||
| 7.10 | Defence legal costs |
69 | ||||||
| 7.11 | Summary average defendant legal costs assumptions |
71 | ||||||
| 8 | Claims Experience – Nil Settlement Rates |
72 | ||||||
| 8.1 | Overview |
72 | ||||||
| 8.2 | Mesothelioma claims |
73 | ||||||
| 8.3 | Asbestosis claims |
74 | ||||||
| 8.4 | Lung cancer claims |
75 | ||||||
| 8.5 | ARPD & Other claims |
76 | ||||||
| 8.6 | Workers Compensation claims |
77 | ||||||
| 8.7 | Wharf claims |
78 | ||||||
| 8.8 | Summary assumptions |
79 | ||||||
| 9 | Economic and Other Assumptions |
80 | ||||||
| 9.1 | Overview |
80 | ||||||
| 9.2 | Claims inflation |
80 | ||||||
| 9.3 | Superimposed inflation |
85 | ||||||
| 9.4 | Discount rates: Commonwealth bond zero coupon yields |
89 | ||||||
| 9.5 | Cross-claim recovery rates |
90 | ||||||
| 9.6 | Settlement Patterns |
91 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10 | Valuation Results |
93 | ||||||
| 10.1 | Central estimate liability |
93 | ||||||
| 10.2 | Comparison with previous valuation |
94 | ||||||
| 10.3 | Comparison of valuation results since 30 September 2006 |
97 | ||||||
| 10.4 | Cashflow projections |
98 | ||||||
| 10.5 | Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations |
100 | ||||||
| 10.6 | Insurance Recoveries |
101 | ||||||
| 11 | Uncertainty |
102 | ||||||
| 11.1 | Overview |
102 | ||||||
| 11.2 | Sensitivity testing |
103 | ||||||
| 11.3 | Results of sensitivity testing |
105 |
Tables
| Table 2.1: Grouping of financial data from claims and accounting databases |
14 | |||
| Table 2.2: Comparison of amounts from claims and accounting databases ($m) |
14 | |||
| Table 3.1: Change in cost of claims during 2014/15 financial year ($m) – claim award component only |
28 | |||
| Table 5.1: Number of claims by disease type |
45 | |||
| Table 5.2: Claim numbers experience and assumptions for 2015/16 |
47 | |||
| Table 6.1: Assumed underlying latency distribution parameters from average date of exposure to date of notification |
54 | |||
| Table 6.2: Modelled peak year of claim notifications |
54 | |||
| Table 7.1: Average attritional non-nil claim award (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) |
58 | |||
| Table 7.2: Average mesothelioma claims assumptions |
59 | |||
| Table 7.3: Average asbestosis claims assumptions |
61 | |||
| Table 7.4: Average lung cancer claims assumptions |
62 | |||
| Table 7.5: Average ARPD & Other claims assumptions |
63 | |||
| Table 7.6: Average Workers Compensation claims assumptions |
64 | |||
| Table 7.7: Average wharf claims assumptions |
65 | |||
| Table 7.8: Summary average claim cost assumptions |
68 | |||
| Table 8.1: Nil settlement rates |
72 | |||
| Table 8.2: Summary nil settlement rate assumptions |
79 | |||
| Table 9.1: Base inflation assumptions |
85 | |||
| Table 9.2: Zero coupon yield curve by duration |
89 | |||
| Table 9.3: Settlement pattern of claims awards by delay from claim reporting |
92 | |||
| Table 10.1: Comparison of central estimate of liabilities |
93 | |||
| Table 10.2: Comparison of valuation results since 30 September 2006 |
97 | |||
| Table 10.3: Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations |
100 | |||
| Table 10.4: Insurance recoveries at 31 March 2015 |
101 | |||
| Table 11.1: Summary results of sensitivity analysis ($m) |
106 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
|
Figures
|
| |||
| Figure 3.1: Illustration of timeline of exposure, latency and claim reporting (example shown is for mesothelioma) |
21 | |||
| Figure 3.2: Consumption and production indices – Australia 1930-2002 |
22 | |||
| Figure 4.1: Number of mesothelioma claims reported annually |
34 | |||
| Figure 4.2: Monthly notifications of mesothelioma claims |
35 | |||
| Figure 4.3: Rolling annualised averages of mesothelioma claim notifications |
36 | |||
| Figure 4.4: Number of mesothelioma claims by State |
37 | |||
| Figure 4.5: Number of mesothelioma claims by type of claim |
38 | |||
| Figure 4.6: Number of mesothelioma claims by number of defendants (direct claims only) |
39 | |||
| Figure 4.7: Number of mesothelioma claims by age of claimant |
40 | |||
| Figure 4.8: Delay from diagnosis of mesothelioma to notification of claim against the Liable Entities |
41 | |||
| Figure 4.9: Number of mesothelioma cases reported nationally compared to the number of claims received by the Liable Entities |
42 | |||
| Figure 4.10: Number of mesothelioma cases reported in NSW |
43 | |||
| Figure 6.1: Mix of claims by duration of exposure (years) |
48 | |||
| Figure 6.2: Exposure (person-years) of all Liable Entities’ claimants to date |
49 | |||
| Figure 6.3: Exposure (person years) of all claimants to date by report year and exposure period |
50 | |||
| Figure 6.4: Latency of mesothelioma claims |
51 | |||
| Figure 6.5: Latency of asbestosis claims |
52 | |||
| Figure 6.6: Latency of lung cancer claims |
53 | |||
| Figure 6.7: Latency of ARPD & Other claims |
53 | |||
| Figure 6.8: Projected future claim notifications for mesothelioma |
56 | |||
| Figure 6.9: Comparison with previous mesothelioma incidence curve assumptions |
56 | |||
| Figure 6.10: Projected future claim notifications for other disease types |
57 | |||
| Figure 7.1: Average attritional awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for mesothelioma claims (excluding large claims) |
59 | |||
| Figure 7.2: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for asbestosis claims |
61 | |||
| Figure 7.3: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for lung cancer claims |
62 | |||
| Figure 7.4: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for ARPD & Other claims |
63 | |||
| Figure 7.5: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for Workers Compensation claims |
64 | |||
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| Figure 7.6: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for wharf claims |
65 | |||
| Figure 7.7: Distribution of individual large claims by settlement year |
66 | |||
| Figure 7.8: Number of mesothelioma large claims by year of notification |
67 | |||
| Figure 8.1: Mesothelioma nil claims experience |
73 | |||
| Figure 8.2: Asbestosis nil claims experience |
74 | |||
| Figure 8.3: Lung cancer nil claims experience |
75 | |||
| Figure 8.4: ARPD & Other nil claims experience |
76 | |||
| Figure 8.5: Workers Compensation nil claims experience |
77 | |||
| Figure 8.6: Wharf nil claims experience |
78 | |||
| Figure 9.1: Trends in Bond Yields |
81 | |||
| Figure 9.2: Trends in CPI and AWOTE |
82 | |||
| Figure 9.3: Age profile of mesothelioma claimants by report year |
83 | |||
| Figure 9.4: Average mesothelioma claim settlement amounts by decade of age |
84 | |||
| Figure 9.5: Average mesothelioma awards of the Liable Entities (uninflated) |
87 | |||
| Figure 9.6: Zero coupon yield curve by duration |
90 | |||
| Figure 9.7: Cross-claim recovery experience |
91 | |||
| Figure 9.8: Settlement pattern derivation for mesothelioma claims: paid as % of ultimate cost |
92 | |||
| Figure 9.9: Settlement pattern derivation for non-mesothelioma claims: paid as % of ultimate cost |
92 | |||
| Figure 10.1: Analysis of change in central estimate liability (discounted basis) |
95 | |||
| Figure 10.2: Analysis of change in central estimate liability (undiscounted basis) |
96 | |||
| Figure 10.3: Comparison of actual net cash outflows with projected net payments at the 30 September 2006 valuation |
98 | |||
| Figure 10.4: Historical claim-related expenditure of the Liable Entities |
98 | |||
| Figure 10.5: Annual cashflow projections – inflated and undiscounted ($m) |
99 | |||
| Figure 11.1: Sensitivity testing results – Impact around the Discounted Central Estimate (in $m) |
105 | |||
| Figure 11.2: Sensitivity testing results – Impact around the undiscounted central estimate (in $m) |
105 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| Appendices
|
| |||||
| A |
Credit rating default rates by duration |
108 | ||||
| B |
Projected inflated and undiscounted cashflows ($m) |
109 | ||||
| C |
Projected inflated and discounted cashflows ($m) |
110 | ||||
| D |
Australian asbestos consumption and production data: 1930-2002 |
111 | ||||
| E |
Data provided by AICFL |
112 | ||||
| F |
Glossary of terms used in the Amended Final Funding Agreement |
114 | ||||
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease | |
|
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust | ||
|
Effective as at 31 March 2015 | ||
|
21 May 2015
|
Executive Summary
Important Note: Basis of Report
This valuation report (“the Report”) has been prepared by KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd (ABN 91 144 686 046) (“KPMG Actuarial”) in accordance with an “Amended and Restated Final Funding Agreement in respect of the provision of long-term funding for compensation arrangements for certain victims of Asbestos-related diseases in Australia” (hereafter referred to as the “the Amended Final Funding Agreement”) between James Hardie Industries NV (now known as James Hardie Industries plc) (hereafter referred to as “James Hardie”), James Hardie 117 Pty Limited, the State of New South Wales and Asbestos Injuries Compensation Fund Limited (“AICFL”) which was signed on 21 November 2006.
This Report is intended to meet the requirements of the Amended Final Funding Agreement and values the asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust.
This Report is not intended to be used for any other purpose and may not be suitable, and should not be used, for any other purpose. Opinions and estimates contained in the Report constitute our judgment as of the date of the Report.
The information contained in this Report is of a general nature and is not intended to address the objectives, financial situation or needs of any particular individual or entity. It is provided for information purposes only and does not constitute, nor should it be regarded in any manner whatsoever as, advice and is not intended to influence a person in making a decision in relation to any financial product or an interest in a financial product. No one should act on the information contained in this Report without obtaining appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the accuracy and appropriateness of the information contained in this Report having regard to their objectives, financial situation and needs.
In preparing the Report, KPMG Actuarial has relied on information supplied to it from various sources and has assumed that the information is accurate and complete in all material respects. KPMG Actuarial has not independently verified the accuracy or completeness of the data and information used for this Report.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
i |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease | |
|
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust | ||
|
Effective as at 31 March 2015 | ||
|
21 May 2015
|
Except insofar as liability under statute cannot be excluded, KPMG Actuarial, its executives, directors, employees and agents will not be held liable for any loss or damage of any kind arising as a consequence of any use of the Report or purported reliance on the Report including any errors in, or omissions from, the valuation models.
The Report must be read in its entirety. Individual sections of the Report, including the Executive Summary, could be misleading if considered in isolation. In particular, the opinions expressed in the Report are based on a number of assumptions and qualifications which are set out in the full Report.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
ii |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Introduction
The Amended Final Funding Agreement requires the completion of an Annual Actuarial Report evaluating the potential asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust. KPMG Actuarial has been retained by AICFL to provide this Annual Actuarial Report as required under the Amended Final Funding Agreement and this is detailed in our Engagement Letter dated 13 November 2014.
The Liable Entities are defined as being the following entities:
| ● | Amaca Pty Ltd (formerly James Hardie & Coy); |
| ● | Amaba Pty Ltd (formerly Jsekarb, James Hardie Brakes and Better Brakes); and |
| ● | ABN60 Pty Ltd (formerly James Hardie Industries Ltd). |
In addition, the liability for Baryulgil claims is deemed to be a liability of Amaca by virtue of the James Hardie (Civil Liability) Act 2005 (NSW). Under Part 4 of that Act, Amaca is liable for the “Marlew Asbestos Claims” or “Marlew Contribution Claims” as defined in that Act.
Our valuation is on a central estimate basis and is intended to be effective as at 31 March 2015. It has been based on claims data and information as at 31 March 2015 provided to us by AICFL.
Overview of Recent Claims Experience and comparison with previous valuation projections
In this section we compare the actual experience in 2014/15 (referred to in the following tables as “FY15 Actual”) with the projections for 2014/15 that were contained within our previous valuation report at 31 March 2014. We will refer to these projections for 2014/15 as “FY15 Expected” in the tables that follow.
Claim numbers
There have been 412 mesothelioma claims reported in 2014/15, an 11% increase on the 370 mesothelioma claims reported in 2013/14.
For non-mesothelioma claims (excluding workers compensation claims), there have been 219 claims reported in 2014/15 compared to 207 claims reported in 2013/14. There has been greater variation within the individual disease types.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
iii |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following table shows the comparison of actual experience with that which had been forecast at the previous valuation.
Table E.1. Comparison of claim numbers
| FY15 Actual | FY15 Expected |
Ratio of Actual to Expected (%) |
FY14 Actual | |||||
| Mesothelioma |
412 | 370 | 111% | 370 | ||||
| Asbestosis |
145 | 120 | 121% | 117 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
25 | 30 | 83% | 26 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
38 | 48 | 79% | 49 | ||||
| Wharf |
11 | 12 | 92% | 15 | ||||
| Workers |
34 | 30 | 113% | 31 | ||||
| Total |
665 | 610 | 109% | 608 |
Average Claim Awards
Average claims awards in 2014/15 have been lower than expectations across all disease types.
There have been seven large mesothelioma claim settlements (being claims in excess of $1m in 2006/07 money terms) in 2014/15, which is lower than our expectations. Total claims expenditure on large claims has been 29% below expectations, reflecting both a lower frequency and a lower average cost than expected.
The following table shows the comparison of actual experience with that which had been forecast at the previous valuation.
Table E.2. Comparison of average claim size of non-nil claims
| FY15 Actual | FY15 Expected |
Ratio of Actual to Expected |
FY14 Actual | |||||
| ($) | ($) | (%) | ($) | |||||
| Mesothelioma |
301,275 | 328,600 | 92% | 311,346 | ||||
| Asbestosis |
99,251 | 121,900 | 81% | 98,795 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
134,262 | 137,800 | 97% | 103,720 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
70,366 | 100,700 | 70% | 96,959 | ||||
| Wharf |
80,024 | 112,360 | 71% | 103,816 | ||||
| Workers |
70,000 | 148,400 | 47% | 20,000 | ||||
| Mesothelioma Large Claims (settled) | ||||||||
| Number |
7 | 9.25 | 76% | 7 | ||||
| Average claim size |
1,940,571 | 2,067,000 | 94% | 1,657,286 | ||||
| Total Cost |
13,584,000 | 19,119,750 | 71% | 11,601,000 |
Note: FY14 Actual values are expressed in 2013/14 money terms. FY15 Actual values and FY15 Expected values are expressed in 2014/15 money terms.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
iv |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Cashflow expenditure: gross and net
Gross cashflow expenditure, at $154.3m, was 4% above expectations.
Net cashflow expenditure, at $121.1m, was 6% below expectations.
Table E.3. Comparison of cashflow
| FY15 Actual
($M) |
FY15 Expected
($M) |
Ratio of Actual to Expected (%) |
FY14 Actual
($M) | |||||
|
Gross Cashflow
|
154.3 | 148.9 | 104% | 140.4 | ||||
|
Insurance and Other Recoveries
|
(17.9) | (20.5) | 87% | (21.5) | ||||
|
Insurance recoveries from HIH / Commutations
|
(15.3) | 0.0 | n/a | (6.0) | ||||
|
Net Cashflow before HIH / Commutations
|
136.4 | 128.4 | 106% | 118.9 | ||||
|
Net Cashflow after HIH / Commutations
|
121.1 | 128.4 | 94% | 112.9 |
Insurance and Other Recoveries have been considerably higher than expected. However, this is entirely due to proceeds from insurance collections from HIH and associated entities as a result of successful applications of Section 562A(4).
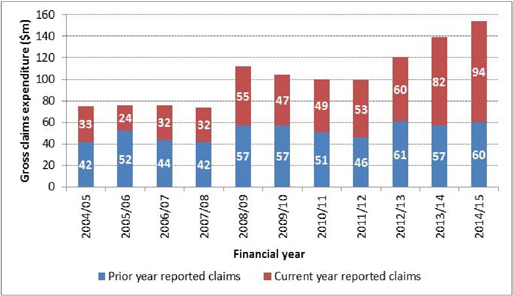
The following chart shows the composition of the gross cashflow between current and prior years’ reported claims.
Figure E.1. Composition of gross cashflow between current and prior years’ reported claims
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
v |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Payments in relation to claims reported in the financial year have shown a further increase compared with the previous year. This is predominantly due to the higher number of mesothelioma claims reported in the year and which have been settled in the year.
Payments in relation to prior years’ reported claims have been relatively stable in the most recent three years.
Liability Assessment
At 31 March 2015, our projected central estimate of the liabilities of the Liable Entities (the Discounted Central Estimate) to be met by the AICF Trust is $2,142.8m (March 2014: $1,870.2m).
We have not allowed for the future Operating Expenses of the AICF Trust or the Liable Entities in the liability assessment.
Table E.4. Comparison of central estimate of liabilities
| 31 March 2015 $m |
31 March 2014 $m | |||||||
| Gross of insurance recoveries |
Insurance recoveries |
Net of insurance recoveries |
Net of insurance
recoveries | |||||
|
Total uninflated and undiscounted cash-flows
|
1,795.2 | 229.3 | 1,565.9 | 1,546.6 | ||||
|
Inflation allowance
|
1,257.5 | 80.5 | 1,177.0 | 1,258.5 | ||||
|
Total inflated and undiscounted cash-flows
|
3,052.7 | 309.8 | 2,742.9 | 2,805.1 | ||||
|
Discounting allowance
|
(656.0) | (56.0) | (600.1) | (934.9) | ||||
|
Net present value liabilities
|
2,396.7 | 253.8 | 2,142.8 | 1,870.2 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
vi |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Comparison with previous valuation
In the absence of any change to the claim projection assumptions from our 31 March 2014 valuation, other than allowing for the changes in the discount rate, we would have projected a Discounted Central Estimate liability of $2,075.0m as at 31 March 2015, i.e. an increase of $204.8m from our 31 March 2014 valuation result.
This increase of $204.8m is due to:
| ● | A reduction of $81.6m, being the net impact of expected claims payments (which reduce the liability) and the “unwind of discount” (which increases the liability and reflects the fact that cashflows are now one year nearer and therefore are discounted by one year less). |
| ● | An increase of $286.4m resulting from the significantly lower discount rates prevailing at 31 March 2015 compared with those adopted at 31 March 2014. |
Our liability assessment at 31 March 2015 of $2,142.8m therefore represents an increase of $67.8m, which arises from changes to the claim projection assumptions.
The increase of $67.8m is principally a consequence of:
| ● | An increase in the projected future number of claims for mesothelioma and asbestosis; |
offset by
| ● | Lower average claims sizes and average defence legal cost assumptions for most disease types; |
| ● | Changes to assumed future patterns of claims settlement; and |
| ● | Favourable settlement experience for claims that were pending at 31 March 2014 relative to case estimates established at 31 March 2014. |
The following chart shows an analysis of the change in our liability assessments from 31 March 2014 to 31 March 2015.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
vii |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure E.2. Analysis of change in central estimate liability (discounted basis)
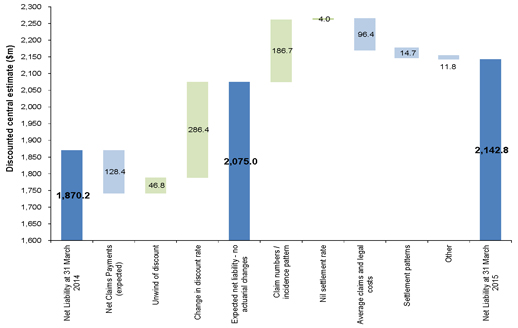
Note: Green bars signal that this factor has given rise to an increase in the liability whilst light blue bars signal that this factor has given rise to a reduction in the liability.
The undiscounted liability as of 31 March 2015 has increased from $2,677m (based on the 31 March 2014 valuation) to $2,743m. This represents an increase of $66m.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
viii |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations
The Amended Final Funding Agreement sets out the basis on which payments will be made to the AICF Trust.
Additionally, there are a number of other figures specified within the Amended Final Funding Agreement that we are required to calculate. These are:
| ● | Discounted Central Estimate; |
| ● | Term Central Estimate; and |
| ● | Period Actuarial Estimate. |
Table E.5. Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations
| $m | ||
|
Discounted Central Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, Insurance and Other Recoveries)
|
2,142.8 | |
| Period Actuarial Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, gross of Insurance and Other Recoveries) comprising: | 544.2 | |
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2015/16
|
171.4 | |
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2016/17
|
185.0 | |
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2017/18
|
187.7 | |
| Term Central Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, Insurance and Other Recoveries)
|
2,135.3 |
The actual funding amount due at a particular date will depend upon a number of factors, including:
| ● | the net asset position of the AICF Trust at that time; |
| ● | the free cash flow amount of the James Hardie Group in the preceding financial year; and |
| ● | the Period Actuarial Estimate in the latest Annual Actuarial Report. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
ix |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Uncertainty
Estimates of asbestos-related disease liabilities are subject to considerable uncertainty, significantly more than personal injury liabilities in relation to other causes, such as CTP or Workers Compensation claims.
It should therefore be expected that the actual emergence of the liabilities will vary from any estimate. As indicated in Figure E.3, depending on the actual out-turn of experience relative to that currently forecast, the variation could potentially be substantial.
Thus, no assurance can be given that the actual liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust will not ultimately exceed the estimates contained in this Report. Any such variation may be significant.
The uncertainties prevailing at this year-end (and at the previous year-end) are higher than historically observed. This is a consequence of the higher than expected level of mesothelioma claims reporting and the uncertainty this brings in relation to the projection of the future number of mesothelioma claims to be received.
We have performed sensitivity testing to identify the impact of different assumptions upon the size of the liabilities. The different scenarios selected are documented at Section 11.2 of this report.
We have not included a sensitivity test for the impact of changes in discount rates although, as noted in this Report, changes in discount rates can introduce significant volatility to the Discounted Central Estimate result reported at each year-end.
We note that these sensitivity test ranges are not intended to correspond to a specified probability of sufficiency, nor are they intended to indicate an upper bound or a lower bound of all possible outcomes.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
x |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure E.3. Sensitivity testing results – Impact around the Discounted Central Estimate (in $m)
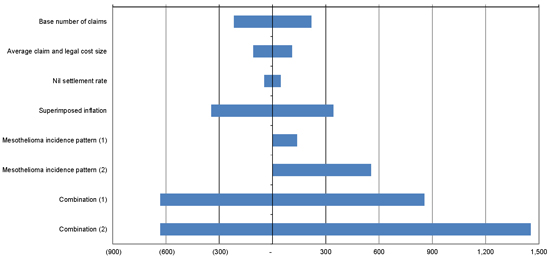
The single most sensitive assumption shown in the chart is the timing of the peak period of claims reporting against the Liable Entities. Shifting the assumed period of peak claims reporting by a further 2 years for mesothelioma (i.e. assuming that claim reporting begins to reduce after 2018/19) together with increased claims reporting from 2026/27 onwards could add a further $555m (26%) on a discounted basis (as shown in the above chart by the scenario labelled “mesothelioma incidence pattern (2)”).
Table E.6. Summary results of sensitivity analysis ($m)
| Undiscounted | Discounted | |||
|
Central estimate
|
2,742.9 | 2,142.8 | ||
|
Low Scenario
|
1,860.4 | 1,510.4 | ||
|
High Scenario
|
4,931.1 | 3,596.7 |
Whilst the table above indicates a range around the discounted central estimate of liabilities of -$632m to +$1,454m, the actual cost of liabilities could fall outside that range depending on the actual experience.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
xi |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Data, Reliances and Limitations
We have been provided with the following data by AICFL:
| ● | Claims dataset at 31 March 2015 with individual claims listings; |
| ● | Accounting transactions dataset at 31 March 2015 (which includes individual claims payment details); and |
| ● | Detailed insurance bordereaux information (being a listing of claims filed with the insurers of the Liable Entities) produced by Randall & Quilter Investment Holdings as at 31 March 2015. |
While we have tested the consistency of the various data sets provided, we have not otherwise verified the data nor have we undertaken any auditing of the data at source. We have relied on the data provided as being complete and accurate in all material respects. Consequently, should there be material errors or incompleteness in the data, our assessment could be affected materially.
Executive Summary Not Report
Please note that this executive summary is intended as a brief overview of our Report. To properly understand our analysis and the basis of our liability assessment requires examination of our Report in full.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
xii |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 1 | Scope and Purpose
| |||
| 1.1 | Introduction |
The Amended Final Funding Agreement requires the completion of an Annual Actuarial Report evaluating the potential asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust.
| 1.1.1 | Liable Entities |
The Liable Entities are defined as being the following entities:
| ● | Amaca Pty Ltd (formerly James Hardie & Coy); |
| ● | Amaba Pty Ltd (formerly Jsekarb, James Hardie Brakes and Better Brakes); and |
| ● | ABN60 Pty Ltd (formerly James Hardie Industries Ltd). |
In addition, the liability for Baryulgil claims is deemed to be a liability of Amaca by virtue of the James Hardie (Civil Liability) Act 2005 (NSW). Under Part 4 of that Act, Amaca is liable for “Marlew Asbestos Claims” or “Marlew Contribution Claims” as defined in that Act.
| 1.1.2 | Personal asbestos claims |
Under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, the liabilities to be met by the AICF Trust relate to personal asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities.
Such claims must relate to exposure which took place in Australia and which have been brought in a Court in Australia.
The precise scope of the liabilities is documented in Section 1.2 and in Appendix F of this Report.
| 1.1.3 | Purpose of report |
KPMG Actuarial has been retained by AICFL to provide an Annual Actuarial Report as required under the Amended Final Funding Agreement and this is detailed in our Engagement Letter dated 13 November 2014.
The prior written consent of KPMG Actuarial is required for any other use of this Report or the information contained in it.
Our valuation is effective as at 31 March 2015 and has been based on claims data and information as at 31 March 2015 provided to us by AICFL.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
1 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 1.2 | Scope of report |
We have been requested to provide an actuarial assessment as at 31 March 2015 of the asbestos-related disease liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust, consistent with the terms of the Amended Final Funding Agreement.
The assessment is on a central estimate basis and is based on the claims experience as at 31 March 2015.
A “central estimate” liability assessment is an estimate of the expected value of the range of potential future liability outcomes. In other words, if all the possible values of the liabilities are expressed as a statistical distribution, the central estimate is an estimate of the mean of that distribution.
It is of note that our liability assessment:
| ● | Relates to the Liable Entities and Marlew (in relation to Marlew Claims arising from asbestos mining activities at Baryulgil). |
| ● | Is intended to cover: |
| - | The amount of settlements, judgments or awards for all Personal Asbestos Claims. |
| - | Claims Legal Costs incurred by the AICF Trust in connection with the settlement of Personal Asbestos Claims. |
| ● | Is not intended to cover: |
| - | Personal injury or death claims arising from exposure to asbestos which took place outside Australia. |
| - | Personal injury or death claims, arising from exposure to Asbestos, which are brought in Courts outside Australia. |
| - | Claims for economic loss, other than any economic loss forming part of an award for damages for personal injury and/or death. |
| - | Claims for loss of property, including those relating to land remediation. |
| - | The costs of asbestos or asbestos product removal relating to asbestos or asbestos products manufactured or used by or on behalf of the Liable Entities. |
| ● | Includes an allowance for: |
| - | Compensation to the NSW Dust Diseases Board or a Workers Compensation Scheme by way of a claim by such parties for contribution or reimbursement from the Liable Entities, but only to the extent that the cost of such claims is within the limits of funding for such claims as outlined within the Amended Final Funding Agreement. |
| - | Workers Compensation claims, being claims from former employees of the Liable Entities, but only to the extent that such liabilities are not met by a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy (see section 1.2.1). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
2 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Assumes that the product and public liability insurance policies of the Liable Entities will continue to respond to claims as and when they fall due. We have not made any allowance for the impact of any disputation concerning Insurance Recoveries, nor for any legal costs that may be incurred in resolving such disputes. |
| ● | Makes no allowance for: |
| - | potential Insurance Recoveries that could be made on product and public liability insurance policies placed from 1986 onwards which were placed on a “claims made” basis. |
| - | the future Operating Expenses of the Liable Entities or the AICF Trust. Separate allowance for future Operating Expenses should be considered by the management of AICFL. |
| - | the inherent uncertainty of the liability assessment. That is, no additional provision (or risk margin) has been included in excess of a central estimate. |
Readers of this Report may refer to our previous reports which are available at www.ir.jameshardie.com.au and www.aicf.org.au.
| 1.2.1 | Workers Compensation |
Workers Compensation claims are claims made by former employees of the Liable Entities. Such past, current and future reported claims were insured with, amongst others, Allianz Australia Limited, QBE and the various State-based Workers Compensation Schemes.
Under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, the part of a future Workers Compensation claim that is met by a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy of the Liable Entities is outside of the AICF Trust. The AICF Trust is, however, to provide for any part of a claim not covered by a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy (e.g. as a result of the existence of limits of indemnity and policy deductibles on those policies of insurance).
On this basis our liability assessment in relation to Workers Compensation claims and which relates to the AICF Trust, includes only the amount borne by the Liable Entities in excess of the anticipated recoveries due from a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
3 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
In making our assessment we have assumed that the Workers Compensation insurance programme will continue to respond to claims by former employees of the Liable Entities as and when they fall due. To the extent that they were not to respond owing to (say) insurer insolvency, Insurer Guarantee Funds may be available to meet such obligations.
| 1.2.2 | Dust Disease Board and Other Reimbursements |
There exists a right under Section 8E (Reimbursement Provisions) of the Dust Diseases Act 1942 for the NSW Dust Diseases Board (“DDB”) to recover certain costs from common law defendants, excluding the employer of the claimant.
This component of cost is implicitly included within our liability assessment as the claims awards made in recent periods and in recent settlements contain allowance for DDB reimbursement where applicable. Furthermore, currently reported open claims have an allowance within their case estimates for the costs of DDB reimbursement where relevant and applicable.
The Amended Final Funding Agreement indicates that the AICF Trust is intended to meet Personal Asbestos Claims and that claims by the DDB or a Workers Compensation Scheme for reimbursement will only be met up to a certain specified limit (aggregated across the DDB and Workers Compensation Schemes), being:
| ● | In the first financial year (2006/07) a limit of $750,000 applied; |
| ● | In respect of each financial year thereafter, that limit is indexed annually in line with the Consumer Price Index. At 31 March 2015, the annual limit is $938,974; |
| ● | There is an overall unindexed aggregate cap of $30m; |
| ● | At 31 March 2015, AICF has paid out $6,648,481 to the DDB. |
The cashflow and liability figures contained within this Report have already removed that component of any reimbursements that will not be met by the AICF Trust owing to the application of these limits and caps.
| 1.2.3 | Baryulgil (“Marlew Claims”) |
“Marlew Asbestos Claims” and “Marlew Contribution Claims” are deemed to be liabilities of Amaca. These claims specifically include:
| ● | Claims made against Amaca Pty Ltd or ABN60 resulting from their past ownership of the mine; and, in the case of Amaca, includes claims made in relation to the joint venture (Asbestos Mines Pty Ltd) established with Wunderlich in 1944 to begin mining at Baryulgil. |
| ● | Claims made against the subsequent owner of the mine (following its sale by James Hardie Industries to Woodsreef in 1976), being Marlew Mining Pty Ltd (“Marlew”) which is in liquidation, are to be met by the AICF Trust except where such claims are Excluded Marlew Claims, which are recoverable by the Claimant from other sources. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
4 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
These claims are discussed further in Section 5.7.
| 1.2.4 | Risk Margins |
Australian-licensed insurance companies are required to hold, and many non-insurance companies elect to hold, insurance and self-insurance claims provisions at a level above the central estimate basis to reflect the uncertainty attaching to the liability assessment and to include an allowance in respect of that uncertainty.
A risk margin is an additional amount held, above the central estimate, so as to increase the likelihood of adequacy of the provisions to meet the ultimate cost of settlement of those liabilities.
We note that the Amended Final Funding Agreement envisages the ongoing financing of the AICF Trust is to be based on a “central estimate” approach and that the Annual Actuarial Report should provide a Discounted Central Estimate valuation.
Accordingly, we have made no allowance for any risk margins within this Report.
| 1.2.5 | Discounting |
We have determined a Discounted Central Estimate in this Report by discounting (to 31 March 2015) the projected future cashflows using yields on Commonwealth Government Bonds.
Conceptually, the Discounted Central Estimate at 31 March 2015 would normally represent an amount of money which, if fully provided in advance (i.e. as of 31 March 2015) and invested in risk-free assets (such as Commonwealth Government Bonds) of term and currency appropriate to the liabilities, would generate the necessary investment income such that (together with the capital value of those assets) it would be expected to be sufficient to pay for the liabilities as they fall due.
To the extent that the actual investments are:
| ● | of different terms; and/or |
| ● | in different currencies; and/or |
| ● | provide different expected rates of return |
investment profits or losses would emerge.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
5 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
One of the uncertainties in our valuation is the fact that fixed interest Commonwealth Government Bonds do not exist at most of the durations of our cashflow projection.
At 31 March 2015, there were 21 fixed interest Commonwealth Government Bonds on issue (with a face value of approximately $330bn), with 7 of them having maturity dates after 31 March 2025 (with a face value of $77bn). At 31 March 2015, the longest-dated maturity was April 2037.
This means we need to take a long-term view on bond yields that is not measured by market-observable rates of return.
We continue to note that the actual funding mechanism under the Amended Final Funding Agreement only provides for up to three years’ worth of projected Claims and Claims Legal Costs expenditure and one year’s worth of Operating Expenses at any one time.
| 1.3 | Areas of potential exposure |
As identified in Section 1.2, there are other potential sources of claims exposure beyond those directly considered within this Report. However, in a number of cases they are unquantifiable even if they have the potential to generate claims. This is especially the case for those sources of future claim where there has been no evidence of claims to date.
| 1.3.1 | General areas of potential exposure |
Areas of potential changes in claims exposure we have not explicitly allowed for in our valuation include, but are not limited to:
| ● | Future significant individual landmark and precedent-setting judicial decisions; |
| ● | Significant medical advancements; |
| ● | Unimpaired claims, i.e. claims for fear, stress, pure nervous shock or psychological illness. In this regard, we note the 2010/11 decisions by the Supreme Court (in relation to two cases: Tamaresis v Amaca and Galea v Amaca) which indicated that the AICF Trust was not required to meet the cost of nervous shock claims brought by individuals who have not been exposed to asbestos; |
| ● | A change in the basis of compensation for asymptomatic pleural plaques for which no associated physical impairment is exhibited; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
6 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | A proliferation (compared to past and current levels of activity) of “third-wave” claims, i.e. claims arising as a result of indirect exposure such as home renovation, washing clothes of family members that worked with asbestos, or from workers involved in the removal of asbestos or the demolition of buildings containing asbestos; |
| ● | Changes in legislation, especially those relating to tort reform for asbestos sufferers; |
| ● | Introduction of new, or elimination of existing, heads of damage; |
| ● | Exemplary and aggravated or punitive damages (being damages awarded for personal injuries caused as a result of negligence or reckless conduct); |
| ● | Changes in the basis of apportionment of awards for asbestos-related diseases for claimants who have smoked (we note the decisions in Amaca v Ellis [2010] HCA 5 and Evans v Queanbeyan City Council [2010] NSWDDT 7 which we understand are consistent with the previous decision in Judd v Amaca [2002] NSWDDT 25); |
| ● | Changes to taxation; and |
| ● | Future bankruptcies of other asbestos claim defendants (i.e. other liable manufacturers or distributors). |
Nonetheless, implicit allowance is made in respect of some of these items in the allowance for superimposed inflation included in our liability assessment. Furthermore, to the extent that some of these have emerged in past claims experience, they are reflected in our projections.
| 1.3.2 | New Zealand and other overseas exposures |
We have made no allowance for the risk of further development in relation to New Zealand exposures and the rights of claims from New Zealand claimants in Australian courts (as per Frost vs. Amaca Pty Ltd (2005), NSWDDT 36 although this decision was successfully appealed by Amaca in August 2006) nor for the risk of additional exposures from overseas. This is because, as noted in Section 1.2, the AICF Trust is not required to meet the cost of these claims as they are Excluded Claims.
In relation to claimants where exposures have involved more than one country (e.g. UK and Australia), we have assumed that the AICF Trust will only meet that part of the cost which is attributable to the Australian-related exposure.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
7 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 1.3.3 | Third-wave claims |
We have made allowance for so-called “third-wave” claims. These are defined as claims for personal injury and / or death arising from asbestos exposure during home renovations by individuals or to builders involved in such renovations. Such claims are allowed for within the projections to the extent to which they have arisen to date and to the extent our exposure model factors in these exposures in its projection.
We have not allowed for a significant additional surge in third-wave claims (over and above current levels of activity) in the future arising from renovations, but conversely we have not allowed for a tempering of those third-wave claims already included within our projection as a result of improved education of individuals as to the risks of such home renovations, or of any local Councils or State Governments passing laws in this regard.
It should be noted that claims for the cost of asbestos or asbestos product removal from homes and properties or any claims for economic loss arising from asbestos or asbestos products being within such homes and properties is not required to be met by the AICF Trust.
| 1.4 | Data reliances and limitations |
KPMG Actuarial has relied upon the accuracy and completeness of the data with which it has been provided. KPMG Actuarial has not verified the accuracy or completeness of the data, although we have undertaken steps to test its consistency with data previously received. However, KPMG Actuarial has placed reliance on the data previously received, and currently provided, as being accurate and complete in all material respects.
| 1.5 | Uncertainty |
It must be understood that estimates of asbestos-related disease liabilities are subject to considerable uncertainty.
This is due to the fact that the ultimate disposition of future claims will be subject to the outcome of events that have not yet occurred. Examples of these events, as noted in Section 1.3, include jury decisions, court interpretations, legislative changes, epidemiological developments, medical advancements, public attitudes, potential additional third-wave exposures and social and economic conditions such as inflation.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
8 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Therefore, it should be expected that the actual emergence of the liabilities will vary, perhaps materially, from any estimate. Thus, no assurance can be given that the actual liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust will not ultimately exceed the estimates contained herein. Any such variation may be significant.
| 1.6 | Distribution and use |
The purpose of this Report is as stated in Section 1.1.
This Report should not be used for any purpose other than those specified.
This Report will be provided to the Board and management of AICFL. This Report will also be provided to the Board and management of James Hardie, the NSW Government and to Ernst & Young in their capacity as auditors to both James Hardie and AICFL.
We understand that this Report will be filed with the ASX and placed on James Hardie’s website in its entirety.
We understand that this Report will also be placed on AICFL’s website in its entirety.
KPMG Actuarial consents to this Report being made available to the above-mentioned parties and for the Report to be distributed in the manner described above.
To the extent permitted by law, neither KPMG Actuarial nor its Executives, directors or employees will be responsible to any third parties for the consequences of any actions they take based upon the opinions expressed with this Report, including any use of or purported reliance upon this Report not contemplated in Section 1.2. Any reliance placed is that party’s sole responsibility.
Where distribution of this Report is permitted by KPMG Actuarial, the Report may only be distributed in its entirety and judgements about the conclusions and comments drawn from this Report should only be made after considering the Report in its entirety and with necessary consultation with KPMG Actuarial.
Readers are also advised to refer to the “Important Note: Basis of Report” section at the front of the Executive Summary of this Report.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
9 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 1.7 | Date labelling convention used in this Report |
In our analyses throughout this Report (unless otherwise stated), the “year” we refer to aligns with the financial year of AICFL and James Hardie and runs from 1 April to 31 March.
A “2008” notified claim would be a claim notified in the period 1 April 2008 to 31 March 2009. This might also be referred to as “2008/09” or “FY09”.
Similarly, a “2014” claim settlement would be a claim settled in the period 1 April 2014 to 31 March 2015. This might also be referred to as “2014/15” or “FY15”.
| 1.8 | Author of the report |
This Report is authored by Neil Donlevy, an Executive of KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd, a Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries (London) and a Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia.
This Report is co-authored by Jefferson Gibbs, an Executive of KPMG Actuarial Pty Ltd, a Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries (London) and a Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia.
In relation to this Report, the primary regulator for both Neil Donlevy and Jefferson Gibbs is the Institute of Actuaries of Australia.
| 1.9 | Professional standards and compliance |
This Report details a valuation of the outstanding claims liabilities of entities which hold liabilities with features similar to general insurance liabilities as self-insured entities, and which have purchased related insurance protection.
In preparing this Report, we have complied with the Professional Standard 300 of the Institute of Actuaries of Australia (“PS300”), “Valuation of General Insurance Claims”.
However, as we note in Section 1.2, this Report does not include an allowance for the future Operating Expenses of the AICF Trust (which are estimated by AICFL) and nor does it include any allowance for a risk margin to reflect the inherent uncertainty in the liability assessment.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
10 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 1.10 | Control processes and review |
This valuation report and the underlying analyses have been subject to technical review and internal peer review.
The technical review focuses on ensuring that the valuation models and supporting claims experience analyses that are carried out are performed correctly and that the calculations are being correctly applied. The technical review also focuses on ensuring that the data that is being used has been reconciled insofar as possible.
Internal peer review involves a review of the approach, the methods, the assumptions selected and the professional judgments applied.
Both the technical review and internal peer review processes are applied to the Report as well as the valuation models.
| 1.11 | Funding position of the AICF Trust |
This Report does not analyse nor provide any opinion on the current, or prospective, funding position of the AICF Trust, nor of its likely funding needs and its potential use of the loan facility provided by the NSW Government.
This is because to do so within this Report would require consideration, estimation and documentation of the future financial performance of James Hardie.
This Report only provides analysis and opinion on the estimates of the future expenditure to be met by the AICF Trust.
The cashflow estimates contained in this Report assume that all claims against the Liable Entities will continue to be paid in full as and when they fall due.
| 1.12 | Basis of preparation of Report |
We have been advised by the management of AICFL to prepare the Report on a “going concern” basis (i.e. we should assume that AICFL will be able to meet the cost of the liabilities of the Liable Entities as they fall due).
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
11 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 2 | Data
| |||
| 2.1 | Data provided to KPMG Actuarial |
We have been provided with the following data by AICFL:
| ● | Claims dataset at 31 March 2015 with individual claims listings; |
| ● | Accounting transactions dataset at 31 March 2015 (which includes individual claims payment details); and |
| ● | Detailed insurance bordereaux information (being a listing of claims filed with the insurers of the Liable Entities) produced by Randall & Quilter Investment Holdings as at 31 March 2015. |
We have allowed for the benefits of the product and public liability insurance policies of the Liable Entities based on information provided to us by AICFL relating to the insurance programme’s structure, coverage and layers.
We have also considered the claims data listings which formed the basis of our previous valuation assessments.
The data structures for the claims and accounting databases provided to us by AICFL as of 31 March 2015 are detailed in Appendix E.
| 2.2 | Data limitations |
We have tested the consistency of the various data sets provided to us at different valuation dates. Section 2.3 outlines the nature of the testing undertaken.
However, we have not otherwise verified the data and have instead relied on the data provided as being complete and accurate in all material respects.
We have relied upon the robustness of AICFL’s internal administration and systems as to the completeness of the data provided.
Consequently, should there be material errors or incompleteness in the data, our assessment could also be affected materially.
| 2.3 | Data reconciliation and testing |
We have performed a reconciliation of the data provided at 31 March 2015 with the data provided at 31 March 2014.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
12 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
We have undertaken a number of tests and reconciliations to test the accuracy of the data to the extent possible, noting the limitations outlined above.
| 2.3.1 | Reconciliation with previous valuation’s data |
We have performed a reconciliation of the claims database as at 31 March 2015 with that provided at 31 March 2014. Our findings are:
| ● | Claims notifications: There were no late notifications (claims with a report date prior to 31 March 2014 that were not present in the database at 31 March 2014). In addition, no claims changed notification date between the two databases. |
| ● | Portfolio Category: Four claims changed category. Of these, 3 related to claims reported in 2013/14 and 1 related to 2012/13. |
| ● | Settlement date: No claims changed their settlement date. |
Changing and developing data is not unexpected or to be considered as adverse. Indeed, changing data is common to all claims administration systems. We do not consider the number or extent of the changes noted above to be unreasonable.
| 2.3.2 | Reconciliation of claims settlement amounts between claims and accounting databases |
The accounting database extract contains the following fields:
| ● | Damages – which are gross of cross-claim recoveries; |
| ● | Costs; |
| ● | DDB reimbursements; |
| ● | Other costs; |
| ● | Payments to Medicare; and |
| ● | Defence legal costs. |
The claims database extract contains the following fields:
| ● | Damages – which in some cases are net of cross-claim recoveries, and which in others are gross of cross-claim recoveries. We are able to identify which records are gross of cross-claims recoveries and which records are net of cross-claim recoveries. We have then restated all damages data to be gross of cross-claim recoveries; |
| ● | Costs; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
13 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | DDB reimbursements; |
| ● | Other costs (Consulting costs and payments to Medicare); and |
| ● | Defence legal costs. |
We then mapped the financial data between the two databases into standardised groupings as follows:
Table 2.1: Grouping of financial data from claims and accounting databases
| CLAIMS DATABASE | ACCOUNTING DATABASE | |||||
| Award | Damages (gross of cross-claims) plus DDB reimbursement plus Medicare (from Accounting Database) | Damages plus DDB reimbursements plus Medicare | ||||
| Costs / Other |
Costs plus Other less Medicare (from accounting database) |
Costs plus Consulting |
||||
|
Defence legal costs |
Defence legal costs |
Defence legal costs |
Note: Recovery amounts are available from the accounting database
We have compared the payment records between the claims database and the accounting database from the earliest date to the current file position. Table 2.2 shows the results of this reconciliation for all claim transactions to date.
Table 2.2: Comparison of amounts from claims and accounting databases ($m)
| CLAIMS DATABASE | ACCOUNTING DATABASE | |||||||||
| Damages (gross of recoveries, excluding medicare) | 1,226.6 | Damages (gross of recoveries) | 1,234.0 | |||||||
| Costs |
35.0 | Costs | 35.7 | |||||||
| DDB |
11.3 | DDB | 11.5 | |||||||
| Other (inc Medicare) |
5.8 | Consulting | 2.3 | |||||||
| Medicare | 3.2 | |||||||||
| Defence legal costs |
157.2 | Defence legal costs | 157.5 | |||||||
| Total Value |
1,435.9 | Total Value | 1,444.2 | |||||||
| Standardisation |
||||||||||
| Award plus Medicare plus DDB |
1,241.1 | Award plus Medicare plus DDB | 1,248.7 | |||||||
| Costs / Other |
37.6 | Costs / Other | 38.0 | |||||||
| Defence legal costs |
157.2 | Defence legal costs | 157.5 | |||||||
| Total Value |
1,435.9 | Total Value | 1,444.2 | |||||||
The standardisation is the most relevant comparison because, as noted earlier, the two database extracts allocate the information (particularly in relation to Medicare) in slightly different ways.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
14 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Once the standardisation has been undertaken, the two datasets reconcile closely – with reconciliation differences totalling approximately $8.3m or 0.6% (31 March 2014: $7.3m).
Our approach for each claim record has been to take the maximum value of the two databases for each claim record. This results in the following overall totals being used in our analysis:
| ● | $1,250.5m for the claims award component; |
| ● | $38.4m for the costs / other component; and |
| ● | $157.5m for the defence legal costs component. |
This approach, of taking the maximum value for each claims record, may result in some minor prudence in our overall analysis although the amount of prudence is not considered to be significant in the context of the size of the potential liabilities and the underlying uncertainty in any valuation estimating future claims costs over the next 40 years or more.
| 2.4 | Data conclusion |
We have not verified the underlying data nor have we undertaken “auditing at source”. No material data issues have been identified and notified to us by the Approved Auditor of AICFL (Ernst & Young) during their testing.
We have tested the data for internal consistency with the data provided at the previous valuation (31 March 2014).
Based on that testing and reconciliation, and subject to the limitations described in Section 1.4, we have formed the view that:
| ● | Generally, the data is consistent between valuations, with any differences in the data being readily explainable; |
| ● | The financial data appears to reconcile reasonably between the two data sources (the claims dataset and the accounting dataset); |
| ● | Any data issues that have emerged are not significant in relation to the size of the liabilities; and |
| ● | Therefore, the data is appropriate for use for the purposes of this Report. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
15 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 3 | Valuation Methodology and Approach
| |||
| 3.1 | Previous valuation work and methodology changes |
We have, in broad terms, maintained the core valuation methodology adopted at our previous valuation at 31 March 2014.
| 3.2 | Overview of current methodology |
The methodology involves assessing the liabilities in two separate components, being:
| ● | Allowance for the cost of settling claims which have already been reported but have not yet been settled (“pending claims”); and |
| ● | Allowance for the cost of settling claims which have not yet been reported (“Incurred But Not Reported” or “IBNR” claims). |
For pending claims, we have used the case estimates (where available) with some adjustments to reflect the extent to which the case estimates (on average) tend to overstate the ultimate cost. For IBNR claims we have used what can best be described as an “average cost per claim method”.
In brief, the overall methodology may be summarised as follows:
| ● | Project the future number of claims expected to be reported in each future year by disease type (for product and public liability) and for Workers Compensation and wharf claims taking into account the expected future incidence of mesothelioma and other diseases and also the past rate of co-joining of the Liable Entities; |
| ● | Analyse past average attritional claim costs of non-nil claims in mid 2014/15 money terms. We have defined attritional claims to be claims which are less than $1m in 2006/07 money terms. We estimate a baseline attritional non-nil average claim cost in mid 2014/15 money terms. This represents the Liable Entities’ share of a claim rather than the total claim settlement. For Workers Compensation claims, the average cost represents only that part of a claim which is borne by the Liable Entities (i.e. it is net of any insurance proceeds from a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy); |
| ● | Analyse past historical average plaintiff/other and defendant legal costs for non-nil claim settlements; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
16 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Analyse past historical average defendant legal costs for nil claim settlements; |
| ● | Estimate a “large claims loading” for mesothelioma claims by estimating the frequency, or incidence rate, and average claim size and legal cost sizes of such claims (being claims which are in excess of $1m in 2006/07 money terms); |
| ● | Project the pattern and incidence of future claims settlements from the claims reporting profile projected. This is done by using a settlement pattern derived from consideration of past experience of the pattern of delay between claim reporting and claim settlement for each disease type; |
| ● | Estimate the proportion of claims which will be settled with no liability against the Liable Entities by reference to past proportions of claims settled for nil claim cost (we refer to this as the “nil settlement rate”); |
| ● | Inflate average claim, plaintiff/other and defence legal costs and large claim costs to the date of settlement of claims allowing for base inflation and (where applicable) superimposed inflation; |
| ● | Multiply the claims numbers which are expected to be settled for non-nil amounts in a period by the inflated average non-nil claim costs (including the “large claims loading”) and plaintiff/other and defence legal costs for that period; |
| ● | Make allowance in defence legal costs for that proportion of settled claims which are expected to be settled for no liability but for which defence costs will be incurred; |
| ● | Inflate average defence legal costs of nil claims to the date of settlement of claims allowing for base inflation; |
| ● | Multiply the claims numbers which are expected to be settled for nil amounts in a period by the inflated average defence legal costs for nil claims for that period; |
| ● | Add the expected claims and legal payments relating to pending claims (after allowance for the potential savings on case estimates) after making allowance for the assumed settlement pattern of pending claims; |
| ● | This gives the projected future gross cashflow for each future financial year; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
17 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Adjust the projected gross cashflow for the impact of the annual and aggregate caps on DDB reimbursements; |
| ● | Estimate the recoveries resulting from cross-claims made by the Liable Entities against other parties (“cross-claim recoveries”); |
| ● | Project Insurance Recoveries to establish the net cashflows; |
| ● | Discount the cashflows using a yield curve derived from yields on Commonwealth Government Fixed Interest Bonds at the valuation date to arrive at our present value liability assessment. |
It should be noted that this description is an outline and is not intended to be exhaustive in consideration of all the stages we consider or all investigations we undertake. Those other stages are outlined in more detail elsewhere in this Report and readers are advised to refer to those sections for a more detailed understanding of the process undertaken.
As discussed elsewhere, the liabilities are established on a central estimate basis.
| 3.3 | Disease type and class subdivision |
| 3.3.1 | Claims records excluded from our analysis |
We have excluded cross-claims brought by the Liable Entities against other defendants. Where the cross-claim is brought as part of the main proceedings the claim is automatically counted in our analysis of the number of claims. However, where the cross-claim by the Liable Entities is severed from the main proceedings, the existence of a separate record in the claims dataset does not indicate an additional claim (or liability against the Liable Entities). In these circumstances such claims records are not counted in our analysis.
We have also excluded “insurance recovery” claims records. This is because the insurance recovery record is a separate record that exists for claims records where an insurance recovery is due. In other words, the claim against the Liable Entity has already been included in our analysis and the insurance recovery record exists for operational purposes only. We have, however, made separate, explicit allowance in the valuation for future insurance recoveries.
| 3.3.2 | Categories of claim |
We have sub-divided the remaining claims into the following groups:
| ● | Product and Public Liability; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
18 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Workers Compensation, being claims by former employees of the Liable Entities; and |
| ● | Wharf claims, being claims by individuals whose occupations involved working on the docks or wharves, or where part of their exposure related to wharves. |
We have separated the Workers Compensation claims from product and public liability claims because claim payments from Workers Compensation claims do not generate recoveries under the product and public liability insurance cover, so that in order to value those insurance policies we need to separately identify the cashflows from product and public liability claims and the cashflows from Workers Compensation claims.
We have separated out wharfside workers claims because such claims are likely to have a different exposure and incidence profile compared with product and public liability claims.
| 3.3.3 | Categories of disease |
For product and public liability claims, we have separately analysed the individual disease types.
We have split the data by disease type because there is sufficient volume of claims to do so, because different disease types display substantially different average claim sizes, and because the incidence pattern of future notifications is expected to vary between the different disease types.
We have not divided the Workers Compensation or wharf claims data by disease type, given their relatively low financial significance and the reduced credibility of the data if sub-divided by disease type (given the low numbers of claims reported).
For the purposes of our analysis, we have allocated each claim once and therefore to one disease only. We have selected the following order of priority, based on the relative severity of the disease:
| ● | Mesothelioma; |
| ● | Lung cancer / Other cancer; |
| ● | Asbestosis; and then |
| ● | Asbestos-Related Pleural Disease and Other (“ARPD & Other”). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
19 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
This means that if a product or public liability claim has mesothelioma as one of its listed diseases, it is automatically included as a mesothelioma claim. If a product or public liability claim has lung cancer or other cancer as one of its listed diseases (but not mesothelioma), it is included as a lung cancer claim. If a product or public liability claim has asbestosis as one of its listed diseases, it is only coded as asbestosis if it has no reference to mesothelioma, lung cancer or other cancer as one of its diseases.
| 3.4 | Numbers of future claims notifications |
To project the pattern of incidence of claims against the Liable Entities, we have constructed a model which utilises the following inputs:
| ● | The exposure to asbestos in Australia, adjusted to allow for the Liable Entities’ particular incidence of usage, noting that for the period to 1987 they had approximately a stable market share, but thereafter were not involved in asbestos products; |
| ● | The average period over which claimants are typically exposed; and |
| ● | The statistical distribution of the latency period from average exposure for each disease type, together with the underlying parameters (the mean and the standard deviation) of the latency model. |
Statistically speaking, the projected peak incidence of mesothelioma is not equal to the peak year of production (or consumption) plus the average latency of mesothelioma.
Instead, the projected peak of claims reporting derived from our model is a function of the overall shape of the exposure and the full distribution of the latency period. In statistical terminology, the projected claims incidence curve is a “convolution” of the statistical distribution of “modelled consumption” and the statistical distribution of the latency period.
Furthermore, the notification pattern will not be symmetrically distributed around the peak year. The notification pattern is derived from the combined impact of the exposure model and the latency model. The exposure model is not a symmetrical distribution; whereas the assumed latency model is a symmetrical distribution.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
20 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following chart shows the timeline of exposure, latency, diagnosis and claims reporting.
Figure 3.1: Illustration of timeline of exposure, latency and claim reporting (example shown is for mesothelioma)
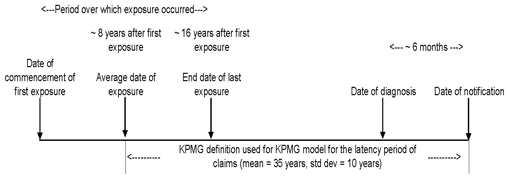
| 3.4.1 | Exposure Model |
We have constructed a proxy for an “exposure model” by reference to statistics showing the levels of Australian usage of asbestos.
We do not have detailed individual exposure information for the Liable Entities, its products or where the products were used and how many people were exposed to those products. However, given the market share of James Hardie over the years (through to 1987) and its relative stability, we have used a national pattern of usage as a reasonable proxy for the Liable Entities’ exposure.
We start by constructing an exposure index from the annual consumption of asbestos within Australia from 1900-2002. We split this between the various asbestos types and by year of consumption.
We have not allowed for multiple exposures with respect to the Liable Entities from each unit of asbestos consumed, e.g. where the Liable Entities were both mining and milling the same asbestos. While there was some (moderate) mining at Baryulgil, in relative terms it is not significant. In any event, we have made separate explicit allowance for mining activities at Baryulgil within our liability assessment.
Figure 3.2 shows measures of the production and consumption of asbestos in Australia in the period 1930 to 2002.
It can be seen that the exposure, being measured in net consumption, appeared to peak in the early-1970s to mid-1970s. It can also be seen that for Australia as a whole, asbestos consumption continued at significant levels until the mid- 1980s and then began to fall through to 2002.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
21 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 3.2: Consumption and production indices – Australia 1930-2002
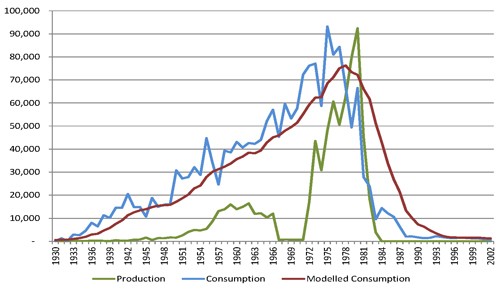
Source: World Mineral Statistics Dataset, British Geological Survey, www.mineralsuk.com
R Virta, USGS Website Annual Yearbook
The data underlying this chart is shown in Appendix D.
The “modelled consumption” is derived as the consumption averaged over the previous eight years, i.e. from the implied start date of exposure to the average date of exposure.
This selection of eight years is based on the analysis contained in Section 6.1 which shows that a typical claimant has an average exposure period of 16 years and that the average date of exposure is therefore typically eight years after the start date of exposure.
It is the “modelled consumption” which is used, together with an assumption about the statistical distribution of the latency period, as a basis for projecting future mesothelioma claim numbers.
There is an implicit assumption within the use of the “modelled consumption” to derive the level of future claim notifications that:
| ● | the consumption of asbestos is directly correlated with, and is a suitable proxy for, the number (and extent of exposure) of people exposed to asbestos in any year; and |
| ● | the rate of incidence of individuals developing an asbestos-related disease arising from exposure to asbestos is the same for each exposure year and is independent of the type of asbestos used or the age of the individuals exposed. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
22 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 3.4.2 | Latency model |
Our assumption is that the latency pattern (from the average date of exposure) for all disease types is statistically distributed with a normal distribution.
The parameters (i.e. the mean and standard deviation) of the distribution have been set by reference to previous work undertaken by Professor Berry et al1, by Jim Leigh et al2 and by Yeung et al3.
The parameters for the mean and, in particular, for the standard deviation have also been set taking into account the claims experience of the Liable Entities to date.
The parameters vary by disease type.
The analysis supporting the selection of these parameters is summarised in Section 6.2.
| 3.4.3 | Projecting the claims notification curve using the exposure and latency model |
Our methodology is to take each year of exposure, using “modelled consumption” of asbestos in tonnage for that year, and project an index of the number of claims we project to emerge in each future reporting year resulting from that exposure year.
The latency period is assumed to be normally distributed with a mean and a standard deviation which vary by disease type.
This means that for any given exposure year, the peak incidence of reporting claims would be (in the case of mesothelioma) 35 years after the average exposure date from that exposure year.
We then aggregate the claims notification index curves projected for each exposure year to produce an overall curve which shows the index of claim notifications arising from all exposure periods.
1 Malignant pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma in former miners and millers of crocidolite at Wittenoom, Western Australia; G Berry, N H de Klerk et al (2004)
2 Malignant Mesothelioma in Australia: 1945-2000; J Leigh et al (2002)
3 Distribution of Mesothelioma Cases in Different Occupational Groups and Industries, 1979-1995: P Yeung, A Rogers, A Johnson (1999)
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
23 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The curve is described as an index because consumption is used as a proxy measure for the number of individuals exposed and because we don’t know what proportion of those people who were exposed will develop asbestos-related diseases.
Therefore the methodology produces a shape of the number of claims, rather than an absolute level of the number of claims to be reported.
This methodology provides not only the shape of claims reporting as an index but it also projects the implied peak year(s) of incidence for each disease type and the rate of decay in claims reporting levels after the peak year of incidence.
We allow for each of the diseases having different average latency periods. This results in different projected peak years for the different diseases.
These are summarised in Sections 6.2 and 6.3.
| 3.4.4 | Calibrating the curve index to current reporting experience |
We take the claim curve index and then calibrate the number of notifications in each future year by reference to the recent levels of claims reporting and the number of claims we have assumed for the 2015/16 financial year.
This approach implicitly assumes that:
| ● | The future rate of incidence of asbestos-related diseases manifesting as a result of a past exposure to asbestos will remain stable; |
| ● | The pattern of diagnosis and the delay between diagnosis and reporting remain stable; |
| ● | The “propensity to claim” by individuals will remain stable; and |
| ● | The rate of co-joining the Liable Entities in claims will remain stable. |
Changes to any of these factors over time will result in changes to the actual pattern of incidence of claims reporting compared with that derived in Section 3.4.3.
Our assumptions for the base number of claims projected to be reported in 2015/16 are summarised in Sections 4.4 and 5.6.
| 3.4.5 | Model adjustments made at 31 March 2014 for mesothelioma claims |
As a consequence of heightened mesothelioma claims reporting observed in 2013/14 (and which has continued in 2014/15), we made some modifications to the future incidence pattern for mesothelioma in our 31 March 2014 valuation.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
24 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The changes were most pronounced for the period of claims reporting to 2016/17 and the changes are documented more extensively in our Annual Actuarial Report effective at 31 March 2014.
At this valuation, we have maintained those modifications to the incidence pattern.
| 3.5 | Incidence of claim settlements from future claim notifications |
We derive a settlement pattern by analysing triangulations of the numbers of settlements and claims payments by delay from the year of notification.
From these settlement pattern analyses, we have estimated the pace at which claims notified in the future will settle, and used this to project the future number, and monetary amount, of settlements in each financial year for each disease type.
Our analysis and assumptions selected are summarised in Section 9.6.
| 3.6 | Average claim costs of IBNR claims |
| 3.6.1 | Attritional claims |
We define a large claim as one for which the award is greater than or equal to $1m in 2006/07 money terms (which equates to approximately $1.37m in mid 2014/15 money terms).
We define an attritional claim as a non-nil, non-large claim. We define a nil claim as one for which the award payable by the relevant Liable Entity is zero.
We have estimated the following five components to the average cost assessment:
| ● | Average award (sometimes including plaintiff legal costs) of a non-nil “attritional” claim. |
| ● | Average plaintiff legal / other costs of a non-nil “attritional” claim. |
| ● | Average defence legal costs of a non-nil “attritional” claim. |
| ● | Average defence legal costs of a nil claim. |
| ● | Large claim awards and legal cost allowances. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
25 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
All of our analyses have been constructed using past average awards, which have been inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms using a historical base inflation index (of 4% per annum). This allows for basic inflation effects when identifying trends in historical average settlements. We then determine a prospective average cost in mid 2014/15 money terms.
We perform the same analysis for the defence legal costs for nil and non-nil claims and for plaintiff legal / other costs in respect of non-nil claims (together “Claims Legal Costs”).
Our analysis and assumptions are summarised in Section 7.
| 3.6.2 | Large claims loading |
We analyse the historical incidence rate of large claims (being measured as the ratio of the number of large claims to the total number of non-nil claims), and the average claim size and legal costs of these claims. We have determined a prospective incidence rate and an average cost in mid 2014/15 money terms to arrive at a “per claim” loading (being the average large claim cost multiplied by the large claim incidence rate per claim) being the additional amount we need to add to our attritional average claim size to allow for large claims.
Our analysis and assumptions are summarised in Section 7.8.
| 3.6.3 | Future inflation of average claim sizes |
Allowance for future claim cost inflation is made. This is modelled as a combination of base inflation plus superimposed inflation. This enables us to project future average settlement costs in each future year, which can then be applied to the IBNR claims numbers as they settle in each future year.
Our analysis and assumptions in relation to claims inflation are summarised in Sections 9.2 and 9.3.
| 3.7 | Proportion of claims settled for nil amounts |
We apply a “nil settlement rate” to the overall number of settlements to estimate the number of claims which will be settled for nil claim cost (i.e. other than in relation to defence legal costs) and those which will be settled for a non-nil claim cost.
The prospective nil settlement rate is estimated by reference to the analysis of past trends in the rate of nil settlements.
Our analysis and assumptions selected are summarised in Section 8.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
26 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 3.8 | Pending claims |
| 3.8.1 | Definition of pending claims |
At 31 March 2015, there were 534 claims (31 March 2014: 506) for which claim awards have not yet been fully settled by the Liable Entities.
Additionally, there are a number of other claims for which defence legal costs have not yet been settled, even though the awards have been settled.
There has been an increase in the number of pending mesothelioma claims during 2014/15 (an increase of 22 claims). This is a result of the higher claims reporting that has been experienced in the year and it reflects the time delay that naturally exists between notification and settlement.
We have adopted three definitions of settlement status:
| ● | Where there is a closure date, there are not expected to be any further award or legal costs incurred. |
| ● | Where there is no closure date but the claim has a settlement date, there is the possibility of further emerging defendant legal costs, even though the claim award has been settled. |
| ● | Where there is no settlement date, there is the possibility of award, plaintiff legal costs and defendant legal costs being incurred. |
| 3.8.2 | Evaluating the liability for pending claims |
The excess amount of the liability for pending claims, over the case estimates held, is what the insurance industry terms Incurred But Not Enough Reported (“IBNER”).
Depending on the case estimation procedure of a company and the nature of the liabilities, IBNER can be either positive or negative, with a negative IBNER implying that the ultimate cost of settling claims will be less than case estimates, i.e. that there is some degree of redundancy in case estimates.
| 3.8.3 | Findings |
Our analysis has indicated that there is a degree of redundancy in case estimates, i.e. a negative IBNER.
The comparison of current case estimates with actuarially-projected future settlement costs for claims reported to date suggests that potential savings from case estimates in relation to the award component could be of the order of 25%.
AICFL’s own analysis also suggests that historically there have also been savings which have typically varied between 20% and 30%.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
27 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Furthermore, we have assessed whether the cost of claims reported up to and including 31 March 2015 has deteriorated (or improved) compared to our prior estimate (as at 31 March 2014).
The table below shows that there has been no deterioration compared to the estimates we previously adopted and are currently adopting (both of which have already made allowance for a 25% saving on case estimates). This analysis lends further support to the view that the allowance we have made for the extent of redundancy in case estimates of 25% is reasonable and is borne out by the actual experience.
We have maintained our assumption for the level of redundancy in case estimates on currently reported claims at 25% at this valuation (March 2014: 25%). This assumption is only applied to the case estimates for the claim award, i.e. it is not applied to plaintiff/other costs or defence costs.
Table 3.1: Change in cost of claims during 2014/15 financial year ($m) – claim award component only
| Figures in $ millions | Current year reported claims |
Prior year reported claims |
Total | |||
|
Estimates for pending claims at 31 March 2014 (undiscounted)
|
0.0 | 86.4 | 86.4 | |||
|
Paid amounts in year to 31 March 2015
|
89.3 | 49.3 | 138.6 | |||
|
Estimates for pending claims at 31 March 2015 (undiscounted)
|
67.9 | 26.8 | 94.7 | |||
|
Incurred Cost in the financial year
|
157.2 | (10.3) | 146.9 |
The table above shows that there has been a $10.3m saving in the case estimates for claims that were reported prior to 31 March 2014.
It should be noted that making allowance for savings from case estimates is expected to have a more significant impact on the near term cash flows and a lesser impact on the longer-term cashflows, with more than 95% of the cost of pending claims expected to be settled within the next six years.
| 3.9 | Insurance Recoveries |
Insurance Recoveries are defined as proceeds which are estimated to be recoverable under the product and public liability insurance policies of the Liable Entities, and therefore exclude any such proceeds from a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy in which the Liable Entities participate or which the Liable Entities hold.
In applying the insurance programme we consider only the projected gross cashflows relating to product and public liability claims.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
28 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
We split out product liability cashflows from public liability cashflows as they are covered by different sections of the insurance policy under different bases:
| ● | Product liability claims are covered by an aggregate policy which provides cover for all product liability claims costs attached to any one year up to an overall aggregate limit for that year; and |
| ● | Public liability claims are covered by an “each and every loss” policy which provides cover for each public liability claim up to an individual claim limit for that year. |
Historical analysis of the claims data suggests that more than 97% of all liability claims by cost have been product liability claims.
We make no allowance for the Workers Compensation cashflows in estimating the Insurance Recoveries, as the insurance programme only provides insurance cover to product and public liability exposures.
| 3.9.1 | Programme overview |
Until 31 March 1985, the Liable Entities had in place General and Products liability insurance policies with a $1m primary policy layer.
In addition, until 31 May 1986, the Liable Entities maintained further excess “umbrella” insurance policies, with varying retentions and policy limits. That is, the insurance policies paid all costs arising from claims with exposure in a specified year from the retention up to the relevant policy limit. All claim costs in relation to a given exposure year in excess of the limit would be retained by the Liable Entities.
Product liability claims were insured under these insurance policies on an “in the aggregate” basis whilst public liability claims were insured on an “each and every loss” basis.
These insurance policies were placed amongst a number of insurance providers on a claims occurring basis.
From 31 May 1986, the insurance policies were placed on a claims made basis in relation to asbestos-related product and public liability cover.
In summary, the insurance policies were placed as follows:
| ● | For the period up to June 1976, the insurance policies were written on a claims occurring basis. The insurance was provided by QBE but the cover provided by these policies was commuted in June 2000 for a consideration of $3.1m per annum for the following 15 years (through to 30 June 2014). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
29 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | For the period from June 1976 to 31 May 1986, the insurance policies were written on a claims occurring basis. CE Heath acted as the underwriting agent and insured the risk in Australia and also into Lloyd’s of London and the London Market. However, during this period CE Heath Underwriting & Insurance (Australia) Pty Ltd (CEH U&I) also insured some of the risk, reinsuring their placement on a facultative basis. |
| ● | For the period 31 May 1986 to 31 March 1989, the insurance policies were written on a claims-made basis. CE Heath acted as the underwriting agent and insured the risk into Lloyd’s of London and the London Market. |
| ● | For the period 31 March 1989 to 31 March 1997, the insurance policies were written on a claims-made basis. However, CE Heath Casualty & General Insurance Ltd (later HIH Casualty & General) acted as the insurer of the programme and reinsured it on a facultative basis into Lloyd’s of London and the London Market. CE Heath Casualty & General Insurance Ltd retained some share on some of the layers. |
| 3.9.2 | Modelling insurance recoveries on the claims occurring programme |
Our methodology for projecting the future insurance recoveries to be collected by AICFL involves the following steps:
| ● | Identify the current contract positions for each insurance policy year. This assumes that all monies due have been collected, and does not allow for the impact of commutations that have taken place. |
| ● | Allocate the projected future gross cashflows to individual insurance policy years using an allocation basis that has been determined by reference to the exposure methodology used to project future claim numbers and also using a “period of exposure” and “time on risk” allocation. |
| ● | This gives a projection of how the insurance programme is utilised over time. |
This method allows us to:
| ● | evaluate the total insurance recoveries due by payment year; |
| ● | determine how the insurance recoveries due will be assigned to each layer and therefore to each insurer; and |
| ● | identify and allow for when the individual layers are projected to be fully exhausted. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
30 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
We then make an additional adjustment to the projected recoveries to exclude those projected future insurance recoveries that are assigned to the participations of insurers who have already commuted their coverage with AICFL and the Liable Entities or insurers who have settled the coverage by way of a Scheme of Arrangement.
| 3.9.3 | Commutations and HIH |
Commutations have been entered into by AICFL, but these commutations have involved the payment of a lump sum amount, rather than an annual cashflow amount paid over a period of time. In these circumstances, we have assumed that the insurance liabilities of that company to the Liable Entities have been fully discharged and no further recoveries will fall due.
We have assumed that all monies have been paid in relation to insurance recoveries for the claims occurring period from HIH. AICFL has collected more than $50m from HIH since 2007 by way of successful Section 562A(4) applications. Any future proceeds from HIH are not expected to be material.
We have made no allowance or adjustment for any future commutations.
| 3.9.4 | Schemes of Arrangement |
For the claims occurring period, where a claim filed against a company under a Scheme of Arrangement has been accepted and payment made, we have assumed that the insurance liabilities of that company to the Liable Entities have been fully discharged and no further recoveries fall due.
| 3.9.5 | Unpaid insurance recoveries |
We have not included within our liability estimate any allowance for insurance recoveries under the claims occurring period that are due but have not yet been collected (“unpaid balances”). We are advised that such monies amount to approximately $4m at 31 March 2015.
These amounts are more appropriately dealt with as being debtors of AICFL.
| 3.9.6 | Claims made insurance protection from 31 May 1986 onwards |
Insurance protection purchased from 31 May 1986 onwards was placed on a “claims made” basis and as such may not provide protection or recoveries against the cost of future claim notifications made by claimants against the Liable Entities.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
31 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
For the purpose of this Report, we have made no allowance for the value of insurance policies placed from 1986 onwards in our liability assessment.
| 3.9.7 | Bad and doubtful debt allowance on Insurance Recoveries |
We have made allowance for bad and doubtful debts on future Insurance Recoveries within our valuation by use of the default rates specified in Appendix A. These have been sourced from Standard & Poors’ 2013 Annual Global Corporate Default Study and Rating Transitions, March 2014 and they are based on bond default rates.
We have considered the credit rating of the insurers of the Liable Entities as at March 2015 and applied the relevant credit rating default rates to the expected future cashflows by year, treaty and insurer.
Where additional information regarding the expected payout rates of solvent and insolvent Schemes of Arrangement is available, we have instead taken the expected payout rates to assess the credit risk allowance to be made in our liability assessment.
| 3.10 | Cross-claim recoveries |
A cross-claim can be brought by, or against, one or more Liable Entities. Cross-claims brought against a Liable Entity (“Contribution Claims”) are included in our analysis of the claims experience.
Cross-claims brought by a Liable Entity relate to circumstances where the Liable Entity seeks to join (as a cross-defendant) another party to the claim in which the Liable Entity is already joined.
To the extent that the Liable Entities are successful in joining such other parties to a claim, the contribution to the settlement by the Liable Entities will reduce accordingly.
Our approach in the valuation has been to separately value the rate of recovery (“cross-claims recovery rate”) as a percentage of the gross award based on historical experience of such recoveries.
Our analysis and assumptions selected are summarised in Section 9.5.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
32 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 3.11 | Discounting cashflows |
Cashflows are discounted on the basis of yields available at the valuation date on Commonwealth of Australia fixed interest Government Bonds (“Commonwealth Government Bonds”) of varying coupon rates and durations to maturity (matched to the liability cashflows), with a long-term discount rate of 6.00% per annum assumed.
It should be recognised that the yield curves and therefore the discount rates applied can vary considerably between valuations and can, and do, contribute significant volatility to the present value of the liability at different valuation dates.
At 31 March 2015, as compared with 31 March 2014, there have been significant decreases in observed yields on Commonwealth Government Bonds at most durations.
Our approach to the determination of the discount rates is unchanged from the approach adopted at 31 March 2014, and is:
| ● | For years 1 to 16, zero coupon spot rates were determined by reference to the prices, coupons and durations of Commonwealth Government Bonds; |
| ● | For years 19 and onwards, we have selected a uniform long-term discount rate of 6.00% per annum; and |
| ● | For years 17 and 18, we have selected spot rates that “linearly interpolate” between the year-16 rate and the year-19 rate (of 6.00%). |
Our selected assumptions are summarised in Section 9.4.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
33 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
|
Claims Experience – Mesothelioma Claim Numbers | ||
| 4 | ||
| 4.1 | Overview |
Figure 4.1 shows the number of mesothelioma claims reported by year of notification.
Figure 4.1: Number of mesothelioma claims reported annually
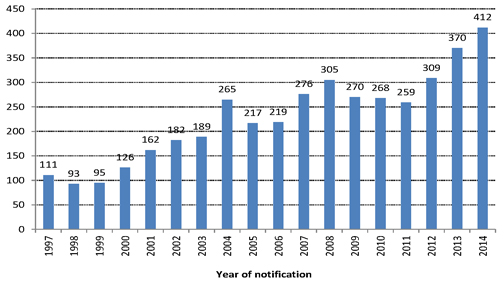
Note: Throughout Sections 4 to 9, the date convention used in tables and charts is that (for example) 2008/09 indicates the financial year running from 1 April 2008 to 31 March 2009. Furthermore, unless clearly identifying a calendar year, the label “2008” in charts or tables would indicate the financial year running from 1 April 2008 to 31 March 2009.
The number of mesothelioma claim notifications increased steadily from 2000/01 (126 claims) to 2003/04 (189 claims). There was an upward step in claim numbers during 2004/05 with 265 claims reported.
In 2008/09, there were 305 claims reported.
The next three years saw lower (and relatively stable) claim numbers reported, with the number of claims varying between 259 and 270 claims.
In 2012/13, the number of claims reported increased to 309, largely reflecting increased numbers of cross-claims from other defendants.
In 2013/14, the number of claims reported increased significantly, to 370 claims, largely reflecting increased numbers of direct claims from claimants.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
34 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
In 2014/15, the number of claims reported increased further to 412 claims.
In the remainder of this section, we have made a number of observations as to the potential drivers of the increase in claims reporting in 2014/15.
| 4.1.1 | Monthly analysis of notifications |
We have examined the number of mesothelioma claims reported on a monthly basis to better understand the nature of the claims experience observed on an annual basis.
Figure 4.2: Monthly notifications of mesothelioma claims
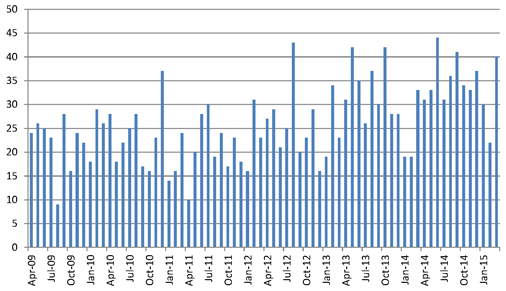
It is observed that:
| ● | The number of claims reported in 2014/15 (412 claims) has been 11% above our previous expectations (370 claims) and also 11% above the level observed in 2013/14. |
| ● | In June 2014, AICFL received 44 mesothelioma claims, the highest number ever received in one month. |
| ● | In 2014/15, eleven months of the year had 30 or more claims reported and three months saw 40 or more claims in the month. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
35 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.1.2 | Rolling averages |
We have reviewed the number of mesothelioma claims reported on a monthly basis and reviewed the rolling 3-month, 6-month and 12-month averages in recent periods.
Figure 4.3: Rolling annualised averages of mesothelioma claim notifications
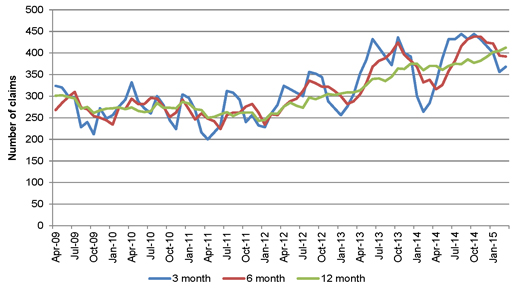
It can be seen that the current annualised rolling averages are between 368 (3-month average) and 412 (12-month average).
Over the past two years, the 6-month and 12-month averages have increased, ranging from 300 to 440 claims per annum.
Not surprisingly, the 3-month averages have shown more volatility, varying between 260 and 450 over the past two years.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
36 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.2 | Profile of mesothelioma claims |
| 4.2.1 | Claims by State |
We have analysed the number of mesothelioma claim notifications by the State in which the claim is filed.
Figure 4.4: Number of mesothelioma claims by State
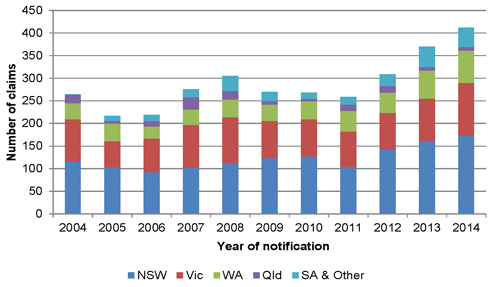
Since 1997, NSW has contributed approximately 50% of all claims reported. However, in the past five years, its proportion has declined and NSW now contributes typically around 45% of all claims by number (although a higher proportion of mesothelioma claims by cost).
It is of note that for 2014/15:
| ● | Overall, mesothelioma reporting activity is at the highest level in the history of claims reporting to the Liable Entities. |
| ● | Claim activity in NSW, VIC and WA have shown material increases in 2014/15 (NSW 13 claims higher, VIC 22 claims higher, and WA 9 claims higher than that experienced in 2013/14). |
| ● | Claim activity in SA has remained unchanged from the level in 2013/14, however this level is still the highest level ever observed. |
| ● | Claims activity in QLD remained unchanged (and activity was lower than periods prior to 2013/14). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
37 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.2.2 | Direct claims and cross-claims |
Figure 4.5 shows the number of claims notified by year of notification and separately as between claims brought by claimants (which we refer to as ‘direct claims’) and claims brought by other defendants, some of which are brought a number of years after the claim was first notified (these claims we refer to as ‘cross claims’).
Figure 4.5: Number of mesothelioma claims by type of claim
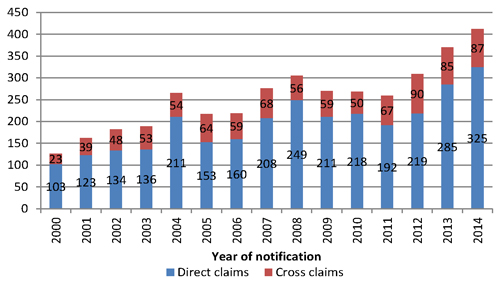
It can be seen that the increase in claim numbers that were observed in 2012/13 was primarily a function of a higher number of cross-claims being brought by other corporations and by State and Federal Government Entities. Direct claims were at levels consistent with (or, in some cases, below) levels observed in the preceding five years.
This higher level of cross claims continued in 2013/14 and 2014/15 with the number of cross claims reported at a similar level to 2012/13, supporting our previous valuation assumption (made at 31 March 2013) that an increased rate of co-joining/cross-claiming should be assumed to be a permanent feature of the claims experience.
NSW is currently the primary source of cross claims (making up approximately 55% of the total number of cross claims in 2014/15).
In 2013/14, there was a material increase in the number of direct claims most notably from NSW, SA and WA. In 2014/15, the primary sources of the increase were NSW, VIC and WA.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
38 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.2.3 | Number of defendants |
Figure 4.6 shows the number of claims notified by year of notification and by number of defendants.
Figure 4.6: Number of mesothelioma claims by number of defendants (direct claims only)
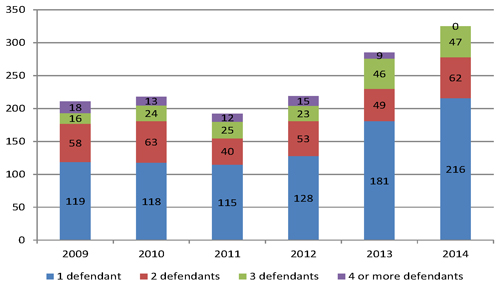
The number of claims reported involving only the Liable Entities (i.e. single-defendant claims) has, for the second successive year, seen the most material increase (in absolute terms) in the year.
Claims in which the Liable Entities are the only defendants to the claim are typically associated with higher average claim sizes whilst claims involving multiple defendants typically involve the Liable Entities paying 60% or less of the total settlement (see Section 7.2).
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
39 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.2.4 | Age profile of claimants |
Figure 4.7 shows the proportion of claims notified by year of notification and by age of claimant.
Figure 4.7: Number of mesothelioma claims by age of claimant
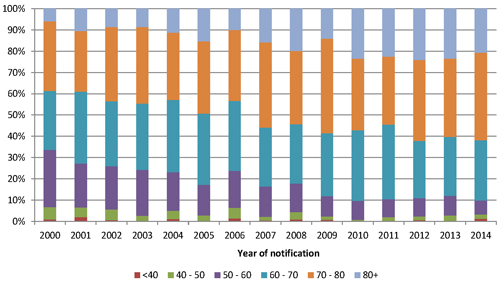
The proportion of claims reported involving claimants over the age of 70 has gradually increased, evident by the downwards trends in the chart from left to right.
The higher proportion of claims involving claimants over 70 years of age has been a contributor to the stability in average claim sizes experienced in the last ten years to date (thereby acting to offset other claims inflation drivers).
The most recent financial year saw an increase in the proportion of claimants between the ages of 70 and 80 accompanied by reductions in the proportions of claimants between ages 50 and 60 and those over 80 years of age.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
40 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.2.5 | Delay from diagnosis to notification |
The chart below measures the time-lag (in days) from diagnosis to notification. The chart shows that direct claims are reported more quickly than cross-claims.
Direct claims have typically taken between 5 months and 8 months to be reported after diagnosis of mesothelioma.
Figure 4.8: Delay from diagnosis of mesothelioma to notification of claim against the Liable Entities
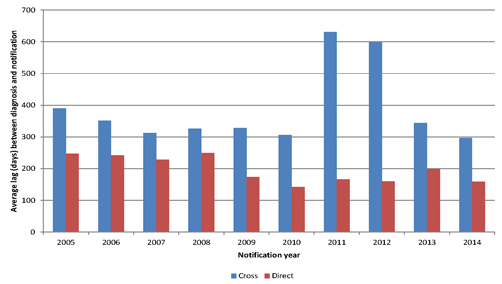
In 2014/15, there has been a speeding up in reporting of claims. This was more noticeable in the first three quarters of the financial year, and may have in part been attributable to concerns pertaining to the implementation of the Approved Payment Scheme (which was announced on 15 September 2014). On 27 February 2015, AICFL announced that it would not be proceeding with the implementation of the Approved Payment Scheme after it reached agreement with the NSW Government to amend the loan facility provided to AICFL by the NSW Government.
In relation to direct claims, the time-lag to notification for the 2014/15 year was 39 days lower than that observed in 2013/14 (160 vs 199).
In relation to cross claims, the time-lag to notification for the 2014/15 year was 47 days lower than that observed in 2013/14 (297 vs 344).
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
41 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 4.3 | External statistics on mesothelioma claims incidence |
Figure 4.9 compares the total number of mesothelioma cases reported (diagnosed) nationally to the number of mesothelioma claims received by the Liable Entities.
The “year” is calendar year for the national cases (i.e. 2012 is the year running from 1 January 2012 to 31 December 2012); whilst for the Liable Entities it is the financial year (i.e. 2012 is the year running from 1 April 2012 to 31 March 2013).
It should be noted that the two sets of data correspond to different definitions of year and so are not directly comparable and some caution should be exercised.
Figure 4.9: Number of mesothelioma cases reported nationally compared to the number of claims received by the Liable Entities
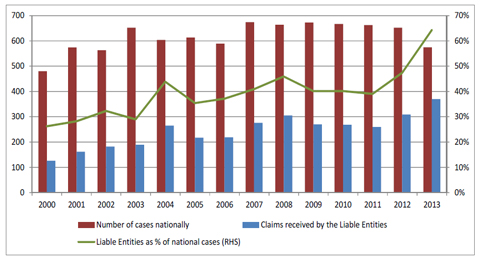
Sources: Australian Cancer Incidence and Mortality book for Mesothelioma, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, updated February 2014 for 2000-2010
Annual Report of the Australian Mesothelioma Registry for 2011 and onwards
The annual number of mesothelioma cases diagnosed nationally was relatively stable for the period 2007 to 2012 varying between 652 to 674 cases.
In calendar year 2013, the number of cases diagnosed nationally fell to 575.
It is notable that the 2012 calendar year saw an increase of 33 incidents from 619, as reported in the 2012 Australian Mesothelioma Registry Report to 652, as reported in the 2013 Australian Mesothelioma Registry Report.
As a consequence, it is possible that the national level of mesothelioma for 2013 has an element of under-reporting. However, it still appears likely that the level observed for 2013 will be lower than the levels observed in 2007 to 2012.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
42 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
It should be noted that not all cases of mesothelioma result in a claim being brought in Common Law. Furthermore, even if a claim is brought, not all claims will involve the Liable Entities.
Analysis of the DDT data in recent years has indicated that around 75%-80% of all diagnoses of mesothelioma resulted in a claim being brought in Common Law in NSW.
Looking at the experience in NSW in more detail, the following chart compares the number of cases of mesothelioma in NSW with the number of claims brought in the Dust Diseases Board of New South Wales (DDB) and the number of claims brought against the Liable Entities under common law.
For the DDB data, the “year” is financial year (i.e. 2012 is the year running from 1 July 2012 to 30 June 2013).
It should be noted that the three sets of data correspond to different definitions of year and so are not directly comparable and some caution should be exercised.
Figure 4.10: Number of mesothelioma cases reported in NSW
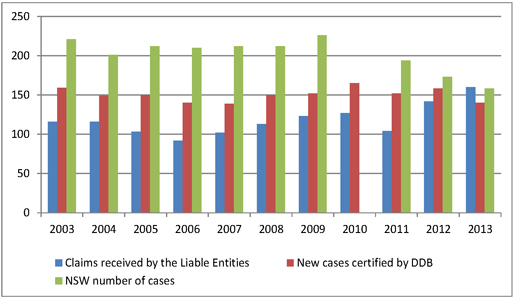
Sources: NSW Central Cancer Registry Reporting Module, 2010 for 2000-2008.
Second Annual Report of the Australian Mesothelioma Registry for 2011 and 2012.
Total number of cases in NSW not identified for 2010.
Workers Compensation (Dust Diseases) Board Annual Report, 2012/13 (Appendix 17).
It can be noted that the number of cases certified by the DDB in 2011 and 2012 has increased as a proportion of the total number of cases reported in NSW for these years.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
43 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
For 2012/13, there was a significant increase in both the number and proportion of claims that the Liable Entities had brought against them compared to the total number of cases of mesothelioma in NSW in total. This experience was again observed in 2013/14 as the number and proportion of claims that the Liable Entities had brought against them compared to the total number of cases of mesothelioma in NSW in total saw further increases.
| 4.4 | Base valuation assumption for number of mesothelioma claims |
In setting a base valuation assumption for 2015/16, we have considered whether the observations in the most recent two years were one-off fluctuations or may be part of a new or ongoing trend.
Cross-claim experience remained stable at the new level observed over the prior two years in 2014/15. Given the assumption made in our March 2013 valuation (that this feature of cross-claims experience may continue into future years), experience to date since has provided support for this decision.
The increase in claims reporting in 2014/15 was primarily due to an increased number of direct claims, and in particular growth in the number of home renovator claims. This was also observed in 2013/14, with both years also having substantial increases in relation to single-defendant claims.
For the purpose of determining an assumption for 2015/16, we have assumed that this feature will recur in 2015/16.
In determining our assumption, we have given some regard to the fact that there appears to have been a speeding-up in reporting of mesothelioma claims.
Based on the above observations, we have assumed 400 claims for 2015/16.
There is, however, material uncertainty in relation to this assumption and it is possible that claims activity could increase further next year, or fall next year.
Depending on the outcome, further changes to the valuation assumptions and therefore to the valuation results may be necessary. Such changes could be material.
As a consequence of the above noted uncertainties, further volatility in relation to the valuation result should be anticipated for at least the next few years.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
44 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
|
Claims Experience – Claim numbers (non-mesothelioma diseases) | ||
| 5 | ||
| 5.1 | Overview |
Table 5.1 shows the number of claims reported by year of notification and by disease category.
Table 5.1: Number of claims by disease type
|
Year of notification |
Asbestosis |
Lung Cancer |
ARPD & Other |
Wharf |
Workers |
Total | ||||||
| 1997 |
32 | 20 | 17 | 2 | 50 | 121 | ||||||
| 1998 |
25 | 12 | 13 | 3 | 30 | 83 | ||||||
| 1999 |
41 | 16 | 12 | 14 | 39 | 122 | ||||||
| 2000 |
46 | 30 | 22 | 26 | 37 | 161 | ||||||
| 2001 |
93 | 24 | 30 | 17 | 59 | 223 | ||||||
| 2002 |
90 | 36 | 41 | 15 | 52 | 234 | ||||||
| 2003 |
101 | 26 | 27 | 10 | 36 | 200 | ||||||
| 2004 |
121 | 34 | 26 | 6 | 62 | 249 | ||||||
| 2005 |
103 | 32 | 17 | 6 | 33 | 191 | ||||||
| 2006 |
161 | 36 | 31 | 7 | 44 | 279 | ||||||
| 2007 |
171 | 28 | 43 | 8 | 46 | 296 | ||||||
| 2008 |
162 | 40 | 45 | 11 | 59 | 317 | ||||||
| 2009 |
120 | 40 | 43 | 3 | 61 | 267 | ||||||
| 2010 |
140 | 13 | 36 | 9 | 30 | 228 | ||||||
| 2011 |
110 | 15 | 36 | 6 | 30 | 197 | ||||||
| 2012 |
128 | 33 | 38 | 7 | 27 | 233 | ||||||
| 2013 |
117 | 26 | 49 | 15 | 31 | 238 | ||||||
|
2014 |
145 | 25 | 38 | 11 | 34 | 253 | ||||||
|
2000-2014 |
1,808 | 438 | 522 | 157 | 641 | 3,566 | ||||||
|
All Years |
2,104 | 567 | 700 | 200 | 1,332 | 4,903 |
| 5.2 | Asbestosis claims |
For asbestosis, the three years of claims reporting from 2006/07 to 2008/09 saw claims reporting activity reasonably stable, at between 161 and 171 claims.
The years 2009/10 to 2013/14 saw claims reporting reduce, varying between 110 and 140 claims.
There have been 145 asbestosis claims reported in 2014/15, with significant increases in claims reporting in September 2014 and October 2014.
We have assumed 144 asbestosis claims will be reported in 2015/16.
| 5.3 | Lung cancer claims |
The number of lung cancer claims reported has typically been between 25 and 40 claims per annum.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
45 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
However, reporting in 2010/11 and 2011/12 was substantially lower, at 13 and 15 claims respectively, and this reduction was attributed to then-recent court cases (Amaca vs. Ellis [2010] HCA 5 and Evans vs. Queanbeyan City Council [2010] NSWDDT 7) in relation to the interaction of smoking and asbestos exposure upon lung cancer.
In 2012/13, the number of claims increased again to 33. In 2013/14, the number of claims reported was 26. In 2014/15, the number of claims reported was 25.
We have assumed 27 lung cancer claims will be reported in 2015/16.
| 5.4 | ARPD & Other claims |
The number of ARPD & Other claims, has typically been between 30 and 45 over the last nine years, although in 2013/14 the number of claims reported was the highest observed historically, at 49 claims.
In 2014/15, the number of claims reported was 38.
We have assumed 42 ARPD & Other claims will be reported in 2015/16.
| 5.5 | Workers Compensation and Wharf claims |
The number of Workers Compensation claims, including those met in full by the Liable Entities’ Workers Compensation insurers, has exhibited some degree of volatility ranging from 27 claims to 61 claims in the most recent six years.
In 2014/15 there were 34 claims reported, in 2013/14 there were 31 claims reported and in 2012/13 there were 27 claims reported.
We have assumed 33 Workers Compensation claims will be reported in 2015/16.
It should be noted that the financial impact of this source of claim is not substantial to the Liable Entities given the proportion of claims which are settled for nil liability against the Liable Entities (typically above 90%), which results from the insurance arrangements in place.
For Wharf claims, we have assumed 12 claims will be notified in 2015/16. This compares with 11 claims reported in 2014/15, 15 claims reported in 2013/14, and 7 claims reported in 2012/13. Again, the financial impact of this source of claim is not currently significant.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
46 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 5.6 | Summary of base claims numbers assumptions (including mesothelioma) |
In forming a view on the numbers of claims projected to be reported in 2015/16, we have taken into account the emerging experience in the latest financial year and a revised view of the expected numbers of claims reported based on recent trends.
As outlined in Sections 4 and 5, our assumptions as to the number of claims to be reported in 2015/16 are as follows:
Table 5.2: Claim numbers experience and assumptions for 2015/16
| 2013/14 actual |
2014/15 actual |
2014/15 H1 (annualised) |
2014/15 H2 (annualised) |
2014/15 expected |
2015/16 Assumption | |||||||
| Mesothelioma |
370 | 412 | 432 | 392 | 370 | 400 | ||||||
| Asbestosis |
117 | 145 | 140 | 150 | 120 | 144 | ||||||
| Lung Cancer |
26 | 25 | 34 | 16 | 30 | 27 | ||||||
| ARPD & Other |
49 | 38 | 36 | 40 | 48 | 42 | ||||||
| Wharf |
15 | 11 | 6 | 16 | 12 | 12 | ||||||
|
Worker |
31 | 34 | 28 | 40 | 30 | 33 | ||||||
|
Total |
608 | 665 | 676 | 654 | 610 | 658 |
Annualised figures do not make allowance for any seasonality of reporting.
They are calculated by multiplying the half-year experience by a factor of 2.
2014/15 Expected is the assumption selected for 2014/15 in our previous valuation report.
| 5.7 | Baryulgil |
Almost half of the claims settled which relate to asbestos mining activities at Baryulgil (as discussed previously in Section 1.2.3) have been settled with no liability against the Liable Entities; and for the remaining settled claims, the Liable Entities have typically borne one-third to one-half of the settlement amount, reflecting the contribution by other defendants to the overall settlement (including those which have since been placed in liquidation).
For the purposes of our valuation, we have estimated there to be 13 future claims reported, comprising 6 mesothelioma claims, 4 other product and public liability claims and 3 Workers Compensation claims.
We have assumed average claims and legal costs, net of Workers Compensation insurances, broadly in line with those described in Section 7.
Our projected liability assessment at 31 March 2015 of the additional provision (for claims not yet reported) that could potentially be required is an undiscounted liability of $4.1m and a discounted liability of $3.5m, all of which is deemed to be a liability of Amaca.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
47 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
|
Exposure and Latency Experience and Incidence Pattern Assumptions | ||
| 6 | ||
| 6.1 | Exposure information |
| 6.1.1 | Average exposure period |
The following chart shows the derivation of, and support for, the assertion that claims have resulted from, on average, approximately 16 years of exposure.
Figure 6.1: Mix of claims by duration of exposure (years)
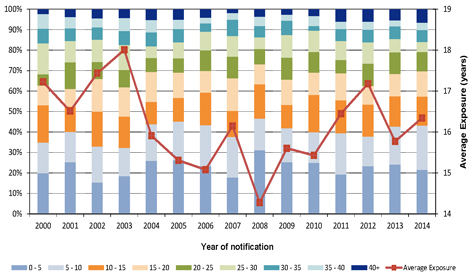
It can be seen that generally the average duration of exposure has varied between 14 years and 18 years and is currently 16.3 years.
| 6.1.2 | Exposure information from claims notified to date |
We have reviewed the actual exposure information available for claims notified to date. This has been conducted by using the exposure dates stored in the claims database at an individual claim level and identifying the number of person-years of exposure in each exposure year. We have reviewed the pattern of exposure for each of the disease types separately, although we note that they all tend to follow a similar pattern.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
48 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 6.2: Exposure (person-years) of all Liable Entities’ claimants to date
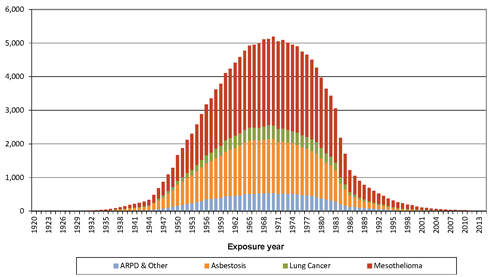
The chart shows that, currently, the peak year of exposure for claims reported to date is in 1970. It should be recognised that there is a degree of bias in this analysis in that the claims notified to date will tend to have arisen from the earlier periods of exposure.
Over time, we expect the right-hand side of this curve to develop and the peak year of exposure to trend towards the early to mid 1970s, and an increase in the absolute level at all periods of exposure as more claims are notified and the associated exposures from these are included in the analysis.
The relatively low level of exposure from 1987 onwards (about 4% of the total) is not unexpected given that all products ceased being manufactured by the Liable Entities by 1987. The exposure after that date likely results from usage of products already produced and sold before that date.
Figure 6.2 is a cumulative chart of the position to date and does not show temporal trends in the allocation of claims to exposure years.
For example, one would expect that more recently reported claims should be associated with, on average, later exposures; and that claims reported in future years would continue that trend towards later exposure periods.
To understand better these temporal trends, we have modelled claimants’ exposures for each past claim report year.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
49 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 6.3: Exposure (person years) of all claimants to date by report year and exposure period
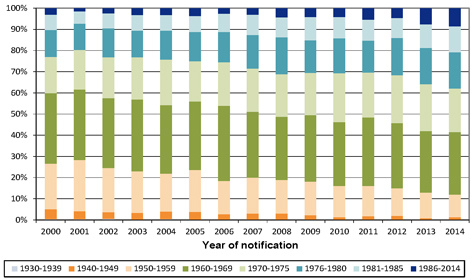
As can be seen in Figure 6.3, there has been a general increasing shift towards the exposure period after 1970, evident by the downwards trends in the chart from left to right indicating that an increasing proportion of the claimants’ exposure relates to more recent exposure periods.
We would expect that such a trend should continue for some time to come and that an increasing proportion of the exposure (in relation to future reported claims) will relate to the period 1981/82 to 1985/86.
| 6.2 | Latency period of reported claims |
Our latency model for mesothelioma assumes the latency period from the average date of exposure is normally distributed with a mean latency of 35 years and a standard deviation of 10 years.
We have analysed the actual latency period of the reported claims of the Liable Entities in order to test the validity of these assumptions.
We have measured the average actual latency period from the average date of exposure to the date of notification of a claim.
In strict epidemiological terms, the latency period should be measured from the date of first exposure to the date of diagnosis.
Because our model utilises latency assumptions from the average date of exposure, the latency period reported in the following charts is not directly comparable with that referred to in epidemiological literature.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
50 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
As indicated in Section 6.1, the average period of exposure for claimants against the Liable Entities is approximately 16 years. This means the actual latency period from the date of first exposure is approximately 8 years greater than indicated in the following charts.
Furthermore, given that the date of notification lags the date of diagnosis by approximately 6 to 8 months for mesothelioma and by approximately 2 years for non-mesothelioma disease types, the latency trends shown in the following charts might slightly overstate the latency to diagnosis.
The charts below show the average latency observed for claims reported in each report year from 2000/01 to 2014/15, and the 25th percentile and 75th percentile observations.
Figure 6.4: Latency of mesothelioma claims
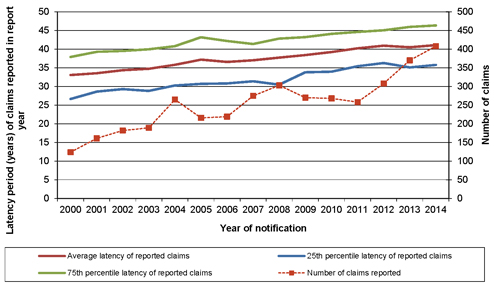
The above chart indicates that the observed average latency period from the average exposure is currently approximately 41 years for mesothelioma.
Epidemiological studies tend to suggest that the observed latency period (from first exposure) for mesothelioma is between 4 and 75 years, with an average latency of around 35 to 40 years and an implied standard deviation of approximately 11 years.
Given the average period of exposure is 16 years, this implies our mean latency assumption from the date of first exposure is approximately 43 years (being 35 + 1⁄2*16). Our model therefore generally accords with epidemiological literature and, if anything, assumes slightly longer latencies than epidemiological studies suggest.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
51 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
At present, given that we are approximately 40 to 45 years after the main period of exposure, claims currently being reported reflect a broad mix of claims of varying latency periods. Accordingly, any analysis of the observed average latency period of reported claims during the most recent 5 to 10 report years:
| ● | Should provide a good indicator of the underlying average latency period of each disease type; and |
| ● | Should have shown an upwards trend given the reduction in exposure in the late 1970s and 1980s. |
Over the past ten years, the observed average latency of mesothelioma claims reported in a report year has increased from 37 years to 41 years, increasing at a rate of about 0.4 years with every year that passes.
The observed average latency of claims reported in future report years should also be expected to show a further upward trend in the coming years.
The currently observed standard deviation of the latency period is 8.2 years.
The claims experience to date and the assumptions selected seem to accord with epidemiological research in relation to mesothelioma, once the relevant adjustments to standardise onto a consistent terminology are made.
The trend in latency periods for other disease types is shown in the following charts.
Figure 6.5: Latency of asbestosis claims
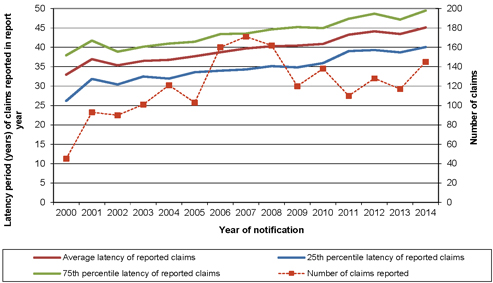
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
52 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 6.6: Latency of lung cancer claims
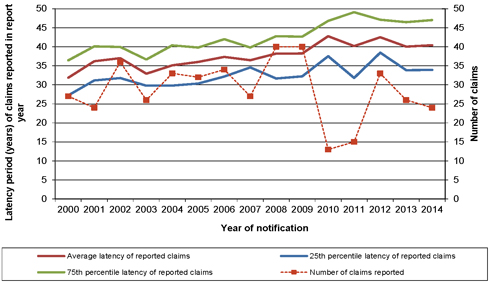
Figure 6.7: Latency of ARPD & Other claims
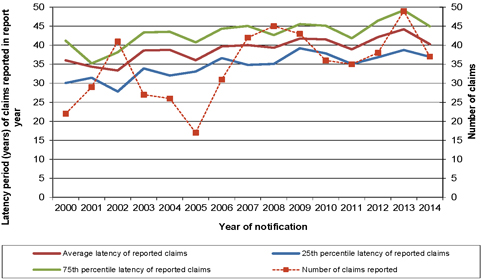
The average observed latency periods for the other disease types show a more surprising trend, appearing to be longer than epidemiological literature has tended to suggest.
A summary of our underlying latency assumptions by disease type are shown below. The mean and standard deviation values quoted are applied to a normal distribution model for the latency period.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
53 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Table 6.1: Assumed underlying latency distribution parameters from average date of exposure to date of notification
| Mean latency (years) |
Standard deviation of latency (years) |
|||||
| Mesothelioma |
35 | 10 | ||||
| Asbestosis |
35 | 8 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
35 | 10 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
32 | 10 | ||||
| Wharf |
n/a | n/a | ||||
|
Workers compensation |
n/a | n/a |
These assumptions are unchanged from the previous valuation.
An indication of how different assumptions would affect the incidence curve and therefore the number of IBNR claims is as follows:
| ● | A higher mean latency period would increase the peak period of claims reporting (i.e. a higher number of IBNR claims). |
| ● | A lower standard deviation would lead to a faster decay in the number of claims being reported after the peak period of claims reporting (i.e. fewer IBNR claims). |
| 6.3 | Modelled peak year of claims |
| 6.3.1 | Modelled assumptions (excluding mesothelioma) |
Based on the application of our exposure model and our latency model, and the assumptions contained explicitly or implicitly within those models, as described in detail in Section 3.4, the peak year of notification of claims reporting against the Liable Entities for each disease type (excluding mesothelioma) is modelled to be as follows:
Table 6.2: Modelled peak year of claim notifications
|
Current valuation |
Previous valuation |
|||||
| Asbestosis |
2008/09 | 2008/09 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
2010/11 | 2010/11 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
2007/08 | 2007/08 | ||||
| Wharf |
2000/01 | 2000/01 | ||||
|
Workers Compensation |
2007/08 | 2007/08 |
These modelled assumptions are unchanged and reflect no changes to the exposure data and no changes to the latency model assumptions at this time.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
54 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
We note that whilst the “modelled peak” derived from our model is as shown above, this does not automatically translate to, nor does it imply that, the “highest claims reporting year” will be those years. This is because variation from year to year is expected due to normal ‘statistical variation’ in claim numbers.
| 6.3.2 | Potential future considerations and impact on future valuations for mesothelioma claims reporting |
At 31 March 2014, we modified the incidence pattern for mesothelioma to reflect the heightened claims reporting that emerged in 2013/14. We adopted a peak period of reporting of 2014/15 to 2016/17.
That change in incidence pattern has been maintained at the current valuation.
At this valuation, we have also increased the levels of future claims reporting across all future reporting periods by approximately 8%.
Should mesothelioma claims reporting continue to escalate, further valuation responses in future years may be necessary.
Such responses would also likely lead to the need to make additional adjustments to the longer-term incidence pattern assumptions and those changes could be material to the valuation result.
The experience in 2013/14 and 2014/15 has created additional uncertainty in setting valuation assumptions for mesothelioma claim numbers and this means that we expect additional valuation volatility for the next few years.
That additional volatility is likely to remain until such time as sufficient experience has been gathered to determine if the 2013/14 and 2014/15 claims experience was aberrational or is a more permanent feature of future levels of mesothelioma claims reporting.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
55 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 6.4 | Pattern of future claim notifications assumed |
| 6.4.1 | Mesothelioma |
The following chart shows the pattern of future notifications which have resulted from the application of our methodology as described in Section 6.3
Figure 6.8: Projected future claim notifications for mesothelioma
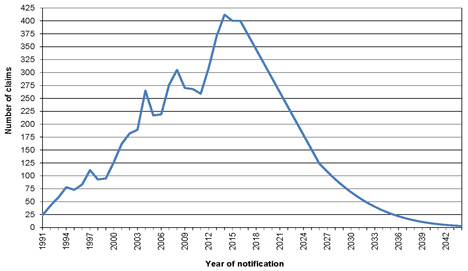
Figure 6.9: Comparison with previous mesothelioma incidence curve assumptions
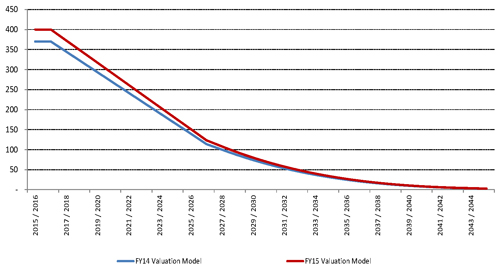
The recognition of the emerging experience in 2014/15 in both our base level assumption for 2015/16 and in our modified claims incidence pattern has increased our projected future number of claims to be reported (from 1 April 2015 onwards) by 295 claims (8%) compared with our previous valuation.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
56 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 6.4.2 | Other disease types |
We have projected the future number of claim notifications from the curve we have derived using our exposure model and our latency model. We have applied this curve to the base number of claims we have estimated for each disease type for 2015/16 as summarised in Section 5.6.
The following chart shows the pattern of future notifications which have resulted from the application of our exposure and latency model and the recalibration of the curve to our revised expectations of claims reporting activity for 2015/16.
Figure 6.10: Projected future claim notifications for other disease types
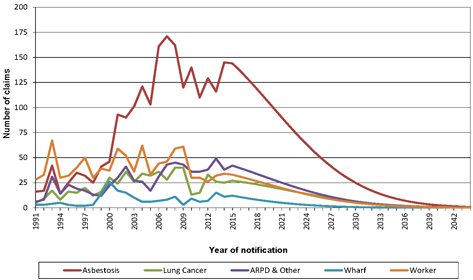
The recognition of the emerging experience in 2014/15 has increased our projected future number of claims to be reported (from 1 April 2015 onwards) by 284 claims (13%) compared with our previous valuation. This increase is primarily due to changes in assumptions for the future level of asbestosis claims.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
57 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
|
Claims Experience – Average Claims Costs and Average Legal Costs | ||
| 7 | ||
| 7.1 | Overview |
We have analysed the average claim awards, average plaintiff/other costs and average defendant legal costs by disease type in arriving at our valuation assumptions.
Table 7.1 shows how the average settlement cost for non-nil attritional claims has varied by client settlement year. All data have been converted into mid 2014/15 money terms using a historical base inflation index of 4% per annum.
We refer to these amounts as “inflated average attritional awards” in the charts and tables that follow.
The average amounts shown hereafter relate to the average amount of the contribution made by the Liable Entities, and does not reflect the total award payable to the plaintiff unless this is clearly stated to be the case.
In particular, for Workers Compensation the average award reflects the average contribution by the Liable Entities for claims in which they are joined but relates only to that amount of the award determined against the Liable Entities which is not met by a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy.
Table 7.1: Average attritional non-nil claim award (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms)
| Client Settlement
|
Mesothelioma | Asbestosis | Lung Cancer | ARPD & Other |
Wharf | Workers Compensation | ||||||
| 2003 |
336,801 |
156,614 |
170,071 |
143,947 |
160,642 |
163,485 | ||||||
| 2004 |
306,728 |
110,034 |
162,090 |
109,993 |
109,266 |
188,231 | ||||||
| 2005 |
290,810 |
100,165 |
77,301 |
101,259 |
111,001 |
172,295 | ||||||
| 2006 |
297,605 |
114,019 |
121,807 |
109,618 |
160,897 |
130,014 | ||||||
| 2007 |
294,142 |
103,493 |
144,456 |
62,091 |
62,251 |
344,022 | ||||||
| 2008 |
337,134 |
108,488 |
106,796 |
113,269 |
183,037 |
69,593 | ||||||
| 2009 |
300,325 |
122,455 |
123,508 |
105,640 |
71,622 |
122,233 | ||||||
| 2010 |
305,162 |
99,841 |
160,554 |
84,447 |
59,614 |
0 | ||||||
| 2011 |
321,349 |
121,876 |
140,656 |
109,805 |
85,591 |
1,012,378 | ||||||
| 2012 |
315,117 |
132,386 |
126,507 |
93,933 |
38,056 |
91,936 | ||||||
| 2013 |
323,800 |
102,747 |
107,869 |
100,838 |
107,968 |
20,800 | ||||||
|
2014 |
301,275 |
99,251 |
134,262 |
70,366 |
80,024 |
70,000 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
58 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.2 | Mesothelioma claims |
In setting our assumption for mesothelioma, we have considered average attritional awards over the past 3, 4 and 5 years.
Figure 7.1: Average attritional awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for mesothelioma claims (excluding large claims)
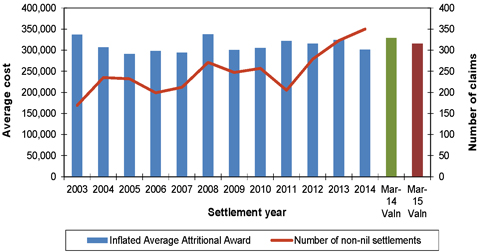
Figure 7.1 shows the historical variability in average claim sizes for mesothelioma, i.e. from $290,000 to $340,000 in mid 2014/15 money terms.
The average of the past three years is $313,000; the average of the past four years is $314,000 and the average of the past five years is $313,000.
The experience in 2014/15 was 8% below expectations.
Taking all of the above factors into consideration, we have adopted a valuation assumption of $315,000 for mesothelioma claims in mid 2014/15 money terms. This assumption represents a 4% reduction in inflation-adjusted terms.
Table 7.2: Average mesothelioma claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
310,000 | 328,600 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 315,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
59 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
It is worth noting the variation between the cost of direct claims and cross claims and between the number of defendants in a “direct claim”.
Figure 7.2: Average attritional awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) split between Direct claims and Cross claims
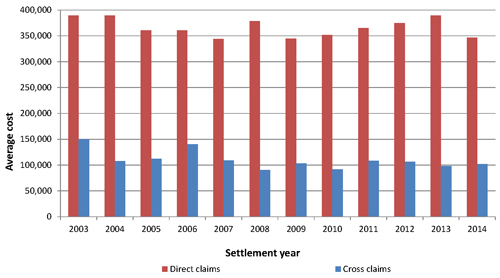
Figure 7.3: Average attritional awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) by number of defendants for Direct claims
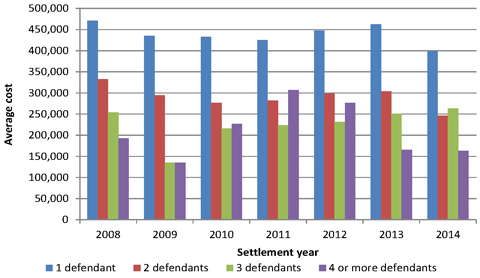
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
60 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.3 | Asbestosis claims |
For asbestosis, it can be seen from Table 7.1 that the period since 2003/04 has had volatile average claim size experience, with average claim sizes ranging from $99,000 to $157,000 (in mid 2014/15 money terms).
Figure 7.2: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for asbestosis claims
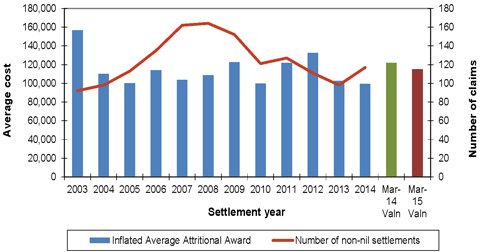
The average of the past three years is $112,000; the average of the past four years is $115,000 and the average of the past five years is $111,000.
In setting an assumption, we also note there has been one asbestosis claim settled for more than $1.37m in 2014/15 money terms (i.e. it is a “large claim” and is not shown in the above analysis).
Taking all of the above factors into consideration, we have adopted a valuation assumption of $115,000 for asbestosis claims in mid 2014/15 money terms. This assumption represents a 6% decrease in inflation-adjusted terms.
Table 7.3: Average asbestosis claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
115,000 | 121,900 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 115,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
61 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.4 | Lung cancer claims |
The average award for lung cancer claims has exhibited some volatility in the past five years, although this is not unexpected given the small volume of claim settlements (approximately 15 to 30 claims per annum).
Figure 7.3: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for lung cancer claims
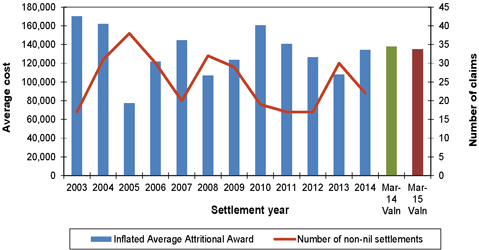
The average of the past three years is $121,000; the average of the past four years is $125,000 and the average of the past five years is $131,000.
At this valuation, we have adopted an average award size of $135,000, which broadly represents the average observed experience in recent years but also takes into consideration the historic volatility in average cost of this disease type. This assumption represents a decrease of 2% in inflation-adjusted terms from our previous assumption.
Table 7.4: Average lung cancer claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
130,000 | 137,800 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 135,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
62 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.5 | ARPD & Other claims |
The average award size over the past eight years has been relatively stable, with the exception of the low average award sizes observed in 2007/08 and 2014/15.
Figure 7.4: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for ARPD & Other claims
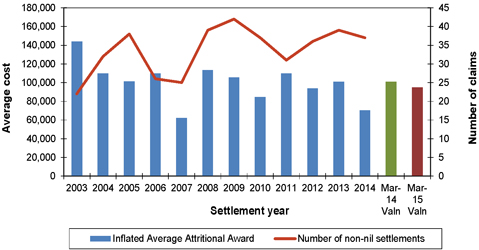
For ARPD & Other claims, the average of the past three years is $89,000; the average of the past four years is $93,000 and the average of the past five years is $91,000.
Taking all of the above factors into consideration, we have adopted a valuation assumption of $95,000 for ARPD & Other claims in mid 2014/15 money terms. This assumption represents a 6% decrease in inflation-adjusted terms.
Table 7.5: Average ARPD & Other claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
95,000 | 100,700 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 95,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
63 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.6 | Workers Compensation claims |
The average award for non-nil Workers Compensation claims has shown a large degree of volatility.
Figure 7.5: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for Workers Compensation claims
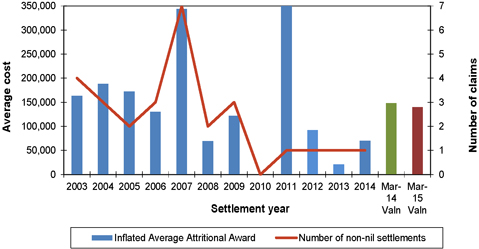
Note: The chart has been “cut-off” at $350,000. The observation for the 2011/12 year was $1,012,378 (inflation adjusted) and related to a single claim.
It should be noted that the high average claim size in 2011/12 is due to one claim of $900,000. Furthermore, we understand that this claim payment was able to be recovered from the workers compensation insurer at a later date.
At this valuation, we have adopted an average award size of $140,000, which represents a decrease of 6% in inflation-adjusted terms from our previous valuation.
This assumption is not material to the overall liability given the high proportion of claims which are settled with no retained liability against the Liable Entities.
Table 7.6: Average Workers Compensation claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
140,000 | 148,400 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 140,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
64 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.7 | Wharf claims |
For wharf claims, the average of the past three years has been $79,000; the average of the past four years has been $80,000 and the average of the past five years has been $75,000.
Figure 7.6: Average awards (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) and number of non-nil claims settlements for wharf claims
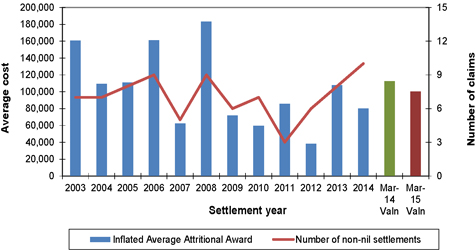
The experience in 2008/09 was impacted by one large claim of almost $600,000. In the absence of this claim, the average claim size for that year would have been $108,000.
We have adopted a valuation assumption of $100,000 in mid 2014/15 money terms which represents a decrease of 11% in inflation-adjusted terms from our previous valuation. Given the small volume of wharf claims, this assumption is not financially significant to the overall results.
Table 7.7: Average wharf claims assumptions
| Claim settlement year | ||||||
| Valuation Report | 2013/14 | 2014/15 | ||||
| 31-Mar-14 |
106,000 | 112,400 | ||||
| 31-Mar-15 |
n/a | 100,000 | ||||
Note: 2013/14 settlements are in 2013/14 dollars whilst 2014/15 settlements are in 2014/15 dollars.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
65 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.8 | Mesothelioma large claim size and incidence rates |
There have been 60 mesothelioma claims settled with awards in excess of $1m in 2006/07 money terms. All of these claims are product and public liability claims.
Figure 7.7: Distribution of individual large claims by settlement year
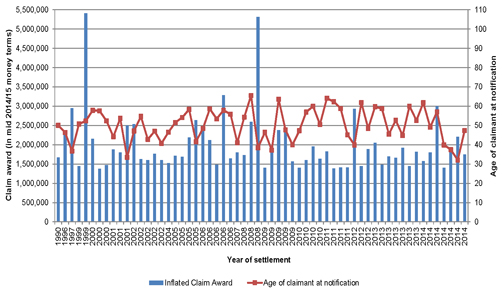
In aggregate these claims have been settled for $120.4m in mid 2014/15 money terms, at an average cost of approximately $2.01m. There have been two claims of more than $5.0m each in mid 2014/15 money terms.
There are two mesothelioma claims which have not yet been settled and for which the case estimate at 31 March 2015 is in excess of $1.37m.
The incidence rate of large claims to non-nil settlements in any one year has been variable, dependent on the random incidence of large claims by settlement year:
| ● | Over the period 1997-2014 there have been 58 large claims at an incidence rate of 1.62% (i.e. the ratio of the number of large claims to the total number of non-nil mesothelioma claims). |
| ● | Over the period 2001-2014 there have been 52 large claims at an incidence rate of 1.60%. |
In selecting a large claim incidence rate, or expected annual number of large claims, we have analysed the number of large claims by year of notification.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
66 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The chart below shows the number of claims that are currently assessed as large. We have separately shown the number of claims that have been settled and the number of claims that are yet to settle but are currently anticipated to be settled as a large claim.
Figure 7.8: Number of mesothelioma large claims by year of notification
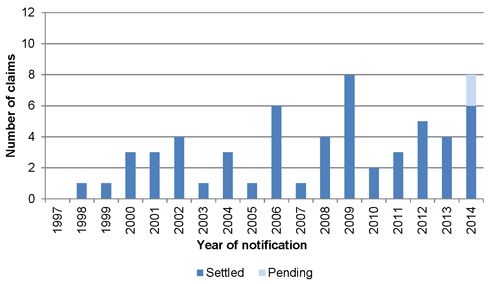
We have assumed a future large claim incidence rate of 2.50% over all future years. This equates to an assumption of 10 large claims being received in 2015/16. The incidence rate assumption (2.50%) is unchanged from our previous valuation.
We have taken the average large claim size experienced to date ($2.01m) as our base assumption, given the small volume of such claims.
Implicitly, this allows for the occasional $5.0m claim at an incidence rate broadly equivalent to past experience (approximately one such claim every five years).
As a consequence, the overall claim cost loading per non-nil mesothelioma claim (excluding legal cost allowances) to make allowance for large claims is $50,250 (being 2.5% x $2,010,000). This is a 3% reduction from our previous valuation assumption of $51,675 (in 2014/15 money terms) (being calculated as 2.5% x $1,950,000 x 1.06).
In relation to legal costs, we have made an additional allowance for plaintiff legal costs to allow for those instances where such costs are made additional to, rather than included with, the claims award. We have also allowed for defence legal costs of $80,000 per large claim.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
67 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The actual incidence of, and settlement of, large claims is not readily predictable and therefore deviations will occur from year to year due to random fluctuations because of the small numbers of large claims (between 5 and 10 per annum).
For other disease types, we observe that there has been (in 2014/15) one asbestosis claim which exceeds the “large claims threshold”. We have made implicit allowance for this claim in setting our attritional claim size assumption for that disease type.
| 7.9 | Summary average claim cost assumptions |
The following table provides a summary of our average claim cost assumptions at this valuation, and those assumed at the previous valuation.
Table 7.8: Summary average claim cost assumptions
| Current
Valuation |
Previous
Valuation |
|||||
| Mesothelioma |
315,000 | 328,600 | ||||
| Asbestosis |
115,000 | 121,900 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
135,000 | 137,800 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
95,000 | 100,700 | ||||
| Wharf |
100,000 | 112,400 | ||||
|
Workers Compensation |
140,000 | 148,400 | ||||
|
Mesothelioma Large Claims (award only) |
Average Size: $2.01m. Frequency: 2.50% |
Average Size: $2.07m. Frequency: 2.50% |
Note: Both the current valuation assumption and the previous valuation assumption are expressed in 2014/15 money terms.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
68 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.10 | Defence legal costs |
| 7.10.1 | Non-nil claims |
The average defence legal costs for non-nil claims by settlement year have been relatively stable over the last eight years for mesothelioma, asbestosis and ARPD & Other.
The average defence costs for lung cancer have shown a greater degree of variability, although this is not unexpected given the small volume of claim settlements (approximately 15 to 30 claims per annum).
Figure 7.9: Average defence legal costs (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) for non-nil claims settlements by settlement year
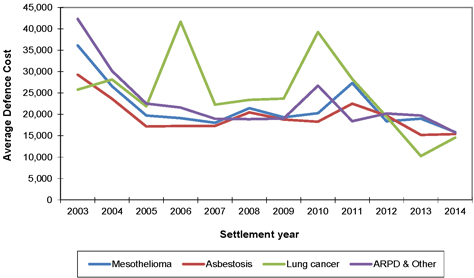
Note: The chart does not include average defence costs for Wharf and Worker claims due to the smaller number of claims involved and the variability that exists as a consequence.
For mesothelioma and asbestosis, defence legal costs have averaged between $17,000 and $20,000 over the past three to five years.
For lung cancer, the average of the past three years is $14,000; the average of the past four years is $17,000 and the average of the past five years is $21,000.
For ARPD & Other, the average of the past three to five years is around $20,000.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
69 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.10.2 | Nil claims |
The average defence legal costs for nil claims by settlement year has been volatile for all disease types.
For mesothelioma, the volatility is a consequence of low nil settlement rate, meaning that there may be 20 to 30 nil claims in any year.
For the other disease types, the number of nil claims might typically be of the order of 10 claims per annum for each disease type.
Figure 7.11: Average defence legal costs (inflated to mid 2014/15 money terms) for nil claims settlements by settlement year
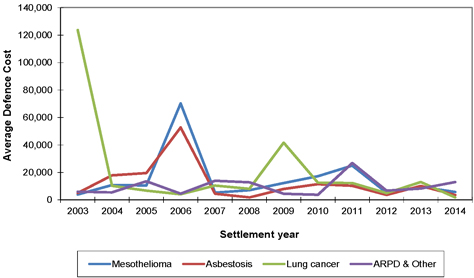
Note: The chart does not include average defence costs for Wharf and Worker claims due to the smaller number of claims involved and the variability that exists as a consequence.
| 7.10.3 | Large claims |
We have also made a separate allowance for defendant legal costs of $80,000 per claim.
The average defence legal costs across all 60 large claims has been $138,000. However, this has been trending downwards over time.
The average defence legal costs for large claims from 2011/12 to 2014/15 has been $83,000 per claim.
The average defence legal costs for large claims from 2012/13 to 2014/15 has been $65,000 per claim.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
70 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 7.11 | Summary average defendant legal costs assumptions |
The following table provides a summary of our defendant legal costs assumptions at this valuation, and those assumed at the previous valuation.
| Current Valuation | Previous Valuation | |||||||
| Non Nil Claims |
Nil Claims |
Non Nil Claims |
Nil Claims | |||||
| Mesothelioma |
20,000 | 21,000 | 21,200 | 21,200 | ||||
| Asbestosis |
17,500 | 14,000 | 19,600 | 17,000 | ||||
| Lung Cancer |
32,000 | 7,500 | 31,800 | 7,400 | ||||
| ARPD & Other |
22,500 | 11,500 | 26,500 | 10,600 | ||||
| Wharf |
22,500 | 2,000 | 23,900 | 2,700 | ||||
| Workers Compensation |
15,000 | 2,500 | 15,900 | 2,700 | ||||
|
Mesothelioma Large |
80,000 | 106,000 | ||||||
Note: Both the current valuation assumption and the previous valuation assumption are expressed in 2014/15 money terms.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
71 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8 | Claims Experience – Nil Settlement Rates
| |||
| 8.1 | Overview |
We have analysed the nil settlement rates, being the number of nil settlements expressed as a percentage of the total number of settlements (nil and non-nil).
Table 8.1 shows the observed nil settlement rates by disease type and by settlement year.
Table 8.1: Nil settlement rates
| Client Settlement Year |
Mesothelioma | Asbestosis | Lung Cancer | ARPD & Other | Wharf | Workers Compensation | ||||||
| 2003 |
7% | 4% | 23% | 12% | 63% | 96% | ||||||
| 2004 |
9% | 8% | 23% | 9% | 0% | 94% | ||||||
| 2005 |
11% | 10% | 28% | 19% | 20% | 95% | ||||||
| 2006 |
14% | 10% | 23% | 38% | 0% | 96% | ||||||
| 2007 |
13% | 9% | 31% | 19% | 72% | 85% | ||||||
| 2008 |
8% | 9% | 24% | 13% | 0% | 95% | ||||||
| 2009 |
8% | 8% | 29% | 2% | 14% | 83% | ||||||
| 2010 |
6% | 6% | 41% | 14% | 0% | 100% | ||||||
| 2011 |
10% | 6% | 32% | 11% | 0% | 67% | ||||||
| 2012 |
9% | 16% | 23% | 20% | 40% | 99% | ||||||
| 2013 |
3% | 8% | 3% | 13% | 20% | 99% | ||||||
|
2014 |
8% | 11% | 12% | 10% | 9% | 97% |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
72 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.2 | Mesothelioma claims |
Figure 8.1 shows the number of claims settled for nil cost, the total number of claims settled and the implied nil settlement rate for each settlement year.
Figure 8.1: Mesothelioma nil claims experience
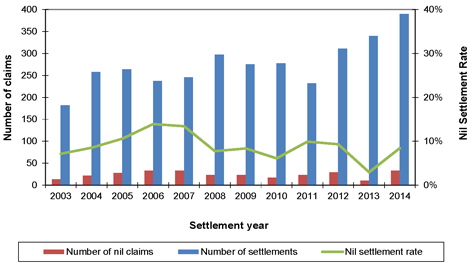
In considering the future nil settlement rate assumption, we note the following:
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the past three years has averaged 7%, for the past four years has averaged 7.5% and for the past five years has averaged 7%. Each of these is significantly impacted by the 3% rate observed in 2013/14. |
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the 2013/14 year at 3% is the lowest nil settlement rate observed historically. |
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the 2014/15 year at 8.5% is more in line with nil settlement rates observed historically. |
| ● | During the past six years, the nil settlement rate has exhibited considerably volatility varying between 3% and 10%. |
Taking all of these factors into consideration and taking a slightly longer term view, we have assumed a future nil settlement rate of 7.5%. This is unchanged from our previous valuation assumption.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
73 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.3 | Asbestosis claims |
As with mesothelioma, the historical asbestosis nil settlement rate has been volatile.
Figure 8.2: Asbestosis nil claims experience
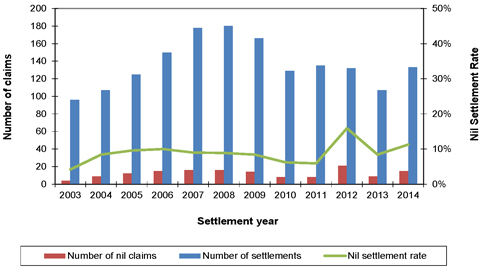
The nil settlement rate for the past three years has averaged 12%, for the past four years has averaged 11% and for the past five years has averaged 10%.
Taking all of these factors into consideration, we have assumed a future nil settlement rate of 9% which is an increase from our previous assumption of 8%.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
74 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.4 | Lung cancer claims |
Given the small volumes of claims, volatility in the nil settlement rate for lung cancer claims is to be expected.
Figure 8.3: Lung cancer nil claims experience
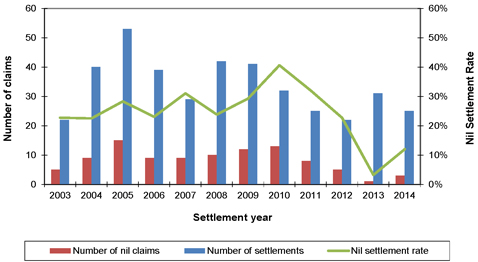
In considering the future nil settlement rate assumption, we note the following:
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the past three years has averaged 12%, for the past four years has averaged 17% and for the past five years has averaged 22%. Each of these is significantly impacted by the 3% rate observed in 2013/14; |
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the 2013/14 year at 3% is the lowest nil settlement rate in the past 15 years; |
| ● | The nil settlement rate for the 2014/15 year at 12% is the second lowest nil settlement rate in the past 10 years; |
| ● | During the past six years, the nil settlement rate has exhibited considerably volatility varying between 3% and 41%. |
Taking all of these factors into consideration, we have assumed a future nil settlement rate of 15% which is a decrease from our previous assumption of 25%.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
75 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.5 | ARPD & Other claims |
As with other disease types, there has been significant volatility in the historical nil settlement rate, given the low numbers of claims for this disease.
Figure 8.4: ARPD & Other nil claims experience
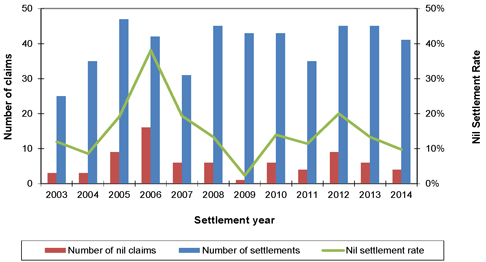
The nil settlement rate for the past three years has averaged 15%, for the past four years has averaged 14% and for the past five years has averaged 14%.
We have selected 13% as our nil settlement rate assumption. This is unchanged from our previous valuation assumption of 13%.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
76 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.6 | Workers Compensation claims |
The nil settlement rates for Workers Compensation claims have been high and reflect the portion of claims whose costs are fully met by a Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy. The proportion of such claims which are fully met by insurance has been relatively stable since 1997/98, typically varying between 80% and 100%.
The nil settlement rate has been in excess of 90% for seven of the past ten years, and it has been above 80% for nine out of the past ten years.
Figure 8.5: Workers Compensation nil claims experience
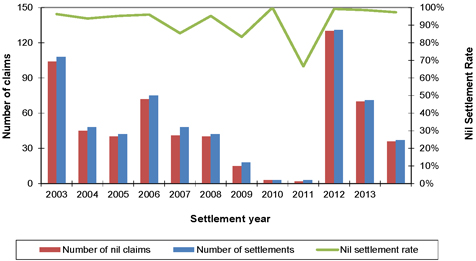
We have selected 95% as our nil settlement rate assumption. This is unchanged from our previous valuation assumption of 95%.
The overall financial impact of this assumption is not material.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
77 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.7 | Wharf claims |
For wharf claims, the nil settlement rate for the past three years has averaged 23%, for the past four years it has averaged 21% and for the past five years it has averaged 17%, although these are affected by the high nil settlement rate in 2012/13 and the absence of nil claims in two of the five most recent years. The experience in 2014/15 was below with the previous valuation assumption of 20%.
Figure 8.6: Wharf nil claims experience
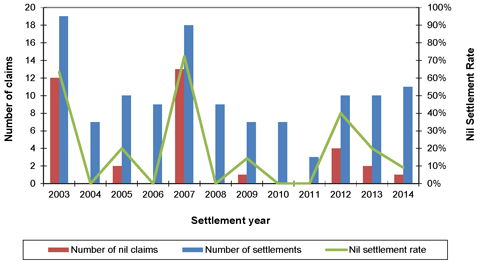
We have selected a nil settlement rate assumption of 20%. This is unchanged from our previous valuation assumption of 20%.
Given the low volume of claims activity for wharf claims, this assumption is highly subjective but is also not material to the overall liability assessment.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
78 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 8.8 | Summary assumptions |
The following table provides a summary of our nil settlement rate assumptions at this valuation, and those assumed at the previous valuation.
Table 8.2: Summary nil settlement rate assumptions
| Current Valuation |
Previous Valuation |
|||||
|
Mesothelioma |
7.5% | 7.5% | ||||
|
Asbestosis |
9.0% | 8.0% | ||||
|
Lung Cancer |
15.0% | 25.0% | ||||
|
ARPD & Other |
13.0% | 13.0% | ||||
|
Wharf |
20.0% | 20.0% | ||||
|
Workers Compensation |
95.0% | 95.0% |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
79 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 9 | Economic and Other Assumptions
| |||
| 9.1 | Overview |
The two main economic assumptions required for our valuation are:
| ● | The underlying claims inflation assumptions adopted to project the future claims settlement amounts and related costs. |
| ● | The discount rate adopted for the present value determinations. |
These are considered in turn in Sections 9.2 to 9.4.
We also discuss the basis of derivation of other assumptions, being:
| ● | The cross-claim recovery rate; and |
| ● | The pattern of settlement of future reported claims and pending claims. |
| 9.2 | Claims inflation |
We are required to make assumptions about the future rate of inflation of claims costs. We have adopted a standard Australian actuarial claims inflation model for liabilities of the type considered in this report that is based on:
| ● | An underlying, or base, rate of general economic inflation relevant to the liabilities, in this case based on wage/salary (earnings) inflation; and |
| ● | A rate of superimposed inflation, i.e. the rate at which claims costs inflation exceeds base inflation. |
| 9.2.1 | Base inflation basis |
Ideally, we would aim to derive our long term base inflation assumptions based on observable market indicators or other economic benchmarks. Unfortunately, such indicators and benchmarks typically focus on inflation measures such as CPI (e.g. CPI index bond yields and RBA inflation targets).
We have derived our base inflation assumption from CPI based indicators together with long term CPI / AWOTE relativities.
| 9.2.2 | CPI assumption |
We have considered two indicators for our CPI assumption:
| ● | Market implied CPI measures. |
| ● | RBA CPI inflation targets. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
80 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
We have measured the financial market implied expectations of the longer-term rate of CPI by reference to the gap between the yield on Commonwealth Government Bonds and the real yield on Commonwealth Government CPI index-linked bonds.
The chart below shows the yields available for 10-year Commonwealth Government Bonds and Index-linked bonds. The gap between the two represents the implied market expectation for CPI at the time.
Figure 9.1: Trends in Bond Yields
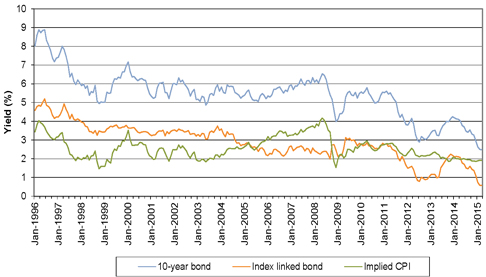
Sources: Reserve Bank of Australia
It can be seen that the implied rate of CPI has varied between 1.5% per annum and 4% per annum during the past 11 years.
At 31 March 2015, the effective annual yield on long-term Commonwealth Government Bonds was 2.48% per annum (31 March 2014: 4.10% per annum) and the equivalent effective real yield on long-term index-linked bonds was approximately 0.58% per annum (31 March 2014: 2.11% per annum). This implies current market expectations for the long-term rate of CPI are of the order of 1.90% per annum.
In considering this result we note that:
| ● | The yield on both nominal and CPI-linked Commonwealth Government Bonds is driven by supply and demand. The yields on both, and their relativity, are subject to some volatility. |
| ● | The RBA’s long term target is for CPI to be maintained between 2% and 3% per annum. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
81 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | The implied CPI rate stayed consistently above 3.2% per annum from March 2006 to September 2008, peaking at almost 4.2% in May 2008. |
| ● | Since October 2008, the implied rate of CPI has remained below 3.0% per annum. |
| ● | Since June 2013, the implied rate of CPI has remained between 1.9% per annum and 2.1% per annum. |
Weighing this evidence together suggests a long term CPI inflation benchmark of 2.50% to 3.00% per annum.
| 9.2.3 | Wages (AWOTE) / CPI relativity |
The following chart summarises the annualised rate of AWOTE and CPI inflation, and their relativity, for the 1970 to 2014 period. The years shown in the chart are calendar years.
Figure 9.2: Trends in CPI and AWOTE
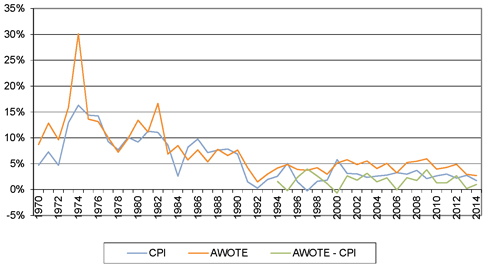
Sources: Reserve Bank of Australia, Australian Bureau of Statistics
In considering the above, we note:
| ● | The period from 1995 reflects largely a continuous period of economic growth which may not be reflective of longer term trends. |
| ● | The longer periods cover a range of business cycles, albeit that the period from 1970 includes the unique events of the early 1970’s (i.e. general inflationary pressures, both locally and worldwide, and the impact of high oil prices owing to the Oil Crisis in 1973). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
82 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Allowing for these factors, the historical data suggests a CPI / AWOTE relativity, or gap, of approximately 1.75% to 2.00% per annum.
Given a longer term CPI benchmark of 2.50% to 3.00%, this suggests a longer-term wage inflation (AWOTE) assumption of 4.25% to 5.00% p.a.
| 9.2.4 | Impact of claimant ageing and non-AWOTE inflation effects |
The overall age profile of claimants is expected to rise over future years with the consequent impact that, other factors held constant, claim amounts should tend to increase more slowly than average wage inflation (excluding any societal changes, e.g. changes in retirement age). This is due to both reduced compensation for years of income or life lost, and a tendency for post retirement age benefits to increase at a rate closer to CPI than AWOTE.
Furthermore, we note that:
| ● | some heads of damage, such as general damages and compensation for loss of expectation of life, would typically be expected to increase at CPI or lower; |
| ● | other heads of damage, including loss of earnings, would be expected to increase at AWOTE (ignoring the ageing effect); and |
| ● | medical expenses and care costs would be expected to increase in line with medical cost inflation which in recent years has been considerably in excess of AWOTE. |
Figure 9.3: Age profile of mesothelioma claimants by report year
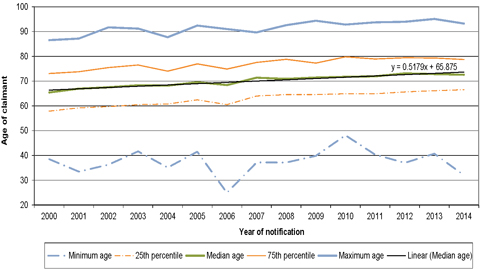
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
83 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The chart indicates that the median age of mesothelioma claimants is increasing.
The claims experience does not indicate a considerable increase in the number (or proportion) of younger claimants. By way of illustration, the proportion of claimants below the age of 60 has reduced from 24% in 2003/04 to 10% in 2014/15.
The chart indicates that the trend for all of the lines in the graph is upwards, indicating that the age profile of claimants is typically increasing.
The chart also indicates that the median age of claimants is increasing by approximately 0.52 years each year, with the median age now in excess of 72 years.
Figure 9.4 shows how average claim size varies by decade of age.
Figure 9.4: Average mesothelioma claim settlement amounts by decade of age
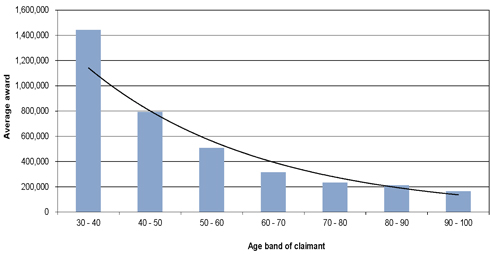
The analysis suggests that the average mesothelioma award reduces by approximately 30% for each increasing decade of age when considering the typical age range of the claimants (i.e. over 60 years of age), although it can be seen that the rate of reduction in award sizes by decade of age decreases after 60 years of age.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
84 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Weighing these various factors together, and allowing for the relative mix of claims between mesothelioma and non-mesothelioma, we consider that a reasonable assumption for the deflationary allowance for the impact of increases in the average age of claimants upon average sizes is approximately 0.75% to 1.00% per annum.
Taking all of these factors into account, we have adopted a long-term base inflation assumption of 4.25% per annum. This assumption is therefore set after having taken into account the negative effect of ageing upon claims awards. This is unchanged from our previous long-term assumption for base inflation.
| 9.2.5 | Adjustments to base inflation assumptions in the short term |
With the current prevailing economic conditions, including lower yields and implied lower outlook for inflation measures, we consider it appropriate to select lower short term assumptions for base inflation.
Our approach (unchanged from the previous valuation) is to reduce the base inflation we adopt for 2015/16 by 50 basis points relative to the longer-term assumption (i.e. 3.75% per annum), and to reduce the base inflation we adopt for 2016/17 by 25 basis points relative to the longer-term assumption (i.e. adopting an assumption of 4.00%).
Table 9.1: Base inflation assumptions
| Current valuation |
Previous valuation |
|||||
| 2014/15 |
n/a | 3.75% | ||||
| 2015/16 |
3.75% | 3.75% | ||||
| 2016/17 |
4.00% | 4.00% | ||||
| Longer-term |
4.25% | 4.25% |
These assumptions apply both to claims awards and legal costs.
| 9.3 | Superimposed inflation |
| 9.3.1 | Overview |
Superimposed inflation is a term used by actuaries to measure the rate at which claims escalate in excess of a base (usually wage) inflation measure.
As a result, superimposed inflation is a “catch-all” for a range of potential factors affecting claims costs, including (but not limited to):
| ● | Courts making compensation payments in relation to new heads of damage; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
85 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Courts changing the levels of compensation paid for existing heads of damage; |
| ● | Advancements in medical treatments – for example, this could lead to higher medical treatment costs (e.g. the cost of the use of new drug treatments); |
| ● | Allowance for medical costs to rise faster than wages because of the use of enhanced medical technologies; |
| ● | Changes in life expectancy; |
| ● | Changes in retirement age – this would have the potential to increase future economic loss awards; |
| ● | Changes in the relative share of the liability to be borne by the Liable Entities’ (which we refer to as “the contribution rate”) and changes in the number of defendants joined in claims; and |
| ● | Changes in the mix of claims costs by different heads of damage. |
Additionally, we have considered the potential for these factors to be offset to some extent by:
| ● | The potential for existing heads of damage to be removed, or for the contraction of these heads of damage; and |
| ● | The effect of an ageing population of claimants on the rate of inflation of overall damages, a component of which relates to economic loss. We have already made some allowance for this by way of an adjustment to the base inflation assumption. |
Whilst the future rate of superimposed inflation is uncertain, and not predictable from one year to the next, it is of note that the average claim costs appear to have been relatively stable in recent years (after adjusting for wage inflation).
For example, mesothelioma average claim sizes (adjusted for wage inflation) have increased by less than $4,000 in an eight-year period from 2006/07 to 2014/15.
However, the emergence of new or expanding heads of damage does not tend to proceed smoothly but progresses in “steps”, depending on the outcome of legislative and other developments.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
86 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 9.3.2 | Analysis of past rates of superimposed inflation |
We have reviewed the rate of inflation of claims costs by settlement year for the past 17 years for mesothelioma claims. We have assessed this by analysing uninflated claim costs and therefore Figure 9.5 measures the trend in the total rate of claims inflation.
Figure 9.5 can then be used to determine the rate of inflation of claim awards over and above base inflation (i.e. measuring the rate of superimposed inflation) in any one year or an annualised rate of superimposed inflation over a longer term. The rate of inflation of claims costs measured by this chart therefore includes the negative effect of ageing upon claim awards.
Figure 9.5: Average mesothelioma awards of the Liable Entities (uninflated)
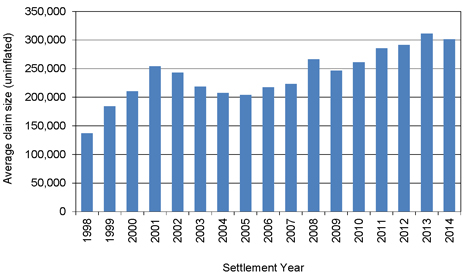
From Figure 9.5, we have the following observations in relation to the rate of total claim inflation (i.e. including both base inflation and superimposed inflation) of the Liable Entities’ share of claims awards:
| ● | Between 1998/99 and 2001/02, claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards averaged approximately 22.9% per annum. |
| ● | Between 2001/02 and 2008/09, claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards averaged approximately 0.7% per annum. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
87 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | Between 2008/09 and 2014/15, claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards averaged approximately 2.1% per annum. |
| ● | The average rate of claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards from 1998/99 to 2014/15 was approximately 5.04% per annum. This would imply superimposed inflation of around 0.75% per annum. |
| ● | The average rate of claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards from 2001/02 to 2014/15 was approximately 1.31% per annum. This would imply superimposed inflation of around -2.75% per annum (i.e. negative superimposed inflation). |
| ● | The average rate of claims inflation of the Liable Entities’ share of mesothelioma claims awards from 2005/06 to 2014/15 was approximately 4.41% per annum. This would imply superimposed inflation of around 0.25% per annum. |
The actuarial approach for this report is to take an average view for superimposed inflation to be applied over the long-term, noting that there will necessarily be deviations from this average on an annual basis and that cashflows are projected for the next 50 or more years.
Furthermore, in considering the future rate of claim inflation, we have had regard to some of the recent court decisions and the impact they can have either directly or indirectly upon claim settlements, as well as a relatively lower level of large claim settlements in the most recent year.
Weighing all of the evidence together, and in particular recognising that the period since 2001/02 has generally been benign and may not therefore be reflective of a longer-term assumption, we have adopted an assumed long-term rate of future superimposed inflation of claims awards of 2.25% per annum. This is unchanged from our previous assumption.
There is no superimposed inflation applied to legal costs.
The outcome of this assumption is a “superimposed inflation allowance” of approximately $350m on a discounted central estimate basis. The majority of this “superimposed inflation allowance” arises in the projected cashflows from 2020 to 2040.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
88 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 9.4 | Discount rates: Commonwealth bond zero coupon yields |
We have calculated the zero coupon yield curve at 31 March 2015 underlying the prices, coupons and durations of Commonwealth Government Bonds for the purpose of discounting the liabilities for this report.
The use of such discount rates is consistent with standard Australian actuarial practice for such liabilities, is in accordance with the Institute of Actuaries of Australia’s Professional Standard PS300 and is also consistent with our understanding of the Australian accounting standards.
The table and chart below show the assumptions for the current valuation and the previous valuation.
Table 9.2: Zero coupon yield curve by duration
| Year | Current Valuation |
Previous Valuation |
||||||
| 1 |
1.99% | 2.59% | ||||||
|
2 |
1.62% | 2.97% | ||||||
|
3 |
1.65% | 3.60% | ||||||
|
4 |
2.02% | 4.02% | ||||||
|
5 |
2.43% | 4.35% | ||||||
|
6 |
2.73% | 4.58% | ||||||
|
7 |
2.93% | 4.77% | ||||||
|
8 |
3.05% | 4.94% | ||||||
|
9 |
3.13% | 5.10% | ||||||
|
10 |
3.22% | 5.24% | ||||||
|
11 |
3.29% | 5.37% | ||||||
|
12 |
3.36% | 5.48% | ||||||
|
13 |
3.42% | 5.57% | ||||||
|
14 |
3.47% | 5.65% | ||||||
|
15 |
3.52% | 5.72% | ||||||
|
16 |
3.56% | 5.77% | ||||||
|
17 |
4.37% | 5.85% | ||||||
|
18 |
5.19% | 5.93% | ||||||
|
19+ |
6.00% | 6.00% |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
89 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 9.6: Zero coupon yield curve by duration
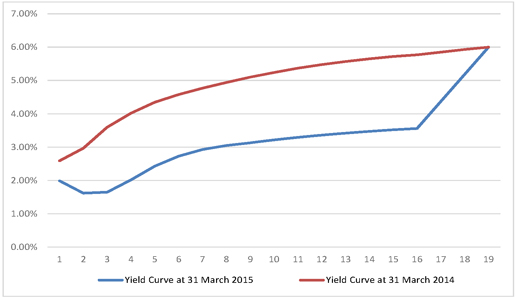
It can be observed that yields have fallen across all durations, with reductions of in excess of 200 basis points at durations 3 years and above. At shorter durations, the reductions are still in excess of 100 basis points.
This reduction in yields has led to a significant increase in the discounted central estimate, by $286m.
If we had assumed a long-term discount rate of 3.75% per annum (instead of the adopted assumption of 6.00% per annum), the discounted central estimate would have increased by a further $22m (approximately equating to a 1% increase in the Discounted Central Estimate).
In other words, the Discounted Central Estimate liability is not overly sensitive to the long-term discount rate assumed; and this reflects the fact that the majority of the projected liability relates to the next 20 years of cash outflows.
| 9.5 | Cross-claim recovery rates |
Cross-claim recoveries have totalled $40m to date. This represents 3.2% of gross claims costs.
The majority of cross-claim recoveries relate to the Hardie-BI Joint Venture with CSR, including more than $4m paid in 2005/06 and more than $2m paid in 2006/07 in relation to cross-claims against CSR and Bradford Insulation in relation to the Hardie-BI Joint Venture.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
90 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following chart shows how the experience of cross-claim recoveries has varied over time, both in monetary terms and expressed as a percentage of gross payments.
Figure 9.7: Cross-claim recovery experience
Cross-claim recoveries in 2005/06 and 2006/07 were significantly impacted by recoveries from CSR and were due also to the impact of the Hardie-BI Joint Venture. Our analysis indicates that such recoveries in part relate to recoveries that ought to have been made earlier (i.e. they reflected an element of catch-up). Therefore, we believe the rate of recovery exhibited in those two years is not a good guide to the likely future level of recovery.
Taking this and the recent trends in the reduction in the cross-claim recovery rate into account we have assumed that future levels of cross-claim recoveries will be 2.0% of the average award. This is a decrease from the previous valuation assumption of 2.25% at 31 March 2014.
| 9.6 | Settlement Patterns |
Triangulation methods are used to derive the past pattern of settlement of claims and are used in forming a view on future settlement patterns.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
91 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following triangles provide an illustrative example of how we perform this:
Figure 9.8: Settlement pattern derivation for mesothelioma claims: paid as % of ultimate cost
| Yr of Notification | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1996 |
47.2% | 96.1% | 96.5% | 99.2% | 99.2% | 99.2% | 99.2% | 99.2% | 99.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1997 |
33.3% | 71.0% | 71.0% | 71.6% | 71.6% | 78.3% | 81.1% | 90.2% | 97.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1998 |
50.2% | 82.2% | 87.1% | 87.4% | 90.8% | 90.8% | 96.1% | 97.4% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1999 |
60.9% | 92.2% | 92.3% | 92.5% | 95.3% | 96.3% | 99.3% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2000 |
60.3% | 90.0% | 95.7% | 97.4% | 99.4% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2001 |
51.8% | 88.2% | 91.3% | 94.4% | 95.6% | 98.5% | 98.5% | 98.5% | 99.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2002 |
54.9% | 90.3% | 95.7% | 98.7% | 99.6% | 99.9% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2003 |
55.2% | 90.6% | 95.6% | 99.4% | 99.4% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 |
52.7% | 93.9% | 97.5% | 98.6% | 99.6% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 |
57.9% | 92.3% | 97.4% | 97.5% | 97.9% | 99.4% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 |
59.6% | 90.6% | 94.4% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 |
50.2% | 92.0% | 94.3% | 94.6% | 94.6% | 94.8% | 94.8% | 94.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 |
65.7% | 94.1% | 95.3% | 96.9% | 97.5% | 97.6% | 97.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 |
57.8% | 88.2% | 92.5% | 99.1% | 99.3% | 99.6% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 |
71.2% | 95.7% | 99.0% | 99.2% | 99.3% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 |
56.4% | 95.6% | 97.8% | 98.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 |
53.9% | 94.8% | 96.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
63.9% | 92.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2014 |
60.9% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure 9.9: Settlement pattern derivation for non-mesothelioma claims: paid as % of ultimate cost
| Yr of Notification | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1996 |
6.5% | 22.6% | 36.1% | 53.3% | 56.6% | 56.6% | 67.7% | 83.2% | 88.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1997 |
4.4% | 36.4% | 67.4% | 72.7% | 82.4% | 85.6% | 92.2% | 97.8% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1998 |
5.0% | 43.9% | 73.5% | 78.0% | 84.8% | 91.9% | 94.0% | 99.6% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1999 |
9.3% | 56.3% | 81.2% | 89.9% | 91.5% | 96.6% | 99.5% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2000 |
15.8% | 45.8% | 64.7% | 80.3% | 83.8% | 86.7% | 89.7% | 89.7% | 93.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2001 |
22.5% | 56.4% | 82.0% | 85.3% | 89.9% | 92.3% | 94.0% | 97.1% | 97.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2002 |
12.6% | 59.5% | 80.3% | 87.7% | 94.9% | 97.2% | 98.3% | 99.0% | 99.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2003 |
17.4% | 68.5% | 86.4% | 92.2% | 95.5% | 99.0% | 99.3% | 99.3% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 |
17.5% | 58.9% | 83.4% | 92.6% | 95.3% | 96.6% | 98.0% | 98.0% | 98.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 |
19.5% | 81.3% | 94.5% | 98.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 |
22.6% | 72.1% | 91.5% | 94.6% | 99.3% | 99.9% | 99.9% | 99.9% | 99.9% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 |
28.8% | 83.1% | 92.9% | 99.5% | 99.9% | 99.9% | 99.9% | 99.9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 |
25.3% | 82.0% | 93.1% | 94.7% | 97.1% | 97.4% | 97.4% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 |
40.0% | 76.8% | 93.1% | 94.8% | 95.0% | 96.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 |
25.9% | 84.0% | 94.9% | 96.6% | 99.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 |
36.4% | 89.0% | 98.6% | 98.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 |
36.4% | 83.8% | 92.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
28.0% | 82.9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2014 |
28.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
We have estimated the settlement pattern for future claim reporting as follows:
Table 9.3: Settlement pattern of claims awards by delay from claim reporting
| Delay (years) | Mesothelioma | Non- mesothelioma |
||||
|
0 |
63.0% | 32.0% | ||||
|
1 |
28.0% | 50.0% | ||||
|
2 |
5.0% | 11.0% | ||||
|
3 |
2.0% | 2.0% | ||||
|
4 |
0.5% | 1.0% | ||||
|
5 |
0.5% | 1.0% | ||||
|
6 |
0.5% | 1.0% | ||||
|
7 |
0.0% | 1.0% | ||||
|
8 |
0.5% | 0.5% | ||||
|
9 |
0.0% | 0.5% |
These assumed settlements patterns have been modified slightly since our previous valuation, resulting in an assumption of a slight speeding up of both mesothelioma and non-mesothelioma claim settlements.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
92 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10 | Valuation Results
| |||
| 10.1 | Central estimate liability |
At 31 March 2015, our projected central estimate of the liabilities of the Liable Entities (the Discounted Central Estimate) to be met by the AICF Trust is $2,142.8m (March 2014: $1,870.2m).
We have not allowed for the future Operating Expenses of the AICF Trust or the Liable Entities in the liability assessment.
The following table shows a summary of our central estimate liability assessment and compares the current assessment with our previous valuation.
Table 10.1: Comparison of central estimate of liabilities
| 31 March 2015 $m |
31 March 2014 $m | |||||||
| Gross
of insurance recoveries |
Insurance recoveries |
Net
of insurance recoveries |
Net of insurance recoveries | |||||
|
Total uninflated and undiscounted cash-flows |
1,795.2 | 229.3 | 1,565.9 | 1,546.6 | ||||
|
Inflation allowance
|
1,257.5 | 80.5 | 1,177.0 | 1,258.5 | ||||
|
Total inflated and undiscounted cash-flows |
3,052.7 | 309.8 | 2,742.9 | 2,805.1 | ||||
|
Discounting allowance
|
(656.0) | (56.0) | (600.1) | (934.9) | ||||
|
Net present value liabilities
|
2,396.7 | 253.8 | 2,142.8 | 1,870.2 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
93 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10.2 | Comparison with previous valuation |
In the absence of any change to the claim projection assumptions from our 31 March 2014 valuation, other than allowing for the changes in the discount rate, we would have projected a Discounted Central Estimate liability of $2,075.0m as at 31 March 2015, i.e. an increase of $204.8m from our 31 March 2014 valuation result.
This increase of $204.8m is due to:
| ● | A reduction of $81.6m, being the net impact of expected claims payments (which reduce the liability) and the “unwind of discount” (which increases the liability and reflects the fact that cashflows are now one year nearer and therefore are discounted by one year less). |
| ● | An increase of $286.4m resulting from the significantly lower discount rates prevailing at 31 March 2015 compared with those adopted at 31 March 2014. |
Our liability assessment at 31 March 2015 of $2,142.8m represents an increase of $67.8m, which arises from changes to the claim projection assumptions.
The increase of $67.8m is principally a consequence of:
| ● | An increase in the projected future number of claims for mesothelioma and asbestosis; |
offset by
| ● | Lower average claims sizes and average defence legal cost assumptions for most disease types; |
| ● | Changes to assumed future patterns of claims settlement; and |
| ● | Favourable settlement experience for claims that were pending at 31 March 2014 relative to case estimates established at 31 March 2014. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
94 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following chart shows an analysis of the change in our liability assessments from March 2014 to March 2015 on a discounted basis.
Figure 10.1: Analysis of change in central estimate liability (discounted basis)
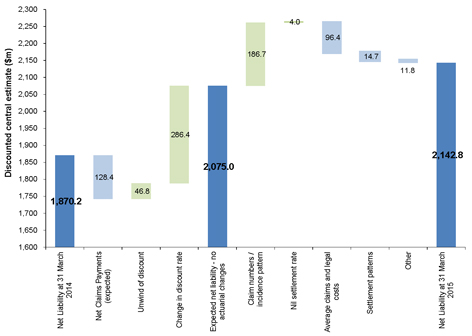
Note: Green bars signal that this factor has given rise to an increase in the liability whilst light blue bars signal that this factor has given rise to a reduction in the liability.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
95 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The following chart shows an analysis of the change in our liability assessments from March 2014 to March 2015 on an undiscounted basis.
Figure 10.2: Analysis of change in central estimate liability (undiscounted basis)
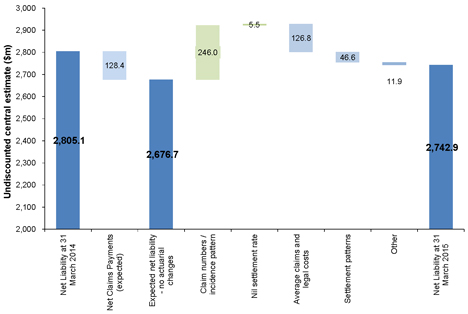
Note: Green bars signal that this factor has given rise to an increase in the liability whilst light blue bars signal that this factor has given rise to a reduction in the liability.
The undiscounted liability as of 31 March 2015 has increased from $2,677m (based on the 31 March 2014 valuation) to $2,743m. This represents an increase of $66m.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
96 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10.3 | Comparison of valuation results since 30 September 2006 |
We have analysed how our valuation results have changed since the Initial Report (as defined in the Amended Final Funding Agreement) at 30 September 2006.
The table below shows the results over time.
We have used the inflated and undiscounted results as the comparison. We consider this to be the most appropriate assessment as it removes the impacts of changes in discount rates and the “unwind of the discount”.
Table 10.2: Comparison of valuation results since 30 September 2006
| FY2007 | FY 2008 | FY 2009 | FY 2010 | FY 2011 | FY 2012 | FY 2013 | FY 2014 | FY 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Valuation result at end of previous financial year | 3,169 | 2,811 | 3,027 | 3,124 | 2,906 | 2,661 | 2,525 | 2,513 | 2,805 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net payments made (actual) | -32 | -55 | -91 | -86 | -76 | -76 | -86 | -113 | -120 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected valuation result (no actuarial changes) | 3,137 | 2,756 | 2,936 | 3,038 | 2,830 | 2,585 | 2,439 | 2,400 | 2,685 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actual valuation at end of financial year | 2,811 | 3,027 | 3,124 | 2,906 | 2,661 | 2,525 | 2,513 | 2,805 | 2,743 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Impact of actuarial valuation changes | -326 | 271 | 188 | -132 | -169 | -60 | 74 | 405 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative changes since 30 September 2006 | -326 | -55 | 133 | 1 | -168 | -228 | -154 | 251 | 309 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note: For FY2007, the starting valuation ($3,169m) is the valuation at 30 September 2006, not the valuation at 31 March 2006.
The table shows that whilst there have been some years where there have been increases and some years where there have been decreases arising from changes to actuarial valuation assumptions, over the period from 30 September 2006 to 31 March 2015 the valuation has deteriorated by $309m (10% of the valuation contained in the Initial Report).
In terms of net cashflows, actual net payments of $736m have been made since 30 September 2006. This compares with an estimate of $816m projected for the same period (1 October 2006 to 31 March 2015) in the valuation at 30 September 2006.
After allowing for removal of the beneficial impact of HIH and other commutations ($72m), actual net cashflows have been $8m below those projected in the valuation at 30 September 2006.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
97 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Figure 10.3: Comparison of actual net cash outflows with projected net payments at the 30 September 2006 valuation
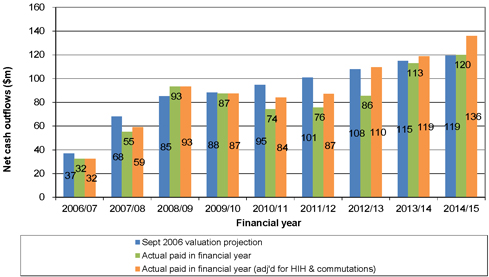
Note: Figures in the above chart differ slightly compared to Table 10.2 owing to accounting accrual adjustments. The aggregate difference is a net amount of $1m across the period.
| 10.4 | Cashflow projections |
| 10.4.1 | Historical cashflow expenditure |
The following chart shows the monthly rate of expenditure by AICF relating to asbestos-related claim settlements over the past eight years.
Figure 10.4: Historical claim-related expenditure of the Liable Entities
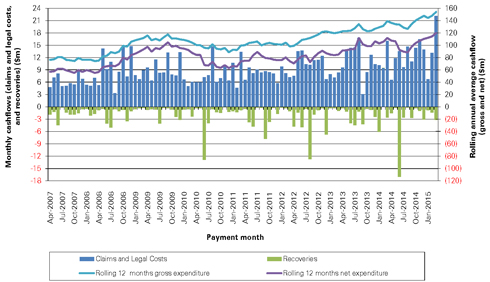
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
98 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Gross cashflow payments in the 12 months to 31 March 2015 were $154.3m (FY14: $140.4m).
Actual net cashflow in 2014/15 ($121.1m) was $7.3m (6%) lower than the net cashflow projected for 2014/15 ($128.4m) in our 31 March 2014 valuation report.
In the absence of the HIH proceeds, actual net cashflow was $8.0m (6%) higher than the net cashflow projected for 2014/15.
| 10.4.2 | Future cashflow projections |
Figure 10.5 shows the projected net cashflows underlying our current valuation and the projected net cashflow projection underlying our previous valuation at 31 March 2014.
We have also indicated the actual annual net cashflows for all financial years since 2000/01 (the green bars) and the level of the actual net cashflows in the absence of HIH recoveries or commutation proceeds (the purple bars represent the incremental amount of those proceeds).
Figure 10.5: Annual cashflow projections – inflated and undiscounted ($m)
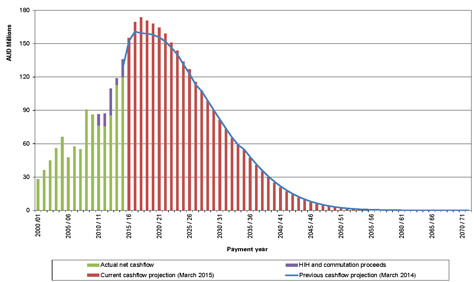
The projected inflated and undiscounted cashflows underlying this chart are documented in Appendix B.
Given the extremely long-tailed nature of asbestos-related liabilities, a small change in an individual assumption can have a significant impact upon the cashflow profile of the liabilities.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
99 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10.5 | Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations |
The Amended Final Funding Agreement sets out the basis on which payments will be made to the AICF Trust.
Additionally, there are a number of other figures specified within the Amended Final Funding Agreement that we are required to calculate. These are:
| ● | Discounted Central Estimate; |
| ● | Term Central Estimate; and |
| ● | Period Actuarial Estimate. |
Table 10.3: Amended Final Funding Agreement calculations
| $m | ||||
|
Discounted Central Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, Insurance and Other Recoveries)
|
2,142.8
| |||
| Period Actuarial Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, gross of Insurance and Other Recoveries) comprising: |
544.2
| |||
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2015/16 |
171.4
| |||
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2016/17
|
185.0
| |||
|
Discounted value of cashflow in 2017/18
|
187.7
| |||
| Term Central Estimate (net of cross-claim recoveries, Insurance and Other Recoveries) |
2,135.3
|
The actual funding amount due at a particular date will depend upon a number of factors, including:
| ● | the net asset position of the AICF Trust at that time; |
| ● | the free cash flow amount of the James Hardie Group in the preceding financial year; and |
| ● | the Period Actuarial Estimate in the latest Annual Actuarial Report. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
100 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 10.6 | Insurance Recoveries |
Our liability valuation has made allowance for a discounted central estimate of Insurance Recoveries of $253.8m. This estimate is comprised as follows:
Table 10.4: Insurance recoveries at 31 March 2015
| $m | Undiscounted central estimate |
Discounted central estimate | ||
| Gross liability |
3,052.7 | 2,396.7 | ||
| Product liability recoveries |
300.5 | 247.8 | ||
| Bad and doubtful debt allowance (product) |
(10.7) | (8.8) | ||
| Public liability recoveries |
20.2 | 14.9 | ||
|
Bad and doubtful debt allowance (public) |
(0.2) | (0.1) | ||
| Insurance recovery asset |
309.8 | 253.8 | ||
| Net liability |
2,742.9 | 2,142.8 | ||
| Insurance recovery rate |
10.5% | 11.0% | ||
| Bad and doubtful debt rate |
3.4% | 3.4% |
The combined bad and doubtful debt rate is 3.4% (2014: 6.1%).
The continued reduction in the rate of bad debt reflects the beneficial impact of the collection activity in relation to HIH since 2012/13.
The AICF Facility Agreement requires the Approved Actuary to calculate the discounted central estimate value of certain Insurance Policies, being those specified in Schedule 5 of the AICF Facility Agreement.
At 31 March 2015, the discounted central estimate of the Insurance Policies, as specified in Schedule 5 of the AICF Facility Agreement, is $237.9m (March 2014: $214.3m).
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
101 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 11 | Uncertainty
| |||
| 11.1 | Overview |
There is uncertainty involved in any valuation of the liabilities of an insurance company or a self-insurer. The sources of such uncertainty include, but are not limited to:
| ● | Parameter error – this is the risk that the parameters and assumptions chosen ultimately prove not to be reflective of future experience. |
| ● | Model error – this is the risk that the model selected for the valuation of the liabilities ultimately proves not to be adequate for the projection of the liabilities. |
| ● | Legal and social developments – this is the risk that the legal environment in which claims are settled changes relative to its current and historical position thereby causing significantly different awards. |
| ● | Future actual rates of inflation being different from that assumed. |
| ● | The general economic environment being different from that assumed. |
| ● | Potential sources of exposure – this is the risk that there exist sources of exposure which are as yet unknown or unquantifiable, or for which no liabilities have yet been observed, but which may trigger future claims. |
In the case of asbestos liabilities, these uncertainties are exacerbated by the extremely long latency period from exposure to onset of disease and notification of a claim. Asbestos-related claims often take in excess of 40 years from original exposure to become notified and then settled, compared with an average delay from exposure to settlement of 4-5 years for many other compensation-type liabilities such as Comprehensive Third-Party injury liabilities or other Workers Compensation liabilities.
Specific forms of uncertainty relating to asbestos-related disease liabilities include:
| ● | The difficulty in quantifying the extent and pattern of past asbestos exposures and the number and incidence of the ultimate number of lives that may be affected by asbestos related diseases arising from such past asbestos exposures; |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
102 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | The timing of the peak level of claims reporting for mesothelioma, particularly in light of the high level of claims reporting activity in 2008/09, the lower levels of activity through to 2011/12 and the significant increase in claims reporting in the most recent three years; |
| ● | The propensity of individuals affected by diseases arising from such exposure to file common law claims against defendants; |
| ● | The extent to which the Liable Entities will be joined in such future common law claims; |
| ● | The fact that the ultimate severity of the impact of the disease and the quantum of the claims that will be awarded will be subject to the outcome of events that have not yet occurred, including: |
| - | medical and epidemiological developments, including those relating to life expectancy in general; |
| - | court interpretations; |
| - | legislative changes; |
| - | changes to the form and range of benefits for which compensation may be awarded (“heads of damage”); |
| - | public attitudes to claiming; |
| - | the potential for future procedural reforms in NSW and other States affecting the legal costs incurred in managing and settling claims; |
| - | potential third-wave exposures; and |
| - | social and economic conditions such as inflation. |
| 11.2 | Sensitivity testing |
As we have noted above, there are many sources of uncertainty. Actuaries often perform “sensitivity testing” to identify the impact of different assumptions on future experience, thereby providing an indication of the degree of parameter error risk to which the valuation assessment is exposed.
Sensitivity testing may be considered as being a mechanism for testing “what will the liabilities be if instead of choosing [x] for assumption [a] we choose [y]?” It is also a mechanism for identifying how the result will change if experience turns out different in a particular way relative to that which underlies the central estimate expectations. As such, it provides an indication of the level of variability inherent in the valuation.
We have performed some sensitivity tests of the results of our central estimate valuation. We have sensitivity tested the following factors:
| ● | number of claims notified: 10% above and below our central estimate assumption (equating to 360 and 440 mesothelioma claims). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
103 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| ● | average claim cost of a non-nil claim: 5% above and below our central estimate assumption. |
| ● | nil settlement rate: 2 percentage points above and below our central estimate assumption. |
| ● | superimposed inflation: being 0% per annum or 4% per annum over all future years. |
| ● | mesothelioma incidence pattern: we have tested two separate alternative outcomes: |
| ¡ | Pattern 1 takes our central estimate pattern through to 2025/26 but assumes an increased rate of joining of the Liable Entities from 2026/27 onwards. |
| ¡ | Pattern 2 takes pattern 1 and shifts it out by a further two years, i.e. mesothelioma claims reporting does not begin to reduce until after 2018/19. This also therefore impacts the incidence pattern for all years after 2018/19. |
There are other factors which influence the liability assessment and which could be sensitivity tested, including:
| ● | The cross-claim recovery rate; |
| ● | The variation in timing of claim notifications (but with no change in the overall number of notifications); and |
| ● | The pattern and delay of claim settlements from claim notification. |
We have not sensitivity tested these factors, viewing them as being of less financial significance individually.
We have not sensitivity tested the value of Insurance Recoveries as uncertainties typically relate to legal risk and disputation risk, and it is not possible to parameterise a sensitivity test in an informed manner.
We have not included a sensitivity test for the impact of changes in discount rates although, as noted in this Report, changes in discount rates can introduce significant volatility to the Discounted Central Estimate result reported at each year-end.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
104 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| 11.3 | Results of sensitivity testing |
Figure 11.1 shows the impact of various individual sensitivity tests on the Discounted Central Estimate of the liabilities, and of a combined sensitivity test of a number of factors.
Although we have tested multiple scenarios of each assumption, one cannot gauge an overall potential range by simply adding these tests together. Accordingly, we have prepared a range based on a combination of factors.
Figure 11.1: Sensitivity testing results – Impact around the Discounted Central Estimate (in $m)
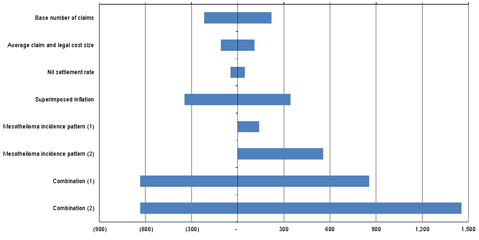
Figure 11.2: Sensitivity testing results – Impact around the undiscounted central estimate (in $m)
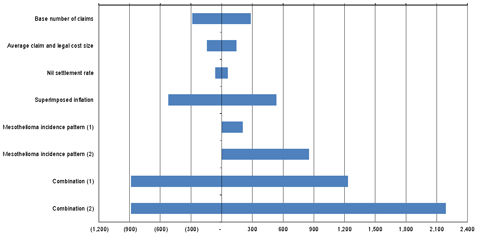
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
105 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
The uncertainties prevailing at this time are higher than historically observed. This is a consequence of the higher than expected level of mesothelioma claims reporting in the most recent two years and the uncertainty this brings in relation to the projection of the future number of mesothelioma claims to be received by AICFL.
The single most sensitive assumption shown in the chart is the peak period of claims reporting against the Liable Entities. Shifting the assumed period of peak claims reporting by a further 2 years for mesothelioma from that currently assumed of 2016/17 (i.e. assuming that claim reporting begins to reduce after 2018/19) together with increased claims reporting from 2026/27 onwards could add a further $555m (26%) on a discounted basis (as shown in Figure 11.1 by the scenario labelled “mesothelioma incidence pattern (2)”).
Table 11.1: Summary results of sensitivity analysis ($m)
| Undiscounted | Discounted | |||||||||
|
Central estimate
|
2,742.9 | 2,142.8 | ||||||||
|
Low Scenario
|
1,860.4 | 1,510.4 | ||||||||
|
High Scenario
|
4,931.1 | 3,596.7 | ||||||||
Whilst the table above indicates a range around the discounted central estimate of liabilities of -$632m to +$1,454m, the actual cost of liabilities could fall outside that range depending on the actual experience.
We further note that these sensitivity test ranges are not intended to correspond to a specified probability of sufficiency nor are they intended to indicate an upper bound or a lower bound of all possible outcomes.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
106 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
APPENDICES
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
107 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| A | Credit rating default rates by duration
| |||
| Rating | Yr. 1 | Yr. 2 | Yr. 3 | Yr. 4 | Yr. 5 | Yr. 6 | Yr. 7 | Yr. 8 | Yr. 9 | Yr. 10 | Yr. 11 | Yr. 12 | Yr. 13 | Yr. 14 | Yr. 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AAA |
0.00% | 0.03% | 0.13% | 0.24% | 0.35% | 0.47% | 0.53% | 0.62% | 0.68% | 0.74% | 0.77% | 0.81% | 0.84% | 0.91% | 0.99% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AA+ |
0.00% | 0.06% | 0.06% | 0.11% | 0.17% | 0.24% | 0.30% | 0.36% | 0.43% | 0.50% | 0.57% | 0.64% | 0.72% | 0.80% | 0.89% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AA |
0.02% | 0.03% | 0.09% | 0.23% | 0.38% | 0.51% | 0.65% | 0.78% | 0.88% | 0.99% | 1.09% | 1.16% | 1.28% | 1.36% | 1.45% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AA- |
0.03% | 0.10% | 0.20% | 0.29% | 0.39% | 0.50% | 0.59% | 0.65% | 0.72% | 0.79% | 0.87% | 0.95% | 0.98% | 1.05% | 1.12% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A+ |
0.06% | 0.11% | 0.24% | 0.40% | 0.53% | 0.64% | 0.78% | 0.93% | 1.10% | 1.29% | 1.46% | 1.65% | 1.88% | 2.14% | 2.36% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A |
0.07% | 0.17% | 0.27% | 0.42% | 0.57% | 0.78% | 0.99% | 1.18% | 1.42% | 1.69% | 1.91% | 2.07% | 2.21% | 2.31% | 2.52% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A- |
0.08% | 0.20% | 0.34% | 0.48% | 0.69% | 0.91% | 1.20% | 1.42% | 1.59% | 1.74% | 1.88% | 2.04% | 2.19% | 2.29% | 2.38% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BBB+ |
0.14% | 0.38% | 0.66% | 0.95% | 1.27% | 1.62% | 1.86% | 2.12% | 2.43% | 2.73% | 3.02% | 3.19% | 3.41% | 3.75% | 4.17% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BBB |
0.20% | 0.51% | 0.80% | 1.24% | 1.69% | 2.12% | 2.55% | 2.98% | 3.44% | 3.91% | 4.42% | 4.86% | 5.24% | 5.37% | 5.60% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BBB- |
0.32% | 0.97% | 1.73% | 2.63% | 3.51% | 4.30% | 5.03% | 5.71% | 6.27% | 6.84% | 7.48% | 8.00% | 8.50% | 9.24% | 9.75% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BB+ |
0.43% | 1.25% | 2.35% | 3.47% | 4.56% | 5.66% | 6.61% | 7.31% | 8.19% | 9.05% | 9.64% | 10.29% | 10.85% | 11.28% | 12.05% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BB |
0.68% | 2.08% | 4.07% | 5.92% | 7.66% | 9.12% | 10.45% | 11.54% | 12.54% | 13.39% | 14.23% | 14.98% | 15.35% | 15.59% | 15.90% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BB- |
1.13% | 3.47% | 5.91% | 8.26% | 10.33% | 12.40% | 14.10% | 15.75% | 17.15% | 18.33% | 19.26% | 19.97% | 20.78% | 21.58% | 22.28% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B+ |
2.31% | 6.26% | 10.15% | 13.52% | 16.05% | 18.02% | 19.82% | 21.43% | 22.84% | 24.25% | 25.36% | 26.23% | 27.05% | 27.79% | 28.45% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B |
4.73% | 10.55% | 15.19% | 18.51% | 21.02% | 23.29% | 24.79% | 25.84% | 26.79% | 27.67% | 28.50% | 29.28% | 29.99% | 30.61% | 31.37% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B- |
7.92% | 15.37% | 20.55% | 24.12% | 26.93% | 28.98% | 30.64% | 31.65% | 32.32% | 32.94% | 33.66% | 34.29% | 34.64% | 35.04% | 35.49% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCC+ |
26.87% | 36.05% | 41.23% | 44.27% | 46.75% | 47.77% | 48.85% | 49.67% | 50.64% | 51.35% | 51.99% | 52.76% | 53.67% | 54.40% | 54.40% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NR |
4.02% | 7.86% | 11.19% | 13.86% | 16.03% | 17.82% | 19.33% | 20.60% | 21.74% | 22.78% | 23.66% | 24.42% | 25.09% | 25.69% | 26.28% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L |
0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R |
100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Standard & Poors’ 2013 Annual Global Corporate Default Study and Rating Transitions, March 2014.
L relates to Lloyds’ of London and Equitas; NR relates to companies which are Not Rated; R relates to companies which have been subject to Regulatory Action regarding solvency.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
108 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| B | Projected inflated and undiscounted cashflows ($m)
| |||
| Payment Year | Mesothelioma Claims |
Asbestosis Claims |
Lung Cancer Claims |
ARPD & Other Claims |
Legal and Other Costs |
Workers Compensation Claims |
Workers |
Wharf Claims | Wharf Legal and Other Costs |
Baryulgil | Cross Claim Recoveries |
Gross | Insurance | Net | ||||||||||||||
| 2015 / 2016 |
137.7 | 12.7 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 16.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 173.1 | 18.0 | 155.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2016 / 2017 |
150.6 | 15.5 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 18.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.5 | 190.2 | 20.7 | 169.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2017 / 2018 |
155.7 | 16.7 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 17.9 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 196.2 | 22.6 | 173.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2018 / 2019 |
152.9 | 16.2 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 17.6 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 192.2 | 21.5 | 170.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2019 / 2020 |
150.9 | 16.1 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 16.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 189.2 | 21.2 | 168.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 / 2021 |
148.5 | 16.1 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 16.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 186.0 | 21.5 | 164.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2021 / 2022 |
144.3 | 15.8 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 15.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.4 | 180.6 | 21.6 | 159.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 / 2023 |
137.8 | 15.4 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 14.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 3.2 | 173.0 | 21.9 | 151.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2023 / 2024 |
131.8 | 14.9 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 14.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 165.6 | 21.8 | 143.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2024 / 2025 |
123.2 | 14.3 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 12.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 154.9 | 21.2 | 133.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2025 / 2026 |
112.7 | 13.5 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 11.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.7 | 142.3 | 15.2 | 127.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2026 / 2027 |
100.3 | 12.6 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 10.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 127.6 | 12.1 | 115.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2027 / 2028 |
91.6 | 11.7 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 9.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.2 | 116.7 | 8.9 | 107.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2028 / 2029 |
84.8 | 10.8 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 107.7 | 9.0 | 98.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2029 / 2030 |
78.0 | 9.9 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 7.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 98.7 | 8.7 | 90.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2030 / 2031 |
71.1 | 8.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 89.8 | 8.3 | 81.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2031 / 2032 |
64.3 | 8.0 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 81.0 | 7.8 | 73.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2032 / 2033 |
57.7 | 7.1 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 72.4 | 7.3 | 65.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2033 / 2034 |
51.3 | 6.2 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 64.2 | 4.5 | 59.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2034 / 2035 |
45.2 | 5.4 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 4.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 56.4 | 2.2 | 54.3 | ||||||||||||||
| 2035 / 2036 |
39.6 | 4.7 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 49.2 | 2.0 | 47.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 2036 / 2037 |
34.3 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 42.5 | 1.8 | 40.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2037 / 2038 |
29.5 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 36.4 | 1.6 | 34.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2038 / 2039 |
25.1 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 31.0 | 1.4 | 29.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2039 / 2040 |
21.2 | 2.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 26.1 | 1.2 | 24.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2040 / 2041 |
17.7 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 21.7 | 1.0 | 20.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2041 / 2042 |
14.7 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 18.0 | 0.9 | 17.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2042 / 2043 |
12.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 14.7 | 0.7 | 14.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2043 / 2044 |
9.8 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 12.0 | 0.6 | 11.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2044 / 2045 |
7.9 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 9.7 | 0.5 | 9.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2045 / 2046 |
6.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 7.7 | 0.4 | 7.3 | ||||||||||||||
| 2046 / 2047 |
5.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 6.1 | 0.3 | 5.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2047 / 2048 |
3.9 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 4.8 | 0.3 | 4.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2048 / 2049 |
3.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 3.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2049 / 2050 |
2.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 2.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2050 / 2051 |
1.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2051 / 2052 |
1.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2052 / 2053 |
1.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 2053 / 2054 |
0.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2054 / 2055 |
0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2055 / 2056 |
0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2056 / 2057 |
0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2057 / 2058 |
0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||
| 2058 / 2059 |
0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 2059 / 2060 |
0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2060 / 2061 |
0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2061 / 2062 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2062 / 2063 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2063 / 2064 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2064 / 2065 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2065 / 2066 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2066 / 2067 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2067 / 2068 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2068 / 2069 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2069 / 2070 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2070 / 2071 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2071 / 2072 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2072 / 2073 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2073 / 2074 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2074 / 2075 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2075 / 2076 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| TOTAL |
2,429.9 | 275.2 | 67.6 | 59.8 | 254.2 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 10.4 | 2.3 | 4.1 | 56.9 | 3,052.7 | 309.8 | 2,742.9 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
109 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| C | Projected inflated and discounted cashflows ($m)
| |||
| Payment Year | Mesothelioma Claims |
Asbestosis Claims |
Lung Cancer Claims |
ARPD & Other Claims |
Legal and Other Costs |
Workers Compensation Claims |
Workers |
Wharf Claims | Wharf Legal and Other Costs |
Baryulgil | Cross Claim Recoveries |
Gross | Insurance | Net | ||||||||||||||
| 2015 / 2016 |
136.3 | 12.6 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 16.7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 171.4 | 17.8 | 153.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2016 / 2017 |
146.5 | 15.1 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 17.9 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.4 | 185.0 | 20.2 | 164.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2017 / 2018 |
149.0 | 16.0 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 17.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.5 | 187.7 | 21.6 | 166.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2018 / 2019 |
143.7 | 15.3 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 16.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 180.7 | 20.2 | 160.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2019 / 2020 |
138.7 | 14.8 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 15.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 173.9 | 19.5 | 154.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 / 2021 |
133.1 | 14.4 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 14.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.1 | 166.7 | 19.3 | 147.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2021 / 2022 |
125.8 | 13.7 | 3.1 | 3.0 | 13.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 157.4 | 18.8 | 138.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2022 / 2023 |
116.6 | 13.0 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 12.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.7 | 146.4 | 18.5 | 127.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2023 / 2024 |
108.2 | 12.2 | 2.8 | 2.7 | 11.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 135.9 | 17.9 | 118.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2024 / 2025 |
98.0 | 11.4 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 10.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.3 | 123.3 | 16.9 | 106.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2025 / 2026 |
86.8 | 10.4 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 9.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 109.6 | 11.7 | 97.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2026 / 2027 |
74.8 | 9.4 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 7.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 95.1 | 9.0 | 86.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2027 / 2028 |
66.1 | 8.5 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 84.2 | 6.4 | 77.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2028 / 2029 |
59.1 | 7.5 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 5.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 75.1 | 6.3 | 68.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2029 / 2030 |
52.5 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 66.5 | 5.9 | 60.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2030 / 2031 |
46.3 | 5.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 4.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 58.4 | 5.4 | 53.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2031 / 2032 |
40.3 | 5.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 50.7 | 4.9 | 45.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2032 / 2033 |
34.5 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 43.2 | 4.4 | 38.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2033 / 2034 |
29.0 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 36.3 | 2.5 | 33.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2034 / 2035 |
24.1 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 30.1 | 1.1 | 29.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2035 / 2036 |
19.9 | 2.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 24.8 | 1.0 | 23.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2036 / 2037 |
16.3 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 20.2 | 0.8 | 19.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2037 / 2038 |
13.2 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 16.3 | 0.7 | 15.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2038 / 2039 |
10.6 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 13.1 | 0.6 | 12.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2039 / 2040 |
8.4 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 10.4 | 0.5 | 9.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 2040 / 2041 |
6.7 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 8.2 | 0.4 | 7.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2041 / 2042 |
5.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 6.4 | 0.3 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2042 / 2043 |
4.0 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 4.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2043 / 2044 |
3.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2044 / 2045 |
2.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 2.7 | ||||||||||||||
| 2045 / 2046 |
1.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2046 / 2047 |
1.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 2047 / 2048 |
1.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2048 / 2049 |
0.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||
| 2049 / 2050 |
0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 2050 / 2051 |
0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 2051 / 2052 |
0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||
| 2052 / 2053 |
0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 2053 / 2054 |
0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 2054 / 2055 |
0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2055 / 2056 |
0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2056 / 2057 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 2057 / 2058 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2058 / 2059 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2059 / 2060 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2060 / 2061 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2061 / 2062 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2062 / 2063 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2063 / 2064 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2064 / 2065 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2065 / 2066 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2066 / 2067 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2067 / 2068 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2068 / 2069 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2069 / 2070 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2070 / 2071 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2071 / 2072 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2072 / 2073 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2073 / 2074 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2074 / 2075 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 2075 / 2076 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||||||||
| TOTAL |
1,905.8 | 213.5 | 51.4 | 47.1 | 204.3 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 8.7 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 44.6 | 2,396.7 | 253.8 | 2,142.8 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
110 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| D | Australian asbestos consumption and production data: 1930-2002
| |||
Figures in this table are in 000’s metric tonnes
| Year | Australian Production - All companies |
Import | Export | Australian Consumption - All companies |
||||||
| 1930 |
82 | - | - | 82 | ||||||
| 1931 |
128 | 1,200 | - | 1,328 | ||||||
| 1932 |
130 | - | - | 130 | ||||||
| 1933 |
279 | 2,676 | - | 2,955 | ||||||
| 1934 |
170 | 2,471 | - | 2,641 | ||||||
| 1935 |
170 | 4,423 | - | 4,593 | ||||||
| 1936 |
239 | 7,817 | - | 8,056 | ||||||
| 1937 |
298 | 6,199 | - | 6,497 | ||||||
| 1938 |
173 | 11,179 | - | 11,352 | ||||||
| 1939 |
78 | 10,081 | - | 10,159 | ||||||
| 1940 |
489 | 14,097 | - | 14,586 | ||||||
| 1941 |
251 | 14,220 | - | 14,471 | ||||||
| 1942 |
331 | 20,176 | - | 20,507 | ||||||
| 1943 |
678 | 14,229 | - | 14,907 | ||||||
| 1944 |
764 | 14,091 | - | 14,855 | ||||||
| 1945 |
1,629 | 9,131 | 32 | 10,728 | ||||||
| 1946 |
620 | 18,697 | 496 | 18,821 | ||||||
| 1947 |
1,377 | 14,246 | 652 | 14,971 | ||||||
| 1948 |
1,327 | 14,857 | 278 | 15,906 | ||||||
| 1949 |
1,645 | 14,767 | 346 | 16,066 | ||||||
| 1950 |
1,617 | 29,536 | 385 | 30,768 | ||||||
| 1951 |
2,558 | 25,289 | 588 | 27,259 | ||||||
| 1952 |
4,059 | 24,686 | 868 | 27,877 | ||||||
| 1953 |
4,970 | 28,784 | 1,631 | 32,123 | ||||||
| 1954 |
4,713 | 26,406 | 2,298 | 28,821 | ||||||
| 1955 |
5,352 | 42,677 | 3,287 | 44,742 | ||||||
| 1956 |
8,670 | 32,219 | 6,859 | 34,030 | ||||||
| 1957 |
13,098 | 23,235 | 11,644 | 24,689 | ||||||
| 1958 |
13,900 | 34,721 | 9,315 | 39,306 | ||||||
| 1959 |
15,959 | 34,223 | 11,584 | 38,598 | ||||||
| 1960 |
13,940 | 36,609 | 7,410 | 43,139 | ||||||
| 1961 |
14,952 | 32,947 | 7,196 | 40,703 | ||||||
| 1962 |
16,443 | 34,915 | 8,695 | 42,663 | ||||||
| 1963 |
11,941 | 32,704 | 2,347 | 42,298 | ||||||
| 1964 |
12,191 | 38,299 | 6,500 | 43,990 | ||||||
| 1965 |
10,326 | 46,179 | 4,295 | 52,210 | ||||||
| 1966 |
12,024 | 49,243 | 4,146 | 57,121 | ||||||
| 1967 |
647 | 46,950 | 2,254 | 45,343 | ||||||
| 1968 |
799 | 59,590 | 718 | 59,671 | ||||||
| 1969 |
734 | 52,739 | 162 | 53,311 | ||||||
| 1970 |
739 | 57,250 | 367 | 57,622 | ||||||
| 1971 |
756 | 71,777 | 174 | 72,359 | ||||||
| 1972 |
16,884 | 61,682 | 2,387 | 76,179 | ||||||
| 1973 |
43,529 | 61,373 | 27,810 | 77,092 | ||||||
| 1974 |
30,863 | 57,051 | 29,191 | 58,723 | ||||||
| 1975 |
47,922 | 69,794 | 24,524 | 93,192 | ||||||
| 1976 |
60,642 | 60,490 | 40,145 | 80,987 | ||||||
| 1977 |
50,601 | 54,267 | 20,510 | 84,358 | ||||||
| 1978 |
62,383 | 42,061 | 37,094 | 67,350 | ||||||
| 1979 |
79,721 | 23,735 | 54,041 | 49,415 | ||||||
| 1980 |
92,418 | 25,239 | 51,172 | 66,485 | ||||||
| 1981 |
45,494 | 20,960 | 38,576 | 27,878 | ||||||
| 1982 |
18,587 | 20,853 | 15,578 | 23,862 | ||||||
| 1983 |
3,909 | 10,113 | 4,460 | 9,562 | ||||||
| 1984 |
- | 14,432 | 22 | 14,410 | ||||||
| 1985 |
- | 12,194 | - | 12,194 | ||||||
| 1986 |
- | 10,597 | - | 10,597 | ||||||
| 1987 |
- | 6,294 | - | 6,294 | ||||||
| 1988 |
- | 2,072 | - | 2,072 | ||||||
| 1989 |
- | 2,128 | - | 2,128 | ||||||
| 1990 |
- | 1,706 | - | 1,706 | ||||||
| 1991 |
- | 1,342 | - | 1,342 | ||||||
| 1992 |
- | 1,533 | - | 1,533 | ||||||
| 1993 |
- | 2,198 | - | 2,198 | ||||||
| 1994 |
- | 1,843 | - | 1,843 | ||||||
| 1995 |
- | 1,488 | - | 1,488 | ||||||
| 1996 |
- | 1,366 | - | 1,366 | ||||||
| 1997 |
- | 1,556 | - | 1,556 | ||||||
| 1998 |
- | 1,471 | - | 1,471 | ||||||
| 1999 |
- | 1,316 | - | 1,316 | ||||||
| 2000 |
- | 1,246 | - | 1,246 | ||||||
| 2001 |
- | 945 | - | 945 | ||||||
|
2002 |
- | 515 | - | 515 |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
111 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| E | Data provided by AICFL
| |||
Claims Dataset
| Claim Details | ||
| State |
State of jurisdiction of the claim | |
| Old Claim ID |
Claim number under the old IT system | |
| New claim ID |
Claim number under the new IT system | |
| Include? |
This defines whether we count the claim record - we exclude insurance recovery records and cross-claim records | |
| Date of Birth |
Date of Birth | |
| Date of Death |
Date of Death | |
| Start 1st Exp |
Start Date of the first Exposure | |
| End 1st Exp |
End Date of the first Exposure | |
| Days 1st Exp |
Number of days exposed during the first exposure | |
| Start 2nd Exp |
Start Date of the second exposure | |
| End 2nd Exp |
End Date of the second exposure | |
| Days 2nd Exp |
Number of days exposed during the second exposure | |
| Start 3rd Exp |
Start Date of the third exposure | |
| End 3rd Exp |
End Date of the third exposure | |
| Days 3rd Exp |
Number of days exposed during the third exposure | |
| Start 4th Exp |
Start Date of the fourth exposure | |
| End 4th Exp |
End Date of the fourth exposure | |
| Days 4th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the fourth exposure | |
| Start 5th Exp |
Start Date of the fifth exposure | |
| End 5th Exp |
End Date of the fifth exposure | |
| Days 5th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the fifth exposure | |
| Start 6th Exp |
Start Date of the sixth exposure | |
| End 6th Exp |
End Date of the sixth exposure | |
| Days 6th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the sixth exposure | |
| Start 7th Exp |
Start Date of the seventh exposure | |
| End 7th Exp |
End Date of the seventh exposure | |
| Days 7th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the seventh exposure | |
| Start 8th Exp |
Start Date of the eighth exposure | |
| End 8th Exp |
End Date of the eighth exposure | |
| Days 8th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the eighth exposure | |
| Start 9th Exp |
Start Date of the ninth exposure | |
| End 9th Exp |
End Date of the ninth exposure | |
| Days 9th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the ninth exposure | |
| Start 10th Exp |
Start Date of the tenth exposure | |
| End 10th Exp |
End Date of the tenth exposure | |
| Days 10th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the tenth exposure | |
| Start 11th Exp |
Start Date of the eleventh exposure | |
| End 11th Exp |
End Date of the eleventh exposure | |
| Days 11th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the eleventh exposure | |
| Start 12th Exp |
Start Date of the twelfth exposure | |
| End 12th Exp |
End Date of the twelfth exposure | |
| Days 12th Exp |
Number of days exposed during the twelfth exposure | |
| ClaimsPOE::OccupationType_c |
Occupations of claimant | |
| ClaimsPOE::ExposureNature_c |
Nature of Exposures of claimant | |
| Pure Home Renovator |
Home renovator indicator field | |
| MedicalAsbestosDiseases_c |
A list of all the diseases specified by the claimant | |
| Disease |
Disease grouping based on hierarchy (mesothelioma, cancer, asbestosis, ARPD&Other) | |
| DefendantAICF_c |
Name of Liable Entity liable for claim | |
| Notification Date |
Date claim was received by Liable Entity | |
| Client Sett Date |
Date claim was settled by the Liable Entity with the claimant | |
| Closure Date |
Date claim record was closed (settled all legal costs, no more activity) | |
| Date of Diag |
Date of diagnosis of asbestos disease | |
| Claim Type |
Standard claim, Cross-claim, Recovery claim, Insurance claim | |
| Transaction Fields | ||
| Settled Damages |
Total Damages awarded to claimant (by all defendants) | |
| AICF Damages |
Total Damages awarded to claimant (by AICF/JH Liable Entities) | |
| Amount Actual Paid Damages |
Total Damages paid to claimant (by AICF/JH Liable Entities) | |
| Settled Costs |
Total Costs (by all defendants) | |
| AICF Costs |
Total Costs to be borne by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Amount Actual Paid Costs |
Total Costs paid by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Settled DDB |
Total DDB Reimbursement Costs (by all defendants) | |
| AICF DDB |
Total DDB Reimbursement Costs to be borne by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Amount Actual Paid DDB |
Total DDB Reimbursement Costs paid by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Settled Other |
Total Other Costs (by all defendants) | |
| AICF Other |
Total Other Costs to be borne by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Amount Actual Paid Other |
Total Other Costs paid by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| AICF Legal Costs Total |
Total Defence Legal Costs to be borne by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Amount Actual Paid Legal Costs Total |
Total Defence Legal Costs paid by AICF/JH Liable Entities | |
| Case Estimate Fields | ||
| Reserve Damages |
Case estimate of damages | |
| Reserve Costs |
Case estimate of costs | |
| Reserve Legal Fees |
Case estimate of defence legal costs | |
| Reserve Disbursements |
Case estimate of other disbursements | |
| Reserve DDB |
Case estimate of payments to DDB |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
112 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Accounting Transactions Datasets
Accruals File
| Date | Date of transaction entry | |
| Claim ID | Claim number under new IT system | |
| Transaction Ref | Transaction reference number | |
| Type | Expense or Income | |
|
This contains the values as follows: Bank Fees, Consulting Costs, Costs, Damages, | ||
| Description | DDB, Interest, Legal Fees, Medicare, Other Bank Charges, Recoveries (or Recovery) | |
| Amount | Amount of transaction | |
| GST | GST component of transaction | |
| Amount - GST | Amount of transaction, net of GST | |
| Account | Which AICF (or MRCF) account the money is credit to or drawn from | |
| The name of the party who has drawn the cheque or from whom a cheque has been | ||
| Drawer of cheque | received |
Transactions File
| Date | Date of transaction entry into system | |
| Claim ID | Claim number under new IT system | |
| Transaction Ref | Transaction reference number | |
| Type | Payment of Receipt | |
| Date Cheque Drawn | Date Cheque Drawn | |
| Date Cheque Banked | Date Cheque Banked | |
| Description | Description of transaction | |
| Amount | Amount of transaction | |
| GST | GST component of transaction | |
| Amt - GST | Amount of transaction, net of GST | |
| The name of the party who has drawn the cheque or from whom a cheque has been | ||
| Drawer of cheque | received |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
113 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| F | Glossary of terms used in the Amended Final Funding Agreement
| |||
The following provides a glossary of terms which are referenced in the Amended Final Funding Agreement and upon which we have relied in preparing our report.
The operation of these definitions cannot be considered in isolation but instead need to be considered in the context of the totality of the Amended Final Funding Agreement.
AICF means the trustee of the Asbestos Injuries Compensation Fund from time to time, in its capacity as trustee, initially being Asbestos Injuries Compensation Fund Limited.
AICF Funded Liability means:
| (a) | any Proven Claim; |
| (b) | Operating Expenses; |
| (c) | Claims Legal Costs; |
| (d) | any claim that was made or brought in legal proceedings against a Former James Hardie Company commenced before 1 December 2005; |
| (e) | Statutory Recoveries within the meaning and subject to the limits set out in the Amended Final Funding Agreement; |
| (f) | a claim or category of claim which James Hardie and the NSW Government agree in writing is a “AICF Funded Liability” or a category of “AICF Funded Liability”. |
but in the cases of paragraphs (a), (c) and (d) excludes any such liabilities or claims to the extent that they have been recovered or are recoverable under a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy.
Claims Legal Costs means all costs, charges, expenses and outgoings incurred or expected to be borne by AICF or the Former James Hardie Companies, in respect of legal advisors, other advisors, experts, court proceedings and other dispute resolution methods in connection with Personal Asbestos Claims and Marlew Claims but in all cases excluding any costs included as a component of calculating a Proven Claim.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
114 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Concurrent Wrongdoer in relation to a personal injury or death claim for damages under common law or other law (excluding any law introduced or imposed in breach of the restrictions on adverse regulatory or legislative action against the James Hardie Group under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, and which breach has been notified to the NSW Government in accordance with Amended Final Funding Agreement), means a person whose acts or omissions, together with the acts or omissions of one or more Former James Hardie Companies or Marlew or any member of the James Hardie Group (whether or not together with any other persons) caused, independently of each other or jointly, the damage or loss to another person that is the subject of that claim.
Contribution Claim means a cross-claim or other claim under common law or other law (excluding any law introduced or imposed in breach of the restrictions on adverse regulatory or legislative action against the James Hardie Group under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, and which breach has been notified to the NSW Government in accordance with Amended Final Funding Agreement):
| (a) | for contribution by a Concurrent Wrongdoer against a Former James Hardie Company or a member of the James Hardie Group in relation to facts or circumstances which give rise to a right of a person to make a Personal Asbestos Claim or a Marlew Claim; or |
| (b) | by another person who is entitled under common law (including by way of contract) to be subrogated to such a first mentioned cross-claim or other claim; |
Discounted Central Estimate means the central estimate of the present value (determined using the discount rate used within the relevant actuarial report) of the liabilities of the Former James Hardie Companies and Marlew in respect of expected Proven Claims and Claims Legal Costs, calculated in accordance with the Amended Final Funding Agreement.
Excluded Claims are any of the following liabilities of the Former James Hardie Companies:
| (i) | personal injury or death claims arising from exposure to Asbestos outside Australia; |
| (ii) | personal injury or death claims arising from exposure to Asbestos made outside Australia; |
| (iii) | claims for economic loss (other than any economic loss forming part of the calculation of an award of damages for personal injury or death) or loss of property, including those relating to land remediation and/or |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
115 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
| Asbestos or Asbestos products removal, arising out of or in connection with Asbestos or Asbestos products manufactured, sold, distributed or used by or on behalf of the Liable Entities; |
| (iv) | any Excluded Marlew Claim; |
| (v) | any liabilities of the Liable Entities other than AICF Funded Liabilities. |
Excluded Marlew Claim means a Marlew Claim:
| (a) | covered by the indemnities granted by the Minister of Mineral Resources under the deed between the Minister, Fuller Earthmoving Pty Limited and James Hardie Industries Limited dated 11 March 1996; or |
| (b) | by a current or former employee of Marlew in relation to an exposure to Asbestos in the course of such employment to the extent: |
| (i) | the loss is recoverable under a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy; or |
| (ii) | the Claimant is not unable to recover damages from a Marlew Joint Tortfeasor in accordance with the Marlew Legislation; |
| (c) | by an individual who was or is an employee of a person other than Marlew arising from exposure to Asbestos in the course of such employment by that other person where such loss is recoverable from that person or under a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy; or |
| (d) | in which another defendant (or its insurer) is a Marlew Joint Tortfeasor from whom the plaintiff is entitled to recover compensation in proceedings in the Dust Diseases Tribunal, and the Claimant is not unable to recover damages from that Marlew Joint Tortfeasor in accordance with the Marlew Legislation. |
Former James Hardie Companies means Amaca, Amaba and ABN 60.
Insurance and Other Recoveries means any proceeds which may reasonably be expected to be recovered or recoverable for the account of a Former James Hardie Company or to result in the satisfaction (in whole or part) of a liability of a Former James Hardie Company (of any nature) to a third party, under any product liability insurance policy or public liability insurance policy or commutation of such policy or under any other contract, including any contract of indemnity, but excluding any such amount recovered or recoverable under a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy.
Liable Entities see Former James Hardie Companies
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
116 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Marlew means Marlew Mining Pty Ltd (in liquidation), ACN 000 049 650, previously known as Asbestos Mines Pty Ltd.
Marlew Claim means, subject to the limitation on Statutory Recoveries, a claim which satisfies one of the following paragraphs and which is not an Excluded Marlew Claim:
| (a) | any present or future personal injury or death claim by an individual or the legal personal representative of an individual, for damages under common law or other law (excluding any law introduced or imposed in breach of the restrictions on adverse regulatory or legislative action against the James Hardie Group under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, and which breach has been notified to the NSW Government in accordance with the Amended Final Funding Agreement) which: |
| (i) | arose or arises from exposure to Asbestos in the Baryulgil region from Asbestos Mining Activities at Baryulgil conducted by Marlew, provided that: |
| A. | the individual’s exposure to Asbestos occurred wholly within Australia; or |
| B. | where the individual has been exposed to Asbestos both within and outside Australia, the amount of damages included in the Marlew Claim shall be limited to the amount attributable to the proportion of the exposure which caused or contributed to the loss or damage giving rise to the Marlew Claim which occurred in Australia; |
| (ii) | is commenced in New South Wales in the Dust Diseases Tribunal; and |
| (iii) | is or could have been made against Marlew had Marlew not been in external administration or wound up, or could be made against Marlew on the assumption (other than as contemplated under the Marlew legislation) that Marlew will not be in the future in external administration; |
| (b) | any claim made under compensation to relatives legislation by a relative of a deceased individual (or personal representative of such a relative) or (where permitted by law) the legal personal representative of a deceased individual in each case where the individual, but for such individual’s death, would have been entitled to bring a claim of the kind described in paragraph (a); or |
| (c) | a Contribution Claim relating to a claim described in paragraphs (a) or (b). |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
117 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Marlew Joint Tortfeasor means any person who is or would be jointly and severally liable with Marlew in respect of a Marlew Claim, had Marlew not been in external administration or wound up, or on the assumption that Marlew will not in the future be, in external administration or wound up other than as contemplated under the Marlew Legislation.
Payable Liability means any of the following:
| (a) | any Proven Claim (whether arising before or after the date of this deed); |
| (b) | Operating Expenses; |
| (c) | Claims Legal Costs; |
| (d) | any liability of a Former James Hardie Company to the AICFL, however arising, in respect of any amounts paid by the AICFL in respect of any liability or otherwise on behalf of the Former James Hardie Company; |
| (e) | any claim that was made or brought in legal proceedings against a Former James Hardie Company commenced before 1 December 2005; |
| (f) | if regulations are made pursuant to section 30 of the Transaction Legislation and if and to the extent the AICFL and James Hardie have notified the NSW Government that any such liability is to be included in the scope of Payable Liability, any liability of a Former James Hardie Company to pay amounts received by it from an insurer in respect of a liability to a third party incurred by it for which it is or was insured under a contract of insurance entered into before 2 December 2005; and |
| (g) | Statutory Recoveries within the meaning and subject to the limits set out in the Amended Final Funding Agreement, |
but in the cases of paragraphs (a), (c) and (e) excludes any such liabilities or claims to the extent that they have been recovered or are recoverable under a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy.
Period Actuarial Estimate means, in respect of a period, the central estimate of the present value (determined using the discount rate used in the relevant actuarial report) of the liabilities of the Former James Hardie Companies and Marlew in respect of expected Proven Claims and Claims Legal Costs (in each case which are reasonably expected to become payable in that period), before allowing for Insurance and Other Recoveries, calculated in accordance with the Amended Final Funding Agreement.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
118 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Personal Asbestos Claim means any present or future personal injury or death claim by an individual or the legal personal representative of an individual, for damages under common law or under other law (excluding any law introduced or imposed in breach of the restrictions on adverse regulatory or legislative action against the James Hardie Group under the Amended Final Funding Agreement, and which breach has been notified to the NSW Government under the Amended Final Funding Agreement) which:
| (a) | arises from exposure to Asbestos occurring in Australia, provided that: |
| (i) | the individual’s exposure to Asbestos occurred wholly within Australia; or |
| (ii) | where the individual has been exposed to Asbestos both within and outside Australia, damages included in the Marlew Claim shall be limited to the amount attributable to the proportion of the exposure which caused or contributed to the loss or damage giving rise to the Personal Asbestos Claim which occurred in Australia; |
| (b) | is made in proceedings in an Australian court or tribunal; and |
| (c) | is made against: |
| (i) | all or any of the Liable Entities; or |
| (ii) | any member of the James Hardie Group from time to time; |
| (d) | any claim made under compensation to relatives legislation by a relative of a deceased individual (or personal representative of such a relative) or (where permitted by law) the legal personal representative of a deceased individual in each case where the individual, but for such individual’s death, would have been entitled to bring a claim of the kind described in paragraph (a); or |
| (e) | a Contribution Claim made in relation to a claim described in paragraph (a) or (b) |
but excludes all claims covered by a Worker’s Compensation Scheme or Policy.
Proven Claim means a proven Personal Asbestos Claim in respect of which final judgment has been given against, or a binding settlement has been entered into by, a Former James Hardie Company, to the extent to which that entity incurs liability under that judgment or settlement, or a Proven Marlew Claim.
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
119 |

|
Valuation of the asbestos-related disease
liabilities of the Liable Entities to be met by the AICF Trust
Effective as at 31 March 2015
21 May 2015
|
Statutory Recoveries means any statutory entitlement of the NSW Government or any Other Government or any governmental agency or authority of any such government (“Relevant Body”) to impose liability on or to recover an amount or amounts from any person in respect of any payments made or to be made or benefits provided by a Relevant Body in respect of claims (other than as a defendant or in settlement of any claim, including a cross-claim or claim for contribution).
Term means the period
| (i) | from the date on which the principal obligations under the Amended Final Funding Agreement will commence to 31 March 2045, |
| (ii) | as may be extended in accordance with the terms of the Amended Final Funding Agreement. |
Term Central Estimate means the central estimate of the present value (determined using the discount rate used in the relevant Annual Actuarial Report) of the liabilities of the Former James Hardie Companies and Marlew in respect of expected Proven Claims and Claims Legal Costs (in each case reasonably expected to become payable in the relevant period) after allowing for Insurance and Other Recoveries during that period, from and including the day following the end of the Financial Year preceding that Payment Date up to and including the last day of the Term (excluding any automatic or potential extension of the Term, unless or until the Term has been extended).
Workers Compensation Scheme or Policy means any of the following:
| (a) | any worker’s compensation scheme established by any law of the Commonwealth or of any State or Territory; |
| (b) | any fund established to cover liabilities under insurance policies upon the actual or prospective insolvency of the insurer (including without limitation the Insurer Guarantee Fund established under the Worker’s Compensation Act 1987 (NSW)); and |
| (c) | any policy of insurance issued under or pursuant to such a scheme. |
| © 2015 KPMG, an Australian partnership and a member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved. Printed in Australia. KPMG and the KPMG logo are registered trademarks of KPMG International. |
120 |